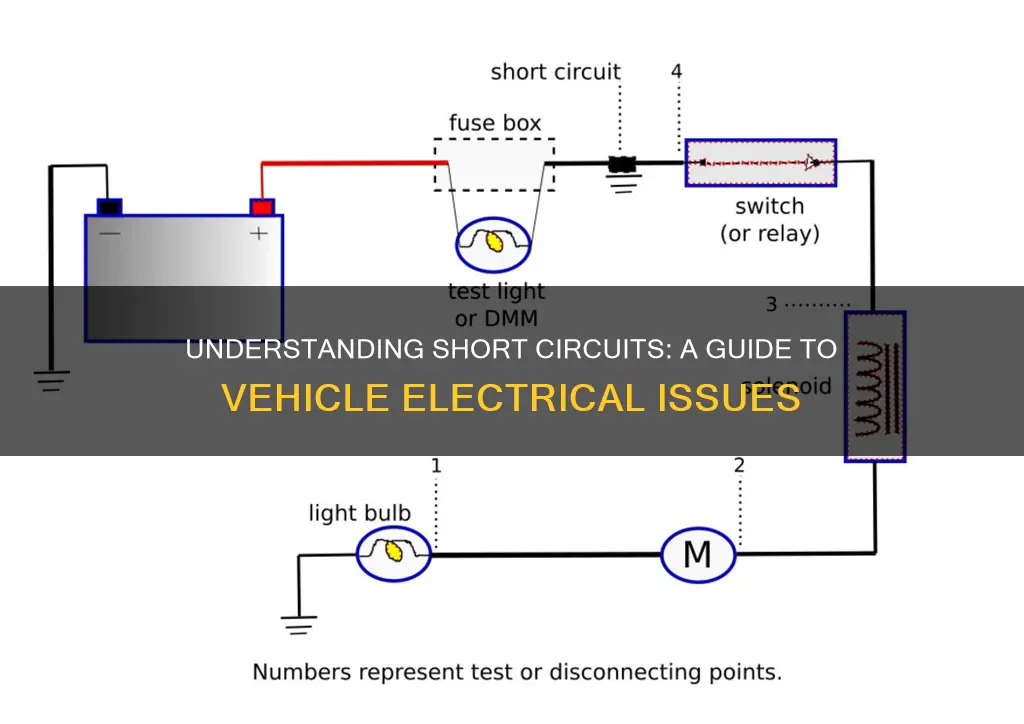
A short circuit in vehicle electrics refers to an unintended electrical connection between two points that are not supposed to be connected, typically resulting in a sudden and excessive flow of current. This can occur due to damaged wiring, faulty components, or improper connections, leading to potential hazards such as blown fuses, damaged wiring harnesses, or even fire risks. Understanding the causes and effects of short circuits is crucial for vehicle owners and mechanics to ensure the safe and efficient operation of a vehicle's electrical system.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | A short circuit occurs when there is an unintended low-resistance path between two points in an electrical circuit, bypassing the normal load. In vehicle electrics, this can happen due to damaged insulation, faulty wiring, or other issues. |
| Symptoms | - Sudden loss of power or functionality in a specific component or system. - Unusual noises or sparks from the electrical system. - Burning smell or visible signs of damage near wiring. - Malfunctioning of lights, indicators, or other electrical accessories. |
| Causes | - Damaged or frayed wiring. - Insulation breakdown. - Faulty switches or connectors. - Shortened or damaged components like fuses or circuit breakers. |
| Risks | - Overheating and potential fire hazards due to excessive current flow. - Damage to sensitive electronic components. - Complete loss of electrical functionality in the affected area. |
| Prevention | - Regular inspection and maintenance of the vehicle's electrical system. - Using high-quality wiring and components. - Ensuring proper insulation and secure connections. - Promptly addressing any signs of damage or wear. |
| Repair/Solution | - Identifying and replacing damaged wiring or components. - Resetting or replacing fuses/circuit breakers. - Professional diagnosis and repair by qualified technicians. |
What You'll Learn
- Short Circuit: A fault where current bypasses normal circuit path, causing damage or malfunction
- Overload: Excessive current flow due to a short circuit, leading to circuit breaker tripping
- Voltage Drop: A short circuit can cause a significant drop in voltage, affecting component performance
- Arc Flash: Short circuits may result in arc flash, a dangerous electrical discharge
- Safety Hazards: Short circuits pose risks like fire, shock, and system failure in vehicle electrics

Short Circuit: A fault where current bypasses normal circuit path, causing damage or malfunction
A short circuit in the context of vehicle electrics is a critical issue that can lead to significant problems and potential hazards. It occurs when there is an unintended and abnormal connection between two points in an electrical circuit, allowing a high volume of electric current to flow through a path that it was not designed for. This sudden surge of current can have detrimental effects on the vehicle's electrical system and components.
In a typical electrical circuit, current flows through the intended path, such as through a resistor or an insulated wire, and is controlled by the components designed for that purpose. However, during a short circuit, the current takes a different route, often bypassing the intended components and creating a direct connection between two points with different voltage levels. This can happen due to various factors, including damaged insulation, faulty wiring, or compromised connections.
