In a surprising turn of events, a certain state has sparked controversy by implementing a ban on electric vehicles, a move that has left many in the automotive industry and environmental sectors perplexed. This decision has ignited debates about the future of sustainable transportation and the potential economic implications for the automotive sector. The state's rationale behind this ban remains a subject of intense discussion, as it challenges the widely accepted benefits of electric mobility.
What You'll Learn
- California's EV Ban: The state's strict emissions standards led to a temporary ban on EVs
- Political Backlash: Some states resisted EV adoption due to political opposition and economic concerns
- Economic Impact: Banning EVs could harm local economies reliant on the auto industry
- Environmental Concerns: Critics argue that EVs are not always greener due to battery production
- Public Opinion: Public support for EVs varies, with some states embracing and others resisting

California's EV Ban: The state's strict emissions standards led to a temporary ban on EVs
California, a pioneer in environmental regulations, has a long history of stringent emissions standards aimed at reducing air pollution. These standards have been instrumental in shaping the state's approach to vehicle emissions, particularly in the context of electric vehicles (EVs). However, the state's strict regulations led to an unexpected consequence: a temporary ban on EVs.
In the early 2000s, California's Air Resources Board (CARB) implemented a zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) program, requiring a certain percentage of new vehicle sales to be zero-emission vehicles. This initiative aimed to accelerate the adoption of EVs and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, the rapid introduction of EVs presented a unique challenge. The state's strict emissions standards, designed to ensure low-pollution vehicles, inadvertently led to a temporary ban on traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. This ban was a result of the strict regulations requiring EVs to meet the same emissions standards as conventional cars, which were not yet fully developed.
The issue arose because the ZEV program's success in promoting EVs also meant that fewer conventional vehicles were being sold. This led to a temporary surplus of EVs in the market, causing a dip in the overall vehicle sales. As a result, some car manufacturers faced challenges in meeting their sales targets, leading to a temporary suspension of EV sales. This ban, though short-lived, highlighted the complexities of implementing rapid changes in vehicle technology and the need for a balanced approach to emissions standards.
To address this, CARB introduced a new regulation, the Advanced Clean Cars (ACC) program, which aimed to phase out sales of conventional vehicles while ensuring a steady supply of EVs. The ACC program set more flexible emissions standards for EVs, allowing for a gradual transition to zero-emission vehicles. This approach not only helped maintain market stability but also ensured that the state's emissions reduction goals were met without causing a temporary ban on traditional vehicles.
The California experience serves as a valuable lesson for other regions considering similar emissions standards. It emphasizes the importance of a well-planned transition strategy, especially when introducing new technologies like EVs. By learning from this temporary ban, policymakers can design more effective regulations that promote environmental sustainability while maintaining a stable market for the automotive industry.
Is Toyota CH-R an Electric Vehicle? Unveiling the Truth
You may want to see also

Political Backlash: Some states resisted EV adoption due to political opposition and economic concerns
The resistance to electric vehicle (EV) adoption in certain states can be attributed to a complex interplay of political and economic factors, often resulting in a backlash against this innovative technology. One of the primary concerns is the potential disruption to the established automotive industry and the jobs it provides. States with a strong automotive sector, such as Michigan and Pennsylvania, have historically relied on the production of internal combustion engine vehicles. The shift to EVs could lead to significant job losses and economic instability in these regions, sparking political opposition from local representatives and unions. This resistance is further fueled by the fear of job displacement, as the transition to a new energy source may render certain skills obsolete, causing anxiety among workers and their communities.
In some cases, political opposition arises from a conservative ideological stance. Certain states with a strong conservative presence have expressed skepticism about the environmental benefits of EVs, questioning the technology's long-term sustainability and potential negative impacts on local ecosystems. This skepticism is often tied to a broader skepticism of government-led initiatives, with some politicians arguing that the push for EVs infringes upon individual freedom and choice. As a result, these states may implement policies that hinder the growth of the EV market, such as imposing higher registration fees or offering fewer incentives for EV buyers.
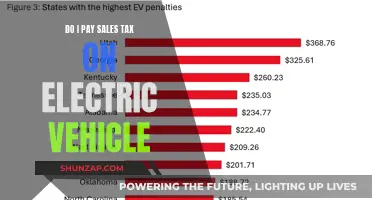
Economic concerns also play a significant role in the political backlash against EV adoption. The initial cost of purchasing an EV is often higher than that of traditional vehicles, and the lack of a robust charging infrastructure can deter potential buyers. States with limited investment in charging stations may face challenges in attracting EV owners, impacting local businesses and the overall economy. Additionally, the potential for reduced tax revenue from the sale of gasoline-powered vehicles could be a political issue, as governments rely on these sales taxes to fund public services and infrastructure.
The political landscape can further complicate the EV adoption process. In highly competitive political environments, where every vote matters, some states might prioritize short-term economic gains over long-term environmental benefits. This could lead to the implementation of policies that favor the status quo, such as extending the lifespan of existing vehicle fleets or providing subsidies for traditional automotive industries. As a result, the transition to EVs may be slowed down or even halted in these states, creating a political barrier to progress.
Despite these challenges, it is important to note that many states are actively working to overcome political and economic resistance. Some have implemented incentives and subsidies to encourage EV purchases, while others are investing in charging infrastructure to address range anxiety. Public awareness campaigns and educational initiatives are also being employed to address misconceptions and build support for EV adoption. By addressing these concerns and implementing strategic policies, states can navigate the political backlash and work towards a more sustainable future with widespread EV adoption.
Maximize Savings: A Guide to Claiming EV Lease Tax Credits
You may want to see also

