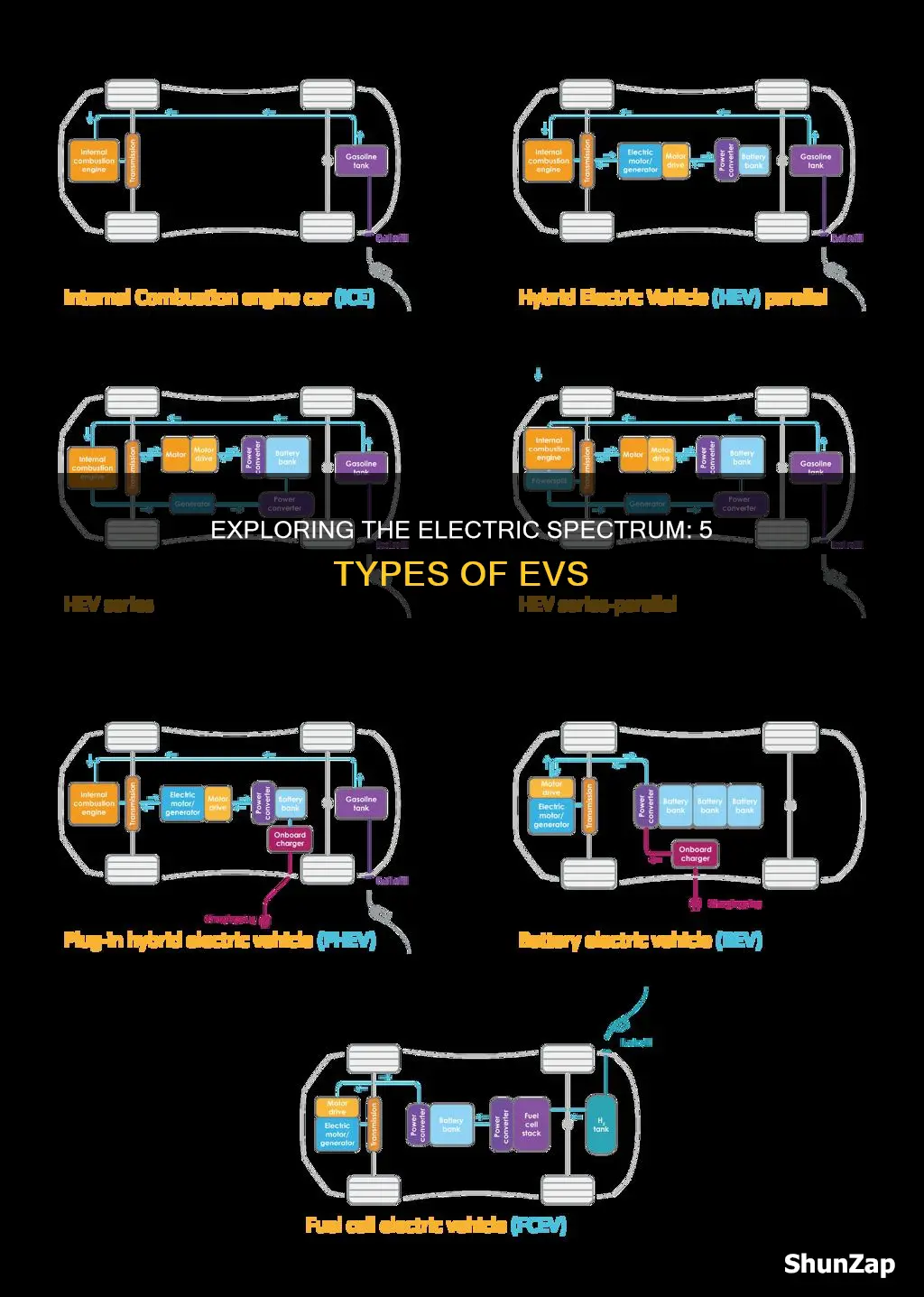
Electric vehicles (EVs) are revolutionizing the automotive industry, offering a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engine cars. There are five primary types of electric vehicles, each with unique characteristics and applications. The first is battery electric vehicles (BEVs), which are fully powered by batteries and produce zero tailpipe emissions. Next are plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), which combine a traditional engine with an electric motor and can be charged from an external power source. Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are another type, utilizing both electric power and a conventional engine, often with regenerative braking. Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) use hydrogen to generate electricity through a fuel cell, emitting only water vapor. Lastly, extended-range electric vehicles (EREVs) feature a small internal combustion engine that provides additional power when needed, extending the vehicle's range. Understanding these different types of EVs is crucial for consumers and policymakers alike as the world transitions towards a more sustainable transportation system.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Electric Vehicles: Cars powered solely by batteries, zero tailpipe emissions
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Combine a gasoline engine with an electric motor for improved efficiency
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Hybrid with a larger electric range, can be charged from an outlet
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles: Use hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, zero direct emissions
- Electric Motorcycles: Two-wheeled EVs, often lighter and more efficient than cars

Battery Electric Vehicles: Cars powered solely by batteries, zero tailpipe emissions
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) are a type of electric vehicle that is revolutionizing the automotive industry. These cars are powered solely by batteries, eliminating the need for traditional internal combustion engines. This design results in zero tailpipe emissions, making BEVs environmentally friendly and contributing to a cleaner, greener future.
The heart of a BEV is its battery pack, which stores electrical energy. These batteries are typically lithium-ion, known for their high energy density and ability to store a significant amount of power. The battery pack is designed to provide the necessary power to the electric motor, which drives the vehicle. When the driver accelerates, the motor receives energy from the battery, delivering instant torque and a smooth, responsive driving experience.
One of the key advantages of BEVs is their zero-emission nature. Unlike conventional vehicles, BEVs produce no harmful exhaust emissions. This is because they don't burn fossil fuels; instead, they convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. As a result, BEVs help reduce air pollution and contribute to improved air quality, especially in urban areas where vehicle emissions can be a significant source of pollution.
BEVs offer a range of benefits to drivers. They are known for their quiet operation, providing a peaceful driving experience. Additionally, BEVs often have lower maintenance costs compared to traditional vehicles due to the absence of complex engine systems. The simplicity of the electric drivetrain means fewer moving parts, reducing the need for frequent servicing.
The charging infrastructure for BEVs is also evolving rapidly. Drivers can charge their vehicles at home using standard power outlets or install dedicated charging stations. Public charging networks are becoming increasingly widespread, providing convenient options for longer journeys. As technology advances, charging times are improving, and battery capacities are increasing, addressing range anxiety and making BEVs even more appealing to a broader audience.
Understanding kWh: Powering Your Electric Vehicle's Range
You may want to see also

Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Combine a gasoline engine with an electric motor for improved efficiency
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are a popular and innovative solution to the challenges of reducing emissions and improving fuel efficiency in the automotive industry. These vehicles combine a traditional internal combustion engine, typically a gasoline engine, with an electric motor and a battery pack. The primary goal of this hybrid system is to enhance overall efficiency by utilizing both power sources, thus reducing fuel consumption and minimizing environmental impact.
In a hybrid electric vehicle, the gasoline engine and the electric motor work in tandem. When the vehicle is started or requires additional power, the electric motor provides the initial boost, ensuring a smooth and quick acceleration. As the vehicle gains speed and the electric motor's power is no longer needed, the gasoline engine takes over, providing the primary power source. This dual-power system allows for a more efficient use of energy, as the electric motor assists during high-demand situations, and the gasoline engine can operate at its most efficient range.
One of the key advantages of HEVs is their ability to recover and store energy that would otherwise be lost during braking. The electric motor acts as a generator, converting the kinetic energy of the vehicle back into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery pack. This process, known as regenerative braking, helps to recharge the battery and improve overall efficiency. As a result, hybrid vehicles can travel a certain distance using only the electric motor, further reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
The design of hybrid electric vehicles also allows for a more flexible and efficient use of space. The battery pack is typically smaller and more compact compared to a conventional vehicle's fuel tank, as the electric motor and battery can provide the necessary power. This design optimization contributes to a more lightweight vehicle, which further enhances fuel efficiency. Additionally, the integration of the electric motor and battery system allows for a more seamless and efficient power distribution, ensuring that energy is utilized effectively whenever needed.