The consequences of a short circuit can be severe. The excessive current can cause rapid heating of wires and components, leading to melting, burning, or even explosions in extreme cases. This can result in damage to the vehicle's wiring harness, fuses, and other electrical parts. Moreover, the short circuit may lead to a sudden loss of power or erratic behavior in the vehicle's electrical system, affecting critical functions like engine control, lighting, and safety mechanisms.
Identifying and addressing short circuits promptly is essential for vehicle safety and reliability. Mechanics and technicians use specialized tools and techniques to detect these faults, such as ohmmeters and voltage testers. When a short circuit is suspected, the affected circuit is isolated, and the cause is traced back to the specific point of failure. Repairs often involve replacing damaged components, re-insulating wires, or tightening connections to restore the integrity of the electrical system.
Preventive measures are also crucial to minimize the risk of short circuits. Regular vehicle maintenance, including checking for frayed or damaged wiring, ensuring secure connections, and using high-quality electrical components, can help prevent such faults. Additionally, understanding the vehicle's electrical system and its unique requirements can aid in identifying potential problem areas and implementing appropriate safety measures.
EU Subsidies: A Boost for Electric Vehicle Adoption?
You may want to see also

Overload: Excessive current flow due to a short circuit, leading to circuit breaker tripping
A short circuit in a vehicle's electrical system is a critical issue that can lead to a variety of problems, including circuit breaker tripping. This occurs when there is an unintended path for electricity to flow, bypassing the normal resistance of the circuit. In the context of vehicle electrics, a short circuit can be caused by various factors, such as damaged wiring, faulty components, or improper connections.
When a short circuit happens, it creates an excessive and unintended flow of current through the circuit. This sudden surge in current can quickly exceed the capacity of the circuit breaker, which is designed to trip and interrupt the circuit when it detects an overcurrent situation. The circuit breaker's primary function is to protect the electrical system from damage caused by excessive current, which can lead to overheating, component failure, or even fire hazards.
Overload, as a result of a short circuit, is a common and potentially dangerous consequence. The excessive current flow can cause the circuit breaker to trip, cutting off the power supply to the affected part of the electrical system. This tripping action is a safety mechanism to prevent further damage and potential hazards. However, it can also lead to inconvenience, as the driver may lose power to essential systems or experience unexpected power loss while driving.
To address this issue, it is crucial to identify and rectify the cause of the short circuit. This may involve inspecting the wiring for any signs of damage, checking for loose or faulty connections, and testing the integrity of electrical components. In some cases, replacing damaged parts or rewiring may be necessary to restore the electrical system's functionality and ensure it operates safely.
Regular maintenance and inspections can help prevent short circuits and overload situations. Vehicle owners should be vigilant and look out for any unusual behavior in their electrical systems, such as flickering lights, unexpected power loss, or unusual noises. Promptly addressing these issues can help avoid more severe problems and ensure the vehicle's electrical system remains reliable and safe.
Can Income Limit Your Electric Vehicle Credit?
You may want to see also

Voltage Drop: A short circuit can cause a significant drop in voltage, affecting component performance
A short circuit in a vehicle's electrical system is a critical issue that can have severe consequences for the overall performance and functionality of the car. When a short circuit occurs, it creates an unintended path for electrical current to flow, bypassing the normal circuit and often leading to a sudden and excessive current draw. This phenomenon is a result of the low resistance offered by the short circuit, which allows a large amount of current to pass through, causing a significant voltage drop across the affected circuit.
In the context of vehicle electrics, voltage drop is a critical parameter that ensures the proper functioning of various components. Each electrical component in a vehicle has specific voltage requirements to operate efficiently and safely. When a short circuit is present, the voltage across the affected circuit drops dramatically, often falling below the minimum threshold required for these components to function optimally. This voltage drop can lead to several issues.
One of the primary consequences is the malfunction or failure of electrical components. For instance, a short circuit in the wiring connected to the engine control unit (ECU) could result in a voltage drop, causing the ECU to receive insufficient power. This might lead to erratic engine behavior, reduced performance, or even a complete failure of the engine management system. Similarly, other critical systems like the lighting, ignition, and fuel injection systems are also susceptible to voltage drops caused by short circuits, which can result in dim lights, misfires, or complete system failures.
The impact of a short circuit on voltage drop is not limited to individual components but can also affect the overall electrical system's performance. In a complex electrical network, where multiple components are interconnected, a short circuit in one area can cause a chain reaction, leading to voltage drops across various parts of the system. This can result in a complete loss of power or functionality in certain areas, rendering the vehicle inoperable or posing safety risks.
To mitigate the effects of short circuits and voltage drops, vehicle manufacturers employ various safety mechanisms and design considerations. These include implementing fuses and circuit breakers that can detect and interrupt excessive current flow, thus preventing damage to the system. Additionally, proper wiring techniques, such as using high-quality insulation and ensuring correct wiring connections, help minimize the chances of short circuits. Regular electrical system inspections and maintenance are also crucial to identify and address potential issues before they cause significant damage.
