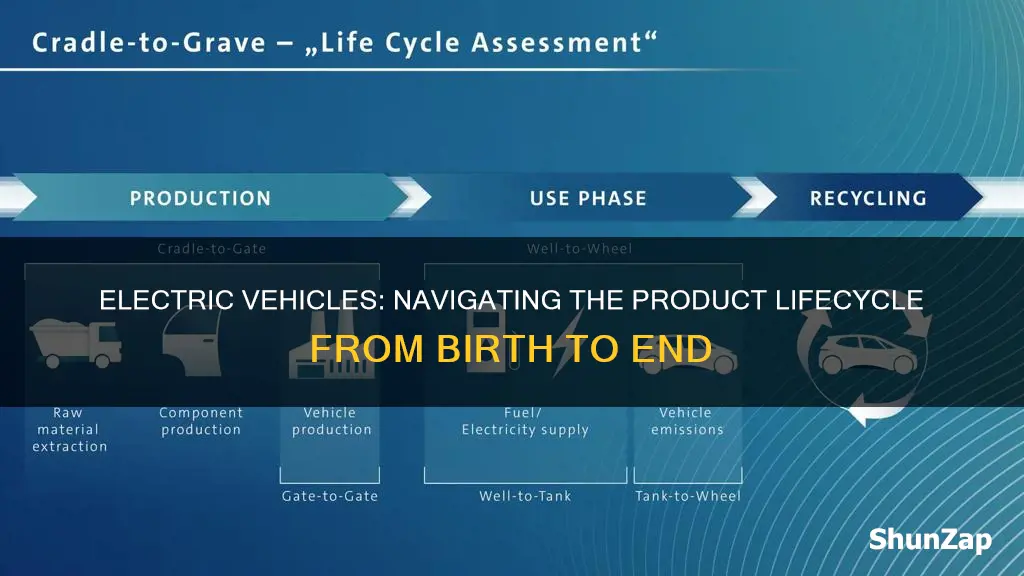
Electric vehicles (EVs) have rapidly evolved since their inception, and their journey through the product lifecycle is an intriguing one. From their early days as experimental prototypes to becoming a mainstream transportation option, EVs have undergone significant transformations. This lifecycle can be divided into several stages: research and development, production, market introduction, growth, and eventual maturity or decline. Understanding the current position of EVs in this lifecycle is crucial as it influences their adoption, performance, and future prospects. The discussion will explore the various factors that have shaped the EV market and its position in the lifecycle, providing insights into the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
What You'll Learn
- Research & Development: Early stages of EV design, focusing on innovation and technology
- Manufacturing & Production: Scaling up production to meet market demand
- Distribution & Sales: Strategies for reaching customers and building a market presence
- Use & Adoption: Consumer behavior, charging infrastructure, and environmental impact
- End-of-Life Management: Recycling, disposal, and second-life applications for retired EVs

Research & Development: Early stages of EV design, focusing on innovation and technology
The early stages of electric vehicle (EV) design are a critical period for innovation and technological advancement, shaping the future of sustainable transportation. This phase involves a deep understanding of the unique challenges and opportunities presented by electric powertrains, aiming to create vehicles that are not only environmentally friendly but also high-performing, efficient, and appealing to consumers.
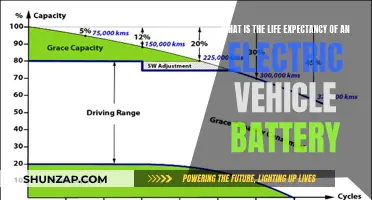
Research and development (R&D) in the initial stages of EV design focus on several key areas. Firstly, battery technology is a central concern. Engineers strive to develop more powerful, energy-dense batteries that can provide longer ranges and faster charging times. This includes exploring advanced materials, such as lithium-ion chemistries with higher energy densities, and solid-state batteries that promise increased safety and efficiency. The goal is to create a battery system that can power the vehicle for extended periods without compromising on performance or safety.
Another critical aspect is the development of efficient and powerful electric motors and power electronics. Engineers aim to optimize motor designs to deliver high torque and power output while minimizing weight and size. This involves advanced cooling systems to manage heat dissipation, ensuring the motor operates efficiently and reliably. Additionally, the integration of power electronics, such as inverters and converters, is crucial for efficiently managing the flow of energy between the battery, motor, and other vehicle systems.
The early design stages also emphasize the importance of lightweight materials and structural design. By utilizing advanced composites, high-strength steels, and aluminum alloys, engineers can reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, improving efficiency and handling. Lightweight materials also contribute to better performance and a more positive environmental impact. Furthermore, the design of the vehicle's structure and chassis is optimized to provide excellent rigidity and safety, ensuring the EV can withstand various driving conditions and potential collisions.
User experience and aesthetics play a significant role in the early R&D phases. Designers and engineers collaborate to create visually appealing and ergonomic interiors and exteriors. This includes the development of intuitive user interfaces, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and connectivity features that enhance the overall driving experience. The goal is to make EVs not just environmentally conscious but also technologically advanced and user-friendly.
In summary, the early stages of EV design are a period of intense innovation and technological advancement. It involves a comprehensive approach to battery technology, motor and power electronics development, lightweight materials, and user experience, all aimed at creating high-performance, efficient, and desirable electric vehicles. This R&D phase is crucial in driving the EV industry forward, ensuring that electric vehicles become a viable and attractive alternative to traditional internal combustion engine cars.
Boosting Electric Vehicle Range: Tips for Longer, Stress-Free Drives
You may want to see also

Manufacturing & Production: Scaling up production to meet market demand
The electric vehicle (EV) market is experiencing rapid growth, and as demