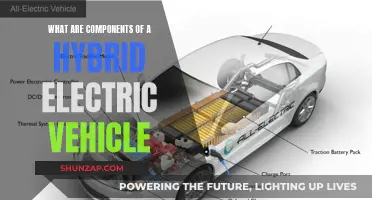
Electric vehicles (EVs) are a rapidly growing segment in the automotive industry, offering an eco-friendly and efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engine cars. The main components of an electric vehicle are designed to power the vehicle using electricity, rather than gasoline or diesel. These components include the electric motor, which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive the wheels; the battery pack, a high-capacity energy storage system that powers the motor; the inverter, which controls the flow of electricity to the motor; and the power electronics, which manage the vehicle's electrical systems. Other key elements include the charger, which replenishes the battery, and the onboard computer, which monitors and optimizes the vehicle's performance. Understanding these components is essential to appreciating the technology behind electric vehicles and their role in the future of sustainable transportation.
What You'll Learn
- Battery: Energy storage, typically lithium-ion, powers the vehicle
- Motor: Converts electrical energy to mechanical motion for propulsion
- Charger: Rechargeable battery systems require an external power source
- Inverter: Converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) for motor use
- Controller: Manages power flow, ensuring efficient and safe operation

Battery: Energy storage, typically lithium-ion, powers the vehicle
The battery is a critical component of electric vehicles (EVs), serving as the primary energy storage system. It is responsible for storing the electrical energy that powers the vehicle's electric motor, enabling it to run without the need for traditional internal combustion engines. The most common type of battery used in EVs is the lithium-ion battery, which has become the industry standard due to its high energy density, lightweight design, and relatively low cost.
Lithium-ion batteries consist of multiple cells, each containing a positive electrode (typically lithium cobalt oxide), a negative electrode (often graphite), and an electrolyte. When the vehicle is in use, the battery undergoes a chemical reaction, moving lithium ions from the negative to the positive electrode, generating an electric current. This process is reversible, allowing the battery to store energy during charging and release it when needed to power the vehicle. The energy storage capacity of these batteries is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), with higher kWh ratings indicating a more powerful and capable battery.
The design and construction of lithium-ion batteries in EVs are carefully engineered to meet specific requirements. These batteries are often modular, allowing for easy replacement or upgrade as technology advances. They are typically housed in a protective casing, designed to withstand various environmental conditions, including temperature fluctuations and vibrations during driving. The battery management system (BMS) is an essential component, monitoring and controlling the battery's performance, ensuring optimal operation, and protecting against overcharging, over-discharging, and overheating.
One of the key advantages of lithium-ion batteries in EVs is their ability to provide high power output, enabling quick acceleration and responsive driving. They also have a relatively long cycle life, allowing for numerous charge-discharge cycles without significant degradation. However, it's important to note that battery technology is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and development focused on improving energy density, charging speed, and overall battery lifespan.
In summary, the battery is the heart of an electric vehicle, providing the necessary energy for propulsion. Lithium-ion technology has revolutionized the automotive industry, offering efficient and reliable power storage solutions. As EV technology advances, the focus remains on enhancing battery performance, safety, and sustainability, ensuring a greener and more sustainable future for transportation.
Unveiling the Secrets: A Comprehensive Guide to Testing Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Motor: Converts electrical energy to mechanical motion for propulsion
The electric motor is a critical component of electric vehicles (EVs), responsible for converting electrical energy into the mechanical motion that propels the vehicle forward. This process is a fundamental aspect of EV technology, allowing for efficient and environmentally friendly transportation. Here's a detailed look at the motor's role and its key characteristics:
Design and Functionality: Electric motors in EVs are typically designed to be compact, lightweight, and highly efficient. They operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where electrical current interacts with a magnetic field to produce mechanical force. When an electric current passes through the motor's windings (coils of wire), it generates a magnetic field that interacts with permanent magnets or other magnetic components, creating rotational motion. This rotational force is then transferred to the vehicle's wheels, enabling movement.
Types of Electric Motors: There are several types of electric motors used in EVs, each with its own advantages and applications. One common type is the DC (Direct Current) motor, which operates on direct current and provides high torque at low speeds. This makes DC motors well-suited for urban driving and acceleration. Another popular choice is the AC (Alternating Current) motor, which is more efficient over a wider speed range and is often used in high-performance EVs. AC motors can be further categorized into synchronous and asynchronous types, each with unique characteristics.