Unveiling the Surprising Environmental Impact of Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Arc Flash: Short circuits may result in arc flash, a dangerous electrical discharge
A short circuit is a critical issue in vehicle electrical systems, and it can lead to a potentially hazardous situation known as an arc flash. This phenomenon occurs when there is an unintended low-resistance path for the current to flow, bypassing the normal intended circuit. In the context of vehicle electrics, a short circuit can happen when a hot wire comes into contact with a grounded or neutral part of the system, often due to damaged insulation or faulty wiring.
When a short circuit occurs, the current in the circuit increases dramatically, as it now has a much lower resistance path to follow. This sudden surge in current can cause the wires to overheat, potentially leading to a fire hazard. However, the more immediate and dangerous consequence is the arc flash. An arc flash is a high-intensity electrical discharge that can occur when the current jumps between two points, creating a visible and potentially harmful arc. This arc can cause severe electrical burns and injuries to anyone in close proximity.
The arc flash is a rapid and intense event. It can generate extremely high temperatures, often exceeding 3000°C (5400°F), which is hotter than the surface of the sun. These intense temperatures can melt and vaporize metal, creating a blast of hot gas and shrapnel that can cause severe injuries. The arc flash can also lead to explosions, especially in systems with high-pressure gases or flammable materials.
To prevent arc flash incidents, it is crucial to identify and address potential short circuits. Regular maintenance and inspections of the vehicle's electrical system are essential. This includes checking for damaged insulation, ensuring all connections are secure and free from corrosion, and replacing any faulty components. Additionally, using circuit breakers and fuses can help protect the system by interrupting the circuit when an overcurrent situation occurs, thus preventing the arc flash from taking place.
Understanding the risks associated with short circuits and arc flash is vital for vehicle owners and mechanics. By implementing proper maintenance routines and using appropriate safety measures, the likelihood of such dangerous incidents can be significantly reduced, ensuring the safety of both the vehicle and its occupants.
Electric Vehicles: Cost-Effective Transportation for Businesses?
You may want to see also

Safety Hazards: Short circuits pose risks like fire, shock, and system failure in vehicle electrics
A short circuit in the context of vehicle electrics is a critical issue that can have severe consequences for the safety and functionality of a vehicle. It occurs when there is an unintended electrical connection between two points in a circuit that are not normally in contact, leading to an unexpected flow of current. This phenomenon can arise due to various factors, such as damaged insulation, faulty wiring, or component failures.
One of the primary safety hazards associated with short circuits is the risk of fire. When a short circuit occurs, it can cause an excessive current to flow, generating heat. If the heat becomes intense enough, it can lead to the melting of wires, insulation, or even the combustion of nearby materials. Vehicle fires can be particularly dangerous, as they may start in hard-to-reach areas or while the vehicle is in operation, giving occupants little time to react.
Electric shocks are another significant concern. Short circuits can create a path of low resistance for electricity, allowing it to flow through the body of a person in contact with the electrical system. This can result in severe shocks, potentially causing injury or even death. The risk of electric shock is especially high in vehicles, as they often have complex electrical systems with high-voltage components.
Furthermore, short circuits can lead to complete system failure. When a short occurs, it can overload the electrical system, causing it to shut down or malfunction. This may result in the loss of critical functions such as power steering, braking, or engine control. In extreme cases, a short circuit can even lead to a vehicle fire, as mentioned earlier, exacerbating the potential for catastrophic failure.
To mitigate these risks, regular vehicle maintenance and inspections are essential. Technicians should check for any signs of damage, wear, or faulty connections in the electrical system. Upgrading to modern, high-quality wiring and components can also reduce the likelihood of short circuits. Additionally, drivers should be aware of the importance of proper electrical maintenance and promptly report any unusual behavior or symptoms to qualified professionals.
Powering the Future: Unveiling the Key Components of Battery Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A short circuit occurs when there is an unintended electrical connection between two points in a circuit that are not supposed to be directly connected. In vehicle electrics, this can happen due to damaged insulation, corrosion, or faulty wiring. It results in a low-resistance path for the current to flow, often leading to a sudden increase in amperage and potential damage to the electrical system.
When a short circuit occurs, it can cause several issues. Firstly, it may lead to a sudden surge in power, which can overload the system and potentially trigger a fuse or breaker. This can result in a loss of power to essential components, such as the engine, lights, or safety systems. Secondly, the excessive heat generated by the high current can damage wires, connectors, and even electronic components, leading to costly repairs.
Short circuits can be caused by various factors. One common reason is physical damage to wiring insulation, often due to wear and tear, accidents, or exposure to harsh environmental conditions. Corrosion at electrical connections or terminals can also create a low-resistance path, leading to a short. Additionally, faulty components like switches, relays, or sensors may have internal shorts, especially if they are damaged or nearing the end of their lifespan. Regular maintenance and inspections can help identify and prevent these issues.