A low-speed electric vehicle (LSEV) is a small, lightweight, and energy-efficient automobile designed for short-distance travel at speeds typically limited to 25 miles per hour or less. These vehicles are often used for urban transportation, offering a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional cars. They are equipped with electric motors and batteries, providing a clean and quiet driving experience while reducing carbon emissions. LSEVs are particularly popular in residential areas, campuses, and commercial zones where they can navigate narrow streets and offer a convenient mode of transport for short commutes.
What You'll Learn
- Definition: Low-speed EVs are electric cars designed for short-distance travel at speeds under 20 mph
- Regulations: These vehicles often have specific legal requirements and restrictions
- Uses: Ideal for urban areas, delivery services, and recreational purposes
- Technology: Powered by electric motors and batteries, offering eco-friendly transportation
- Benefits: Environmentally friendly, low maintenance, and cost-effective for short commutes

Definition: Low-speed EVs are electric cars designed for short-distance travel at speeds under 20 mph
Low-speed electric vehicles (LS EVs) are a specialized category of electric cars that are specifically designed for short-distance travel at very low speeds, typically under 20 miles per hour (mph). These vehicles are often referred to as neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs) or low-speed electric cars. The primary purpose of LS EVs is to provide an environmentally friendly and cost-effective transportation option for short commutes within urban or suburban areas.
One of the key characteristics of LS EVs is their limited speed, which is intentionally restricted to ensure safety and compliance with regulations. This speed cap of 20 mph makes them ideal for intra-city travel, allowing drivers to navigate through residential areas, parking lots, and other low-speed zones without posing a significant risk to other road users. The design and engineering of these vehicles prioritize safety, often featuring a sturdy frame, robust brakes, and a limited top speed to prevent accidents.
These electric cars are typically equipped with a small battery pack, an electric motor, and a simple control system. The battery provides the necessary power for the motor, which drives the vehicle's wheels. LS EVs are known for their simplicity and ease of use, often featuring a single-speed transmission and a straightforward control panel. They are designed to be accessible and user-friendly, making them attractive to individuals who prefer a low-maintenance and environmentally conscious mode of transportation.
The market for LS EVs has been growing, particularly in regions with specific regulations governing low-speed vehicles. These vehicles are popular among elderly individuals, people with limited mobility, and those seeking an affordable and eco-friendly transportation option. Additionally, they are often used in commercial settings, such as golf courses, resorts, and industrial sites, where short-distance travel is common.
In summary, low-speed electric vehicles are a niche but essential segment of the automotive industry, catering to the needs of short-distance travelers in urban and suburban environments. Their limited speed, environmental benefits, and simplicity make them a practical choice for specific applications, contributing to a more sustainable and accessible transportation ecosystem.
The Future of Transportation: Should You Still Buy Non-Electric Vehicles?
You may want to see also

Regulations: These vehicles often have specific legal requirements and restrictions
Low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) are a unique category of electric vehicles designed for urban and low-speed applications. These vehicles are typically smaller, lighter, and less powerful than traditional electric cars, making them ideal for short-distance travel and navigating through crowded areas. However, their lower speed and power output also mean they are subject to specific legal regulations and restrictions to ensure safety and compliance with local laws.
Regulations for LSEVs vary depending on the region and country. In the United States, for example, the federal government has established guidelines for LSEVs under the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) regulations. These guidelines define the maximum speed and power output for LSEVs, which is typically limited to 25 miles per hour (40 km/h) or less. This classification is often referred to as the "neighborhood electric vehicle" (NEV) or "low-speed electric vehicle" category. The NHTSA's regulations also mandate specific safety features, such as a maximum of 150 volts for the vehicle's electrical system and a requirement for a seat belt or a restraint system for the driver.
In addition to federal regulations, individual states and local governments may have their own rules and restrictions for LSEVs. Some areas may require these vehicles to be registered and licensed, similar to traditional motor vehicles. This includes obtaining a vehicle identification number (VIN) and adhering to insurance and safety inspection requirements. Local authorities might also impose speed limits on specific roads or areas where LSEVs are permitted to operate, further restricting their use.
The legal requirements for LSEVs often extend to their design and manufacturing processes. Manufacturers must ensure that these vehicles meet specific safety standards, including crashworthiness, lighting, and braking systems. The vehicles should also be equipped with a clear and visible speedometer and a warning system to alert the driver of potential hazards. Furthermore, LSEVs may be subject to emissions regulations, as they still produce some form of emissions, even though they are electric.
Understanding and adhering to these regulations is crucial for both manufacturers and operators of LSEVs. Compliance ensures that these vehicles are safe, environmentally friendly, and legally operated. It also allows for the integration of LSEVs into urban transportation systems, providing an alternative for short-distance travel and potentially reducing traffic congestion in densely populated areas.
Unlocking EV Battery Investing: Strategies for a Sustainable Future
You may want to see also