In summary, hybrid electric vehicles offer a compelling solution to the environmental and efficiency challenges of traditional automobiles. By combining a gasoline engine with an electric motor, these vehicles provide improved performance, reduced fuel consumption, and lower emissions. The dual-power system, regenerative braking, and space optimization make HEVs a practical and environmentally friendly choice for drivers seeking a more sustainable transportation option. This technology continues to evolve, contributing to a greener and more efficient future for the automotive industry.
Li-ion: Powering the Future of Electric Vehicles?
You may want to see also

Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Hybrid with a larger electric range, can be charged from an outlet
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) are a unique breed of hybrid vehicles that offer a larger electric range compared to their conventional hybrid counterparts. These vehicles are designed to provide both the efficiency of electric power and the convenience of a traditional combustion engine. One of the key advantages of PHEVs is their ability to be charged from an outlet, allowing for a more sustainable and cost-effective driving experience.
In terms of design, PHEVs often resemble traditional hybrid vehicles, such as the Toyota Prius or the Hyundai Sonata PHEV. However, they typically have a larger battery pack, which increases their electric range. This range can vary significantly, but it often allows for 10 to 50 miles of all-electric driving before the combustion engine engages. The battery capacity and electric range can vary depending on the model and manufacturer. For example, the BMW X5 xDrive45e has an electric range of around 19 miles, while the Chevrolet Volt extended-range electric vehicle offers up to 380 miles in total driving range.
Charging a PHEV is straightforward and can be done in several ways. The most common method is to plug the vehicle into a standard electrical outlet or a dedicated charging station. This process is similar to charging a smartphone or an electric toothbrush. Most PHEVs come with a charging cable and a charging port, which is usually located near the front or rear of the vehicle. Some models even offer wireless charging capabilities, where the vehicle can be parked over a charging pad, eliminating the need for a physical connection.
The charging time for PHEVs can vary depending on the battery size and the charging method. Typically, a full charge can take anywhere from 2 to 8 hours, depending on the charging speed and the battery's capacity. For example, the Ford Fusion Energi can fully charge in around 2 hours using a 240-volt charger, while the Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV takes approximately 4 hours to charge using a standard 120-volt outlet.
In addition to their electric range, PHEVs also benefit from the efficiency of hybrid technology. The combustion engine in a PHEV can act as a backup power source, providing additional range when the battery is depleted. This dual-power system ensures that drivers can travel longer distances without the range anxiety often associated with all-electric vehicles. Furthermore, the regenerative braking system in PHEVs helps to recharge the battery during deceleration, further improving efficiency.
In summary, Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles offer a compelling solution for those seeking a more sustainable and efficient driving experience. With their larger electric range and the ability to be charged from an outlet, PHEVs provide a practical and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional vehicles. As technology advances, we can expect to see more innovative designs and improved performance in the world of plug-in hybrids.
Uncovering the Profitable Segments in the EV Supply Chain
You may want to see also

Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles: Use hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, zero direct emissions
Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) are a fascinating and innovative type of electric vehicle that utilizes a unique power generation system. These vehicles are designed to provide a clean and efficient mode of transportation, offering a promising alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. At the heart of FCEVs lies the fuel cell, a device that converts chemical energy from hydrogen into electricity through a process called electrochemical reactions. This technology is a key player in the quest for zero-emission transportation.
The fuel cell's operation is a complex yet elegant process. It involves the reaction of hydrogen gas, typically stored in high-pressure tanks, with oxygen from the air. This reaction occurs at the anode and cathode of the fuel cell, generating electricity, water, and heat. The electricity produced is then used to power the vehicle's electric motor, providing a clean and efficient source of energy. One of the most significant advantages of FCEVs is their ability to produce zero direct emissions, making them an environmentally friendly choice.
In an FCEV, the hydrogen fuel is fed into the fuel cell stack, where it undergoes a series of chemical reactions. These reactions split the hydrogen atoms, releasing electrons that create an electric current. This current is then harnessed to power the vehicle, with water as the only byproduct, emitted as steam. This process is in stark contrast to conventional vehicles, which burn fossil fuels, releasing harmful pollutants and greenhouse gases. The efficiency of fuel cells is impressive, with a higher energy conversion rate compared to traditional combustion engines.