Performance and Efficiency: The motor's performance is measured by its power output, torque, and efficiency. Power output determines how quickly the vehicle can accelerate, while torque is responsible for the motor's ability to overcome resistance and provide smooth, responsive driving. Efficiency is crucial for maximizing the vehicle's range, as it directly impacts energy consumption. Modern electric motors aim to achieve high efficiency by minimizing energy losses during the conversion process.
Control and Management: The motor's performance is carefully managed by sophisticated control systems. These systems regulate the flow of electrical energy to the motor, adjusting speed, torque, and power output as needed. Advanced control algorithms optimize performance, ensuring smooth acceleration, efficient energy use, and precise control over the vehicle's dynamics. Additionally, regenerative braking technology, which converts kinetic energy back into electrical energy, further enhances the motor's efficiency and contributes to the overall driving experience.
In summary, the electric motor is the heart of an electric vehicle, transforming electrical energy into the mechanical force required for propulsion. Its design, functionality, and performance characteristics are carefully engineered to meet the demands of modern transportation. As EV technology continues to evolve, advancements in motor technology will play a pivotal role in improving efficiency, range, and overall driving experience.
Sparking Safety: A Guide to Electrical Fire Hazards in Cars
You may want to see also

Charger: Rechargeable battery systems require an external power source
The charging system of an electric vehicle (EV) is a crucial component that enables the replenishment of its power source, ensuring the vehicle can continue its operation. This system is designed to efficiently transfer electrical energy from an external power source to the vehicle's rechargeable battery pack. The primary purpose of this process is to maintain the battery's charge level, allowing the EV to travel longer distances without the need for frequent refueling.
At the heart of this process is the charger, a device that plays a pivotal role in converting the alternating current (AC) from the power grid into direct current (DC) suitable for charging the vehicle's battery. This conversion is essential because the battery in an EV typically stores energy in the form of DC, which is then used to power the vehicle's electric motor. The charger's efficiency is a critical factor in the overall performance and range of the electric vehicle.
There are various types of chargers available, each with its own set of characteristics and capabilities. One common type is the Level 1 charger, which is typically a standard household outlet and provides a relatively slow charging rate. This type of charger is convenient for overnight charging at home but may not be sufficient for rapid charging needs. Level 2 chargers, on the other hand, offer faster charging speeds and are often used in public charging stations or installed in residential areas with dedicated EV charging infrastructure. These chargers can provide a significant charge in a shorter amount of time, making them ideal for quick top-ups during longer journeys.
For rapid charging, which can significantly reduce charging times, there are Level 3 (DC fast) chargers. These chargers are designed to provide high-power DC directly to the vehicle's battery, often using specialized connectors and cables. Level 3 chargers are commonly found in public charging stations along highways and are capable of replenishing a substantial portion of the battery's charge in a matter of minutes, making them essential for long-distance travel. The availability and accessibility of these charging stations are vital considerations for EV owners, influencing their overall driving experience and confidence in adopting electric vehicles.
In summary, the charger is a critical component in the ecosystem of electric vehicles, facilitating the transfer of energy from the grid to the vehicle's battery. The choice of charger type and the infrastructure supporting it significantly impact the convenience and efficiency of EV ownership. As technology advances, the charging process continues to evolve, aiming to provide faster, more efficient, and widely accessible charging solutions for the growing electric vehicle market.
Exploring the World of All-Electric Vehicles: Powering a Sustainable Future
You may want to see also

Inverter: Converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) for motor use
The inverter is a crucial component in an electric vehicle's power train, responsible for a critical conversion process. It takes the direct current (DC) electricity stored in the vehicle's battery and transforms it into alternating current (AC) suitable for powering the electric motor. This conversion is essential because the electric motor operates on AC power, and the inverter ensures that the motor receives the correct voltage and frequency required for efficient and optimal performance.
In the context of an electric vehicle, the inverter's role is to bridge the gap between the energy storage system and the motor. When the driver engages the accelerator, the inverter receives the DC signal from the controller, which then initiates the conversion process. This conversion is rapid and precise, ensuring that the motor receives the necessary power to accelerate the vehicle. The inverter's efficiency is vital for maintaining the vehicle's performance and range, as any power loss during conversion could impact the overall driving experience.