Economic Impact: Banning EVs could harm local economies reliant on the auto industry
The economic implications of a ban on electric vehicles (EVs) could be significant, particularly for states heavily reliant on the auto industry. These states have often invested heavily in EV manufacturing and related infrastructure, creating a complex web of economic dependencies. A sudden ban on EVs would disrupt this intricate network, leading to a series of negative consequences.
Firstly, the auto industry is a major employer in these regions, providing jobs in manufacturing, assembly, and related services. A ban on EVs could result in job losses as the industry shifts focus away from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. This would not only affect the direct employees in the auto sector but also those in supporting industries, such as suppliers of parts and materials, and service providers like mechanics and technicians. The ripple effect of job losses could lead to reduced consumer spending and a decline in local businesses, further exacerbating the economic downturn.
Secondly, the auto industry is a significant contributor to state and local tax revenues. Sales taxes, income taxes, and property taxes from auto-related businesses provide a substantial financial boost to local and state governments. A ban on EVs could lead to a decrease in these tax revenues, impacting public services, infrastructure development, and social programs. This financial strain could force governments to make difficult decisions, potentially leading to budget cuts or increased taxes on other sectors to compensate for the loss.
The transition to a post-EV world would also disrupt the supply chain and infrastructure that have been developed over years of investment. Many states have established charging station networks, developed battery recycling facilities, and trained professionals in EV maintenance and repair. A ban would render these investments obsolete, leading to significant financial losses and wasted resources. The cost of retraining and re-equipping the workforce to adapt to a new industry could be substantial, further straining local economies.
In summary, a ban on EVs could have a devastating economic impact on states that rely heavily on the auto industry. The disruption of jobs, tax revenues, and established infrastructure would create a ripple effect, harming local businesses, consumers, and governments. While the environmental benefits of EVs are well-documented, the economic consequences of a ban should be carefully considered to ensure a sustainable and equitable transition to a greener future.
Mastering Vehicle Electrical Repairs: A Guide to Replacing Connectors
You may want to see also

