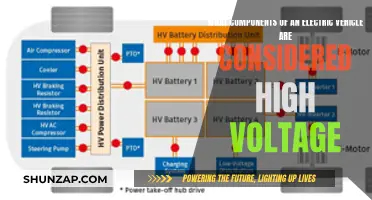
The concept of an electric vehicle (EV) mandate has gained traction as governments and policymakers seek to accelerate the transition to sustainable transportation. This initiative involves setting legal requirements or standards that mandate the use of electric cars, buses, or other vehicles in specific sectors or regions. The primary goal is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and combat climate change. With the growing concern over environmental degradation and the urgent need to adopt cleaner technologies, many countries are considering implementing such mandates to encourage the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and promote a greener future. This paragraph introduces the topic by highlighting the potential benefits and the increasing global interest in establishing EV mandates.
What You'll Learn
- Environmental Impact: How EV mandates reduce emissions and pollution
- Infrastructure Development: The need for charging stations and grid upgrades
- Economic Benefits: Job creation and cost savings for consumers
- Policy Implementation: Strategies for introducing and enforcing EV regulations
- Public Acceptance: Overcoming resistance and promoting EV adoption

Environmental Impact: How EV mandates reduce emissions and pollution
The concept of electric vehicle (EV) mandates is gaining traction as a powerful strategy to combat climate change and improve air quality. These mandates, which require a certain percentage of vehicles sold to be electric, have the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants. Here's an exploration of how EV mandates contribute to a cleaner environment:
Emission Reduction: One of the most significant environmental benefits of EV mandates is the substantial reduction in tailpipe emissions. Traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles are major contributors to air pollution, emitting a range of harmful substances, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These emissions have detrimental effects on human health and contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain. In contrast, electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release these pollutants directly into the atmosphere. By mandating the sale of EVs, governments can accelerate the transition to cleaner transportation, leading to improved air quality and public health.
Lowering Carbon Footprint: The environmental impact of EV mandates extends beyond local air pollution. The transportation sector is a significant contributor to global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, with ICE vehicles being a major source. The widespread adoption of electric cars, encouraged by mandates, can significantly lower the carbon footprint of the transportation industry. EVs produce zero direct emissions, and when powered by renewable energy sources, their overall carbon emissions can be close to zero. This shift in the transportation sector plays a crucial role in meeting global climate goals and reducing the overall greenhouse gas emissions associated with mobility.
Encouraging Renewable Energy: The success of EV mandates is closely tied to the development and integration of renewable energy sources. As the demand for electric vehicles increases, so does the need for clean electricity to power them. Governments can incentivize the growth of renewable energy infrastructure by mandating the sale of EVs. This includes investments in solar, wind, and hydroelectric power plants, which provide the electricity required to charge the growing number of electric cars. The transition to renewable energy sources is essential for long-term environmental sustainability, as it reduces the reliance on fossil fuels and further decreases the environmental impact of the transportation sector.
Long-Term Environmental Benefits: The environmental advantages of EV mandates are not limited to the immediate reduction in emissions. Over time, the cumulative effect of these mandates can lead to significant ecological improvements. As more EVs hit the roads, the overall air quality in urban areas improves, benefiting both the environment and public health. Additionally, the reduced demand for fossil fuels can lead to a more stable energy market and potentially lower fuel prices. The long-term environmental impact includes a cleaner, healthier planet, with reduced pollution levels and a more sustainable approach to transportation.
In summary, EV mandates are a powerful tool in the fight against climate change and environmental degradation. By encouraging the adoption of electric vehicles, governments can directly contribute to the reduction of emissions and pollution, fostering a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future. The environmental impact of these mandates is far-reaching, affecting not only local air quality but also global efforts to combat climate change.
The State That Banned Electric Vehicles: A Shocking Decision
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Development: The need for charging stations and grid upgrades
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is an essential step towards a sustainable future, and it is imperative that we prepare our infrastructure to support this transition. As the demand for electric mobility increases, the need for comprehensive charging station networks and grid upgrades becomes increasingly apparent. This infrastructure development is crucial to ensure that EV owners have convenient access to charging facilities and that the power grid can handle the additional load.
Charging stations are the lifeblood of the EV ecosystem. They provide the necessary power to recharge batteries, enabling drivers to continue their journeys. The strategic placement of these stations is vital to cater to the diverse needs of EV owners. Public charging stations along highways and in urban areas will facilitate long-distance travel and provide convenience for city dwellers. Additionally, residential charging solutions, such as home charging points, are essential to encourage EV ownership among individuals. By offering a range of charging options, we can ensure that the transition to electric mobility is seamless and accessible to all.