The design of the inverter is sophisticated, incorporating multiple switching devices and electronic circuits. These components work together to rapidly switch the DC power on and off, creating a waveform that resembles the AC power required by the motor. The inverter's output is carefully controlled to match the motor's specifications, ensuring that the power delivered is consistent and reliable. This level of control is essential for maintaining the vehicle's performance, especially during rapid acceleration or when navigating varying driving conditions.
In addition to its primary function, the inverter also plays a role in regenerative braking. When the driver applies the brakes, the motor operates in generator mode, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy. The inverter then manages this process, converting the generated AC power back into DC to recharge the battery. This regenerative braking system is an efficient way to recover energy and extend the vehicle's range.
Modern electric vehicles often feature advanced inverter technology, such as pulse-width modulation (PWM) inverters or more sophisticated vector control inverters. These advancements allow for improved efficiency, faster response times, and enhanced control over the motor's performance. The inverter's role is pivotal in delivering a smooth and responsive driving experience, making it a key component in the overall success of electric vehicles.
Can Australia Lead the EV Revolution? Exploring Local Manufacturing Potential
You may want to see also

Controller: Manages power flow, ensuring efficient and safe operation
The controller is a critical component in the intricate system of an electric vehicle (EV), acting as the brain that orchestrates the complex dance of power management. Its primary role is to regulate and optimize the flow of electrical energy, ensuring the vehicle's efficient and safe operation. This component is the conductor of the EV's symphony, making sure that power is distributed precisely where it's needed, when it's needed, and in the right amounts.
In the heart of an EV, the controller is a sophisticated electronic device, often a microcontroller or a dedicated control unit. It is designed to handle the complex task of managing the vehicle's power electronics, which include the inverter, charger, and battery management system. The controller's intelligence lies in its ability to interpret sensor data, make real-time decisions, and execute control strategies to maintain optimal performance.
Its primary function is to manage the power flow between the battery, the electric motor, and the vehicle's electrical systems. When the driver engages the accelerator, the controller receives input and calculates the required power to the motor. It then adjusts the power level, ensuring the vehicle accelerates smoothly and efficiently. During braking, the controller manages the regenerative braking system, capturing and storing energy back into the battery, further enhancing the vehicle's efficiency.
Safety is a paramount concern in EV design, and the controller plays a vital role in ensuring it. It monitors the vehicle's operating conditions, such as temperature, voltage, and current, to prevent overloading, overheating, or other potential hazards. For instance, if the battery temperature exceeds a safe limit, the controller can activate cooling systems or reduce power output to maintain stability. Additionally, the controller manages the charging process, ensuring the battery is charged safely and efficiently, preventing overcharging or damage.
The controller's efficiency is key to the overall performance of the EV. It optimizes power distribution, minimizing energy losses and maximizing range. It also contributes to the vehicle's responsiveness, ensuring quick acceleration and smooth driving experiences. With its ability to manage power flow, the controller is the unsung hero, working tirelessly behind the scenes to make electric vehicles a practical, efficient, and safe mode of transportation.
Electric Vehicles: Cost-Effective Transportation for Businesses?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles primarily consist of several essential components that work together to power the car and provide a smooth driving experience. These include the electric motor, battery pack, power electronics, and a sophisticated control system. The electric motor is the heart of the EV, converting electrical energy into mechanical motion to propel the vehicle. The battery pack stores the electrical energy, and the power electronics manage the flow of electricity between the battery and the motor. A sophisticated control system monitors and optimizes the performance of these components, ensuring efficient and safe operation.
The battery pack in an EV is a high-capacity energy storage system, typically composed of multiple lithium-ion cells. These cells store electrical energy, which is then used to power the vehicle. When the driver engages the accelerator, the control system manages the flow of electricity from the battery to the electric motor, providing the necessary power for acceleration. The battery pack's capacity and efficiency are crucial factors in determining the vehicle's range and performance. Modern EVs often feature advanced battery management systems to monitor and maintain optimal performance, ensuring longevity and safety.
The electric motor is a critical component that directly impacts an EV's performance and driving experience. It is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical power, which drives the wheels and propels the vehicle forward. Electric motors offer several advantages, including instant torque, smooth acceleration, and high efficiency. They provide a responsive driving feel, delivering power to the wheels with minimal delay. Additionally, the electric motor's design and efficiency contribute to the overall range of the vehicle, making it a key factor in the EV's overall performance and appeal to drivers.