The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) has brought a new challenge for first responders: the lack of knowledge about the unique dangers posed by these fiery machines. While traditional gasoline and diesel vehicles have well-known risks, EVs present a different set of hazards that are not always immediately apparent to those who respond to emergencies. This article aims to shed light on the critical aspects that first responders should be aware of, including the potential for high-voltage fires, the challenges of extinguishing EV fires, and the importance of specialized training to handle these modern vehicles effectively.
What You'll Learn
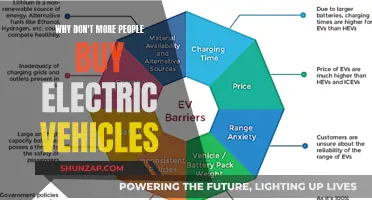
- Battery Fire Hazards: First responders may lack knowledge about the unique challenges of extinguishing battery fires
- High-Voltage Dangers: Electric vehicles pose risks of high-voltage electrocution, which first responders may not be trained to handle
- Rapid Charge Risks: Rapid charging can lead to overheating and fires, a topic often overlooked by first responders
- Fire Suppression Methods: Traditional fire suppression techniques may not be effective against the fires in electric vehicle batteries
- Post-Fire Hazards: After a fire, electric vehicles can still pose risks due to residual heat and chemical hazards

Battery Fire Hazards: First responders may lack knowledge about the unique challenges of extinguishing battery fires
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) on our roads has brought numerous benefits, including reduced emissions and improved energy efficiency. However, it has also introduced new challenges for first responders, particularly when it comes to dealing with battery-related incidents. One critical aspect that first responders may not fully comprehend is the unique hazards associated with extinguishing battery fires.
Battery fires in electric vehicles present a distinct set of challenges compared to traditional vehicle fires. The high-energy density of lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in EVs, can lead to intense and rapid fires when compromised. These fires are not your typical gasoline or diesel blazes; they require specialized knowledge and equipment to handle effectively. First responders often lack the training and understanding of the specific techniques needed to combat these modern fires.
When a battery fire occurs, the initial response might involve standard fire suppression methods, which could inadvertently worsen the situation. For instance, using water or foam to extinguish a lithium-ion battery fire can cause thermal runaway, a self-perpetuating chain reaction that intensifies the fire. This is because water and foam can react with the battery's electrolytes and electrodes, generating more heat and potentially leading to an explosion. Therefore, first responders must be aware of the potential risks and employ appropriate measures to prevent further damage.
To address this knowledge gap, it is crucial to provide specialized training for emergency services personnel. This training should cover the unique properties of EV batteries, including their chemical composition, potential fire risks, and the appropriate extinguishing agents to use. By educating first responders on the specific challenges of battery fires, we can ensure a more effective and safe response, minimizing the potential for injury and property damage.
In summary, as the adoption of electric vehicles continues to grow, it is essential to equip first responders with the necessary knowledge and skills to handle battery-related incidents. This includes understanding the hazards of extinguishing battery fires and implementing appropriate safety measures. By doing so, we can ensure that emergency services are well-prepared to respond to these modern challenges and provide effective assistance when every second counts.
Upgrading Your Ride: A Guide to Converting Vehicle Axles to Electric Brakes
You may want to see also

High-Voltage Dangers: Electric vehicles pose risks of high-voltage electrocution, which first responders may not be trained to handle
Electric vehicles (EVs) are revolutionizing the automotive industry, offering efficient and environmentally friendly transportation. However, beneath their sleek designs and zero-emission credentials lies a hidden danger that first responders may not be adequately prepared to handle: high-voltage electrocution. As the popularity of EVs continues to rise, it is crucial to shed light on this emerging challenge and educate both drivers and emergency personnel about the potential risks.
The advanced technology in electric cars involves high-voltage batteries, often reaching up to 400 volts, which is significantly higher than the standard 120-volt household electrical supply. This elevated voltage presents a unique hazard, as a single touch or even proximity to certain components can result in severe electrical shocks. First responders, including police officers, firefighters, and paramedics, may encounter these vehicles during accidents, breakdowns, or rescue operations. Without proper knowledge and training, they could inadvertently expose themselves and others to dangerous electrical currents.
One critical aspect that first responders should be aware of is the location of high-voltage components within the vehicle. Unlike traditional cars, EVs have batteries and power systems positioned in various places, sometimes in hard-to-reach areas. For instance, some models have their batteries located under the floor or integrated into the vehicle's structure. During an accident, these components can become damaged, leading to potential electrocution risks for anyone nearby. It is essential for emergency personnel to understand these unique design features to minimize the chances of accidental electrocution.
Training and education are key to addressing this issue. Specialized courses and workshops can be organized to inform first responders about the high-voltage dangers associated with EVs. These sessions should cover the identification of critical components, safe handling procedures, and the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). By equipping emergency personnel with the necessary knowledge, they can better protect themselves and the public while responding to EV-related incidents. Additionally, manufacturers can play a role by providing clear and accessible information about their vehicle's electrical systems, ensuring that first responders have the resources they need.
In conclusion, as the world embraces the benefits of electric vehicles, it is imperative to acknowledge and address the high-voltage dangers they present. First responders, often the first line of defense in emergencies, require specialized training to handle these risks effectively. By raising awareness and providing comprehensive education, we can ensure that both drivers and emergency services are prepared to manage the unique challenges posed by fiery electric vehicles, ultimately saving lives and minimizing potential harm.
Peach Pass: Free EV Charging or a Rip-Off?
You may want to see also

Rapid Charge Risks: Rapid charging can lead to overheating and fires, a topic often overlooked by first responders
The rapid advancement of electric vehicle (EV) technology has brought numerous benefits, including faster charging times, which are a significant advantage over traditional gasoline vehicles. However, this convenience comes with a hidden danger that first responders may not be fully aware of: the potential for rapid charging to cause overheating and fires.
Rapid charging, while efficient, can generate excessive heat within the vehicle's battery pack. This heat can lead to a chain of events that may result in a fire. The high-power charging process can cause the battery cells to reach temperatures above their safe operating limits, leading to a phenomenon known as thermal runaway. During thermal runaway, the battery cells can ignite, releasing flammable gases and potentially causing a fire. This risk is particularly concerning for first responders who may not have the necessary knowledge or equipment to handle such incidents effectively.
The issue is often overlooked because the risks are not immediately apparent. Unlike a traditional vehicle fire, which may be caused by a spark or electrical fault, the fire in an EV can originate from within the battery pack, making it more challenging to identify and combat. First responders might not recognize the signs of overheating, such as unusual noises or smoke, especially if it occurs during the charging process, which is often conducted in a controlled environment. As a result, they may not take the necessary precautions or have the specialized training to address these unique challenges.
To mitigate these risks, it is crucial for first responders to receive specialized training on EV fire safety. This training should cover the unique characteristics of EV batteries, the potential hazards of rapid charging, and the appropriate response procedures. Additionally, having access to specialized equipment, such as fire-resistant suits and cutting tools designed for EV battery packs, can significantly improve the chances of a successful outcome during an emergency response. By addressing this often-overlooked aspect of EV technology, first responders can better prepare for and manage potential fires, ensuring the safety of both themselves and the public.
The Future of EV Tax Credits: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Fire Suppression Methods: Traditional fire suppression techniques may not be effective against the fires in electric vehicle batteries
The increasing prevalence of electric vehicles (EVs) on our roads presents a unique challenge for first responders and emergency services. While these vehicles offer numerous benefits, their advanced battery technology can lead to unexpected and dangerous situations when involved in fires. Traditional fire suppression methods, which have been effective for decades, may not be sufficient to combat the intense and rapid fires that can erupt in EV batteries.
One of the primary issues is the chemical composition of EV batteries. Unlike conventional vehicles, which primarily use gasoline or diesel, electric cars rely on lithium-ion batteries. These batteries contain volatile organic solvents and lithium metal, which can ignite and release toxic gases when exposed to high temperatures. The rapid spread of fire in these batteries is a significant concern for first responders, as it can quickly escalate from a small blaze to a full-scale inferno.
Traditional fire suppression techniques, such as water or foam, are often ineffective against the unique characteristics of EV fires. Water, for instance, can cause the battery to short-circuit and release even more flammable gases, leading to a more intense fire. Foam, while useful for some fires, may not penetrate the battery's sealed casing, allowing the flames to continue burning. Moreover, the high heat generated by EV fires can cause the batteries to rupture, releasing corrosive chemicals that pose a risk to both firefighters and the surrounding environment.
To address this challenge, fire departments are now exploring specialized training and equipment. This includes understanding the specific hazards associated with EV fires, such as the potential for explosive gas release and the risk of secondary fires caused by battery damage. Firefighters are being trained to use dry powder or carbon dioxide extinguishers, which can effectively suppress the flames without causing further damage. Additionally, the development of specialized fire-fighting suits and equipment is crucial to protect firefighters from the extreme heat and toxic fumes generated by these fires.
In conclusion, the unique nature of fires in electric vehicle batteries demands a reevaluation of traditional fire suppression methods. First responders must stay informed about the latest advancements in EV technology and adapt their strategies accordingly. By recognizing the limitations of conventional techniques and adopting specialized training, emergency services can better protect themselves and effectively manage these complex fire situations.
Is the Grid Ready for the Electric Vehicle Revolution?
You may want to see also

Post-Fire Hazards: After a fire, electric vehicles can still pose risks due to residual heat and chemical hazards
The aftermath of a fire in an electric vehicle (EV) presents unique challenges and potential dangers that first responders may not be fully aware of, which could impact their decision-making and safety protocols. One of the primary concerns is the residual heat generated by the fire and the subsequent cooling process. Even after a fire is extinguished, the battery pack and other components can retain significant heat for an extended period. This residual heat can lead to the release of hazardous gases, such as hydrogen gas, which is highly flammable and can pose a risk of explosion or fire. First responders must be cautious and employ appropriate safety measures, including the use of personal protective equipment and controlled ventilation, to mitigate these risks.
Furthermore, the chemical composition of EV batteries introduces additional complexities. These batteries contain various chemicals, including lithium, which can react with water or moisture to produce flammable gases and corrosive substances. When exposed to high temperatures during a fire, these chemicals can release toxic fumes and potentially hazardous materials. First responders should be trained to recognize these chemical hazards and take necessary precautions, such as wearing protective gear and using specialized equipment to contain and neutralize any dangerous substances.
Another critical aspect is the potential for secondary fires or explosions. Even if the initial fire is contained, there is a risk of further incidents due to the intricate electrical systems within the vehicle. High-voltage components, such as the battery pack and power electronics, can still be live and pose a shock hazard. Additionally, the fire may have damaged these systems, leading to short circuits or the release of flammable liquids. First responders must approach the scene with caution, ensuring they are aware of the potential electrical hazards and taking steps to prevent accidental contact or ignition sources that could reignite the fire.
In the aftermath of a fire, the structural integrity of the vehicle's frame and body may also be compromised. The intense heat can cause metal deformation and potential collapse, creating a hazardous environment. First responders should assess the structural stability of the vehicle to ensure it is safe to enter and extract any occupants or victims. This assessment may require specialized tools and knowledge to identify hidden damage and potential structural weaknesses.
Lastly, the presence of hazardous materials and chemicals within the EV, such as lithium-ion battery electrolytes and other flammable substances, requires careful handling. These materials can pose risks to both the environment and human health if not managed properly. First responders should be trained in the proper procedures for containing, transporting, and disposing of these hazardous materials to minimize the potential impact on the surrounding area and the public.
California's 2030 EV Law: A Green Revolution or a Costly Burden?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
First responders are equipped with specialized training and equipment to tackle the unique risks associated with fiery electric vehicles. When dealing with a fire in an EV, they focus on containing the blaze, preventing the spread of flames, and minimizing the release of toxic fumes. This often involves using dry chemical agents or foam extinguishers, which are designed to suppress fires in lithium-ion batteries without causing additional hazards.
Electric vehicles pose some distinct challenges for firefighters. The high-voltage batteries in EVs can remain live even after the vehicle is turned off, creating a risk of electric shock. Firefighters must be cautious and follow specific protocols, such as using insulated tools and wearing protective gear, to ensure their safety. Additionally, the advanced materials in EVs, like lithium-ion batteries, can release flammable gases when overheated, leading to more intense and unpredictable fires compared to conventional vehicles.
Staying updated with the latest advancements in electric vehicle technology is crucial for first responders. Manufacturers regularly release new models with different battery configurations and charging systems. First responders should attend training sessions, workshops, and industry conferences to learn about the specific characteristics of various EV models. By understanding the technical aspects, they can better prepare for emergency situations and provide effective responses, ensuring the safety of both themselves and the public.