The current power grid infrastructure may not be adequately equipped to handle the surge in EV charging demand. Upgrading the grid is a critical aspect of supporting the EV mandate. This involves increasing the capacity of power lines, transformers, and substations to accommodate the higher electricity usage associated with EV charging. Smart grid technologies can also play a significant role in managing the load. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and control, allowing for efficient load balancing and ensuring that the grid remains stable even with the increased demand.
Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid is essential for a sustainable future. Solar and wind power, for instance, can provide clean energy to charge EVs, reducing the carbon footprint of the transportation sector. Upgrading the grid to accommodate these renewable sources will not only support the EV mandate but also contribute to a greener and more environmentally friendly energy infrastructure.
In summary, the development of a robust charging station network and the modernization of the power grid are vital components of the EV mandate. These infrastructure upgrades will facilitate the widespread adoption of electric vehicles, ensuring convenience, accessibility, and environmental sustainability. As the world moves towards a more electric future, investing in these essential infrastructure projects is a necessary step to support the transition and create a more efficient and eco-friendly transportation system.
Unraveling the Price Tag: Why Electric Vehicles Cost More
You may want to see also

Economic Benefits: Job creation and cost savings for consumers
The introduction of an electric vehicle (EV) mandate can have significant economic implications, particularly in terms of job creation and cost savings for consumers. Here's an overview of these benefits:
Job Creation: The EV mandate would stimulate the growth of the electric vehicle industry, creating a demand for various professionals. This includes EV manufacturers, who would need to expand their workforce to meet production targets. As a result, jobs in assembly, engineering, design, and quality control would be created, providing employment opportunities for skilled workers. Additionally, the expansion of the EV industry would lead to a ripple effect, with the need for additional support staff in areas like sales, marketing, customer service, and after-sales support. This surge in employment could significantly reduce unemployment rates and provide a boost to local economies.
Cost Savings for Consumers: Electric vehicles offer substantial cost savings compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars. Firstly, EVs have lower running costs due to the absence of fuel expenses. While the initial purchase price might be higher, the long-term savings are considerable. With no fuel costs, drivers can save money on a monthly basis, which adds up over time. Moreover, the maintenance and servicing of EVs are generally less expensive. Traditional cars require frequent oil changes, engine repairs, and other maintenance tasks, which are not necessary for electric vehicles. This translates to significant savings for consumers, especially those who drive long distances or frequently.
The mandate would also encourage the development of supporting infrastructure, such as charging stations, which would create additional job opportunities. As the EV market expands, there will be a growing need for professionals to install, maintain, and manage these charging facilities, further contributing to job creation.
In summary, an electric vehicle mandate has the potential to drive economic growth by creating numerous job opportunities across various sectors. Simultaneously, it offers consumers substantial cost savings through reduced fuel and maintenance expenses, making EVs an economically attractive and environmentally friendly choice.
Unveiling Porsche's Electric Revolution: A Sustainable Sports Car Evolution
You may want to see also

Policy Implementation: Strategies for introducing and enforcing EV regulations
The introduction of electric vehicles (EVs) and the implementation of regulations to support their adoption is a complex process that requires careful planning and strategic policy design. Here are some strategies to consider when introducing and enforcing EV regulations:
Public Awareness and Education: Before implementing any mandate, it is crucial to educate the public about the benefits of EVs. This can be achieved through awareness campaigns, workshops, and community engagement programs. Informing citizens about the environmental advantages, reduced pollution, and long-term cost savings of EVs can foster a positive perception and encourage voluntary adoption. Providing clear and accessible information about the new regulations and their impact will also help build public support.
Gradual Implementation: A phased approach to introducing EV regulations can be more manageable and effective. Start with a pilot program or a limited mandate in specific regions or for certain vehicle types. This allows for a controlled environment to identify and address potential challenges. Gradually expanding the mandate to cover more areas or vehicle categories can ensure a smooth transition and provide valuable learning opportunities. For instance, you could begin with a mandate for government-owned fleets, then extend it to commercial vehicles, and finally, include personal vehicles.
Incentives and Subsidies: Financial incentives can play a significant role in encouraging EV adoption. Governments can offer subsidies, tax benefits, or grants to individuals and businesses purchasing electric vehicles. These incentives can reduce the upfront cost barrier, making EVs more affordable and attractive to potential buyers. Additionally, providing subsidies for charging infrastructure development and offering tax credits for EV-related research and development can further stimulate the market.