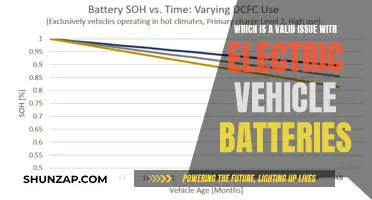
Environmental Concerns: Critics argue that EVs are not always greener due to battery production
The debate surrounding the environmental benefits of electric vehicles (EVs) has sparked a crucial discussion about the sustainability of this emerging technology. Critics argue that despite the reduced emissions during operation, the production and disposal of EV batteries raise significant environmental concerns.
One of the primary issues is the energy-intensive process of manufacturing lithium-ion batteries, which are the most common type used in EVs. The extraction and processing of raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, require substantial energy and often involve environmentally damaging practices. For instance, the extraction of lithium can lead to water pollution and habitat destruction, especially in regions with limited water resources. Additionally, the energy consumption during the manufacturing phase is substantial, often relying on fossil fuels, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, the disposal and recycling of EV batteries present another challenge. As batteries age or become obsolete, proper disposal methods are essential to prevent hazardous waste. Improper handling and disposal can result in soil and water contamination due to the release of toxic chemicals. Recycling processes for lithium-ion batteries are complex and energy-intensive, and not all batteries can be effectively recycled, leading to potential environmental harm.
Critics also highlight the environmental impact of the mining and processing of raw materials. The extraction of these materials often occurs in regions with poor environmental regulations, leading to habitat destruction, water pollution, and human rights issues. The supply chain for EV batteries is long and complex, and ensuring ethical and sustainable practices throughout this chain is a significant challenge.
Despite these concerns, it is important to note that ongoing research and development aim to address these issues. Improvements in battery technology, recycling methods, and sustainable sourcing of raw materials are being explored to make EVs even greener. However, until these advancements are widely implemented, the environmental impact of EVs remains a critical aspect of the discussion, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive approach to sustainable transportation.
Understanding 'Ready': Unlocking EV Potential
You may want to see also

Public Opinion: Public support for EVs varies, with some states embracing and others resisting
The relationship between public opinion and the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is a complex and varied one, with a significant impact on the success of EV policies and initiatives across different states. Public support for EVs has been a crucial factor in the widespread acceptance and integration of these vehicles into the transportation landscape.
In states where environmental concerns and sustainability are at the forefront of public consciousness, there is often a strong embrace of EVs. Residents in these areas are more likely to view electric cars as a viable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional gasoline vehicles. For instance, California, known for its progressive environmental policies, has seen a high level of public support for EVs, with many residents actively advocating for their adoption. This support has led to incentives and subsidies that encourage the purchase of electric vehicles, making it a popular choice for car buyers.
On the other hand, in states with a more traditional or conservative mindset, public opinion towards EVs can be more resistant. Some residents may view electric vehicles as an unnecessary innovation, especially if they perceive it as a threat to established industries or personal freedoms. For example, in certain Southern states, there has been a more cautious approach to EV adoption, with concerns raised about the reliability of the technology and the potential impact on established automotive markets. This resistance can sometimes be fueled by misinformation or a lack of understanding about the benefits of EVs, making it a challenge for policymakers to gain public support.
The varying levels of public opinion have a direct impact on state-level policies and regulations. States with higher public support for EVs often implement more comprehensive incentives and infrastructure development, making it easier for residents to make the switch. These states may offer tax credits, rebates, and subsidies to lower the financial barrier to entry for potential EV owners. Additionally, they invest in charging station networks, ensuring that EV drivers have convenient access to charging facilities, which further encourages adoption.
Conversely, states with less favorable public opinion may struggle to implement effective EV policies. They might face challenges in securing funding for infrastructure projects and may need to invest more in public awareness campaigns to educate residents about the benefits of electric vehicles. Some states might even consider implementing stricter regulations or outright bans on certain types of vehicles, which could be a result of public pressure or a desire to protect local industries.
In summary, public opinion plays a pivotal role in the success of EV integration across different states. Embracing states with strong public support can drive policy changes and infrastructure development, while resisting states may need to address public misconceptions and concerns to foster a more positive reception for electric vehicles. Understanding and catering to these varying opinions are essential steps in the global transition towards a more sustainable transportation system.
Powering the Future: Understanding Electric Vehicle Fleets
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
As of my cut-off date in January 2023, no state has completely banned the sale of electric vehicles (EVs). However, some states have imposed restrictions or incentives that could indirectly affect EV sales. For example, Texas has a law that requires utilities to provide a certain amount of renewable energy credits to EV owners, which has encouraged the adoption of EVs.
There have been discussions and proposals in various states regarding potential bans or restrictions on EVs, often driven by concerns about the environmental impact of battery production and the reliance on fossil fuels for charging. For instance, some states have proposed regulations to phase out gas-powered vehicles, which could indirectly affect the sale of EVs. However, these are still under consideration and not yet implemented.
The reasons for potential bans or restrictions on EVs vary and are often complex. Some states might be concerned about the environmental impact of EV battery production, the sourcing of raw materials, and the potential increase in energy demand for charging. Additionally, there could be economic considerations, such as protecting the traditional automotive industry or ensuring a stable supply of fossil fuels. These factors often lead to debates and policy discussions at the state level.