The technology behind fuel cell electric vehicles has been a subject of research and development for decades, and it has shown great potential. FCEVs offer a range of benefits, including rapid refueling, similar to conventional vehicles, and a longer driving range compared to battery electric vehicles. They are particularly attractive for heavy-duty applications, such as buses and trucks, where the need for frequent and quick refueling is essential. Additionally, the technology can be scaled down for smaller vehicles, making it a versatile solution for various transportation needs.
The widespread adoption of fuel cell electric vehicles faces some challenges, including the availability of hydrogen refueling stations and the cost of fuel cell technology. However, as research and development continue, these obstacles are being addressed. Many countries and organizations are investing in the infrastructure to support FCEVs, recognizing their potential to revolutionize the automotive industry and contribute to a more sustainable future. With ongoing advancements, fuel cell electric vehicles are poised to play a significant role in the transition to cleaner and more efficient transportation.
Electric Vehicle Sales: The 1-Million Milestone Reached
You may want to see also

Electric Motorcycles: Two-wheeled EVs, often lighter and more efficient than cars
Electric motorcycles, also known as e-bikes, are a rapidly growing segment in the world of electric vehicles (EVs). These two-wheeled wonders offer a unique blend of sustainability, efficiency, and performance, making them an attractive choice for urban commuters and enthusiasts alike. Here's an overview of electric motorcycles and their distinct characteristics:
Design and Efficiency: Electric motorcycles are designed with a focus on lightweight construction, often utilizing materials like aluminum or carbon fiber to reduce overall weight. This lightweight design contributes to their exceptional efficiency, as they can achieve impressive energy efficiency ratios compared to larger vehicles. The reduced weight also enhances their agility, making them ideal for navigating through city traffic and narrow roads.
Performance and Range: Despite their compact size, electric motorcycles pack a powerful punch. They are equipped with high-torque electric motors that deliver instant acceleration, providing a thrilling riding experience. The range of these bikes varies, with some models offering over 100 miles on a single charge, making them suitable for longer commutes. Modern electric motorcycles often feature advanced battery technology, ensuring longer-lasting performance and reduced charging times.
Environmental Impact: One of the most significant advantages of electric motorcycles is their minimal environmental footprint. By eliminating the need for traditional internal combustion engines, these bikes produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air in urban areas. Additionally, the use of electric power reduces noise pollution, making them a quieter and more environmentally friendly alternative to gasoline-powered motorcycles.
Regulations and Safety: The rise of electric motorcycles has led to the implementation of specific regulations and safety standards. Many regions have introduced classification systems for e-bikes, categorizing them based on speed and power output. These classifications help determine the legal use of electric motorcycles, such as whether they can be ridden on bike lanes or require helmets in certain areas. Safety features like regenerative braking, ABS, and advanced suspension systems are common, ensuring a secure riding experience.
Electric motorcycles represent a sustainable and efficient transportation option, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional motorcycles. With ongoing technological advancements, these bikes are becoming increasingly popular, providing an exciting and environmentally conscious riding experience.
Flood-Proofing Your EV: What to Do When Water Strikes
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles (EVs) can be broadly categorized into five main types based on their power source and driving mechanism: Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs), Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs), and Electric Range Extender Vehicles (EREVs).
BEVs are fully electric and run exclusively on electricity stored in their batteries. They produce zero tailpipe emissions and are charged by plugging into an external power source, typically an electric charger or a wall outlet. BEVs offer a pure electric driving experience and are known for their efficiency and environmental benefits.
HEVs use a combination of an internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors, with the primary power source being the gasoline engine. HEVs typically have smaller battery packs and can recharge the battery while driving. PHEVs, on the other hand, have larger battery packs that can be charged from an external source, allowing them to drive in electric-only mode for a certain distance before switching to the internal combustion engine. PHEVs offer more flexibility and longer electric-only ranges compared to traditional HEVs.