Infrastructure Development: The success of EV mandates heavily relies on the availability of adequate charging infrastructure. Governments should invest in the development of a comprehensive charging network, ensuring accessibility and convenience for EV owners. This includes installing charging stations in public areas, residential complexes, and along major transportation routes. Providing incentives for private businesses to invest in charging infrastructure can also accelerate the process. Well-planned infrastructure will address range anxiety and make EVs a more practical choice for the general public.
Enforcement and Monitoring: Effective enforcement mechanisms are essential to ensure compliance with EV regulations. This may involve regular inspections of vehicles, especially for commercial fleets, to verify their electric nature. Implementing a tracking system for EVs and their usage can help monitor the impact of the mandate. Additionally, providing clear guidelines and penalties for non-compliance will deter potential rulebreakers. Collaboration with law enforcement agencies and industry stakeholders can enhance enforcement capabilities.
Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement: Introducing EV regulations should be a collaborative effort involving various stakeholders, including government bodies, industry representatives, environmental organizations, and consumer groups. Regular consultations and feedback sessions can help identify potential challenges and tailor the policy to meet the needs of all parties. Engaging with stakeholders throughout the implementation process ensures a more robust and sustainable approach.
Australia's Electric Car Revolution: A Look at the Growing EV Market
You may want to see also

Public Acceptance: Overcoming resistance and promoting EV adoption
Public acceptance and the willingness of citizens to embrace electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical factor in the success of any electric vehicle mandate or incentive program. While governments and industries are increasingly pushing for a transition to electric mobility, public resistance and skepticism can hinder progress. Overcoming this resistance and promoting EV adoption requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses common concerns and highlights the benefits of electric vehicles.
One of the primary challenges in gaining public acceptance is the perception of EVs as a luxury item, often associated with higher prices and limited accessibility. To counter this, governments and EV manufacturers can focus on making electric vehicles more affordable and accessible to a wider population. Incentives such as tax credits, subsidies, and reduced registration fees can significantly lower the upfront cost of EVs, making them more attractive to potential buyers. Additionally, providing financing options tailored to different income groups can further enhance the appeal of electric vehicles.
Another strategy to overcome resistance is to educate the public about the environmental and economic advantages of EVs. Many people are unaware of the significant environmental benefits, such as reduced carbon emissions and improved air quality. Running awareness campaigns and providing accessible information about the positive impact of electric vehicles on the environment can help change public perception. Moreover, highlighting the long-term cost savings of EVs compared to traditional gasoline vehicles can address financial concerns and make the transition more appealing.
Building a robust charging infrastructure is essential to alleviate range anxiety, a common concern among potential EV buyers. Governments and energy providers should invest in expanding the charging network, ensuring convenient and accessible charging options for EV owners. This includes installing charging stations in residential areas, workplaces, and public spaces, making it more convenient for individuals to charge their vehicles. By addressing the practical aspects of EV ownership, such as charging convenience, the transition to electric mobility becomes more feasible and attractive.
Lastly, community engagement and involvement play a vital role in promoting EV adoption. Local governments and EV enthusiasts can organize events, workshops, and awareness campaigns to engage with the public directly. These initiatives can provide hands-on experiences with EVs, allowing people to test-drive and interact with the technology. By fostering a sense of community and sharing personal experiences, the adoption of electric vehicles can be encouraged and resistance can be reduced.
Subaru's Electric Evolution: Exploring the Future of Green Driving
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The electric vehicle mandate is a policy or regulation that aims to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) by setting targets or requirements for vehicle manufacturers and/or governments. It typically involves incentives, subsidies, or penalties to promote the sale and production of electric cars, buses, and other vehicles powered by electricity.
The mandate can be implemented in various ways. One common approach is to set a minimum percentage of electric vehicles that must be sold or produced within a specific market or region. This could be a direct quota or a cap-and-trade system where manufacturers buy or sell credits based on their sales. Governments may also offer incentives like tax credits, rebates, or grants to consumers and businesses to accelerate the transition to electric mobility.
Electric vehicle mandates are crucial for several reasons. Firstly, they help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality by encouraging the shift from internal combustion engine vehicles to cleaner, more sustainable alternatives. Secondly, they can stimulate economic growth by creating new jobs in the EV manufacturing and supply chain. Additionally, mandates can drive innovation, leading to advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and overall vehicle performance.
While electric vehicle mandates offer numerous benefits, there are some challenges to consider. One concern is the potential strain on the power grid, especially if a large number of EVs are charged simultaneously. This can lead to increased energy demand and strain on existing infrastructure. Another challenge is the potential for higher upfront costs for consumers, as electric vehicles often have a higher initial price tag compared to traditional cars. However, these challenges can be addressed through smart grid management, investment in charging infrastructure, and various financial incentives.