Uses: Ideal for urban areas, delivery services, and recreational purposes
Low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) are an innovative and sustainable transportation solution, particularly well-suited for urban environments. These vehicles are designed to operate at speeds typically below 20 mph, making them ideal for navigating through densely populated areas where traditional cars might be less practical. In urban settings, LSEVs offer a range of benefits that contribute to a more efficient and environmentally friendly transportation system.
One of the primary uses of LSEVs in urban areas is for last-mile delivery services. These vehicles are perfect for making short, frequent trips to deliver goods, packages, or food. With their compact size and maneuverability, LSEVs can easily navigate through city streets, reaching destinations that might be challenging for larger delivery vehicles. This not only reduces traffic congestion but also minimizes the carbon footprint associated with urban deliveries, making it an eco-friendly choice for businesses and customers alike.
In addition to delivery services, LSEVs are also gaining popularity for recreational purposes. Many cities and communities are adopting these vehicles for eco-friendly transportation options. For instance, LSEVs can be used for guided tours, providing visitors with a unique and environmentally conscious way to explore urban areas. They are also suitable for short-distance commuting, allowing individuals to travel to and from work or other destinations while reducing their reliance on public transportation or personal cars.
The design of LSEVs often includes features that enhance their usability in urban environments. These vehicles are typically equipped with advanced safety systems, such as collision avoidance sensors and backup cameras, ensuring safe operation in crowded spaces. Additionally, LSEVs often have a comfortable and spacious interior, making them suitable for carrying passengers or cargo. Some models even offer features like folding seats or removable cargo areas, providing versatility for various urban applications.
Furthermore, the environmental benefits of LSEVs are significant. By utilizing electric power, these vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to improved air quality in urban areas. The use of LSEVs can help reduce noise pollution, making cities quieter and more pleasant places to live and work. With their ability to operate efficiently and sustainably, LSEVs are becoming an increasingly popular choice for urban transportation, offering a greener and more convenient alternative to traditional vehicles.
Unlocking EV Tax Credits: A Guide to Maximizing Your Federal Benefits
You may want to see also

Technology: Powered by electric motors and batteries, offering eco-friendly transportation
Low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) are a type of eco-friendly transportation that has gained popularity in recent years. These vehicles are designed to operate at low speeds, typically under 20 miles per hour, and are often used for short-distance travel, such as commuting to work, running errands, or transporting children to school. The primary technology that powers these vehicles is electric motors and batteries, which offer a clean and efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engines.
At the heart of an LSEV is an electric motor, which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle forward. These motors are designed to be compact and lightweight, allowing for easy integration into the vehicle's design. The motor's power output is carefully calibrated to match the vehicle's intended speed range, ensuring efficient performance within the low-speed domain. When the driver applies power, the motor engages, providing a smooth and quiet acceleration experience.
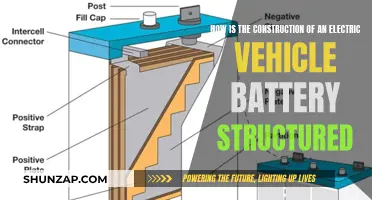
The energy source for these vehicles is a rechargeable battery pack, typically made up of multiple lithium-ion cells. These batteries store electrical energy, which is then supplied to the electric motor when needed. The capacity and voltage of the battery pack determine the vehicle's range and performance. Modern LSEVs often feature advanced battery management systems that optimize charging, monitor temperature, and ensure the longevity of the battery pack.
One of the key advantages of LSEVs is their environmental friendliness. By eliminating the need for gasoline or diesel, these vehicles significantly reduce carbon emissions and air pollution. The absence of exhaust pipes and the use of clean electricity make LSEVs a greener choice for urban transportation. Additionally, their low-speed nature makes them ideal for navigating through congested city streets, offering a more efficient and environmentally conscious way to travel.
In terms of technology, LSEVs also incorporate various innovative features. Many models are equipped with regenerative braking systems, which convert kinetic energy back into electrical energy during deceleration, further improving efficiency. Some vehicles also offer advanced driver-assistance systems, such as lane-keeping assist and automatic parking, enhancing safety and convenience. The integration of smart connectivity allows for over-the-air updates, ensuring the vehicle's software remains current and secure.
Understanding Short Circuits: A Guide to Vehicle Electrical Issues
You may want to see also

Benefits: Environmentally friendly, low maintenance, and cost-effective for short commutes
Low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) are an innovative and sustainable transportation option that offers numerous advantages for both individuals and the environment. These vehicles are designed to operate at speeds typically below 20 miles per hour, making them ideal for short-distance travel within urban areas. One of the most significant benefits of LSEVs is their environmental friendliness. By utilizing electric motors and rechargeable batteries, these vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing air pollution and carbon footprints compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars. This feature makes LSEVs a cleaner and greener choice for daily commutes, especially in congested city centers where pollution levels are often high.
In terms of maintenance, LSEVs are built to be low-maintenance machines. The simplicity of their design, with fewer moving parts compared to conventional vehicles, results in reduced wear and tear. This simplicity translates to less frequent servicing, lower maintenance costs, and fewer trips to the mechanic. Additionally, the absence of complex internal combustion engines means that LSEVs are less prone to mechanical breakdowns, ensuring a more reliable and hassle-free driving experience.
The cost-effectiveness of LSEVs is another compelling advantage, particularly for short commutes. These vehicles are generally more affordable to purchase and operate compared to traditional cars. The initial investment in an LSEV is often lower due to their smaller size and simpler technology. Moreover, the cost of electricity to power these vehicles is typically much lower than gasoline, leading to significant savings over time. This makes LSEVs an attractive option for individuals seeking an economical mode of transportation for their daily urban travels.
For short commutes, LSEVs provide a practical and efficient solution. Their low speed and maneuverability make navigating through traffic and narrow streets easier, reducing travel time and frustration. The ability to park in smaller spaces and the overall ease of use make LSEVs a convenient choice for urban dwellers. Additionally, the quiet operation of electric motors contributes to a more peaceful and less disruptive driving experience, especially in residential areas.
In summary, low-speed electric vehicles offer a range of benefits that make them an attractive and sustainable transportation choice. From their environmentally friendly nature and low maintenance requirements to their cost-effectiveness for short commutes, LSEVs provide a practical and efficient solution for urban mobility. As cities continue to prioritize sustainability and reduce their carbon footprint, LSEVs are likely to play a significant role in shaping the future of urban transportation.
The Debate: Electric Scooters: A Vehicle or Not?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A low-speed electric vehicle is a small, lightweight, and efficient electric car designed for short-distance travel, typically within residential areas, neighborhoods, or low-speed zones. These vehicles are often used for personal transportation, last-mile commuting, or recreational purposes.
LSEVs are specifically engineered for low-speed applications and have several distinct features. They are usually smaller in size, have a lower top speed, and are equipped with simpler drivetrains compared to high-speed electric vehicles. LSEVs often prioritize accessibility, affordability, and ease of use for urban mobility.
These vehicles offer numerous advantages, including reduced environmental impact due to zero tailpipe emissions, lower operating costs compared to gasoline-powered cars, and ease of parking in tight urban spaces. LSEVs are also known for their high energy efficiency, making them cost-effective for short daily commutes.
Yes, LSEVs are designed with safety in mind, especially for low-speed environments. They typically have a slower maximum speed, reduced noise levels, and improved visibility, making them less of a hazard to pedestrians and cyclists. Many LSEVs also feature advanced safety features like braking systems and stability control.
While LSEVs are primarily designed for short-distance travel, some models offer extended range options or the ability to be used for longer trips with proper planning and charging infrastructure. However, for long-distance travel, traditional electric cars or hybrid vehicles might be more suitable due to their higher top speeds and longer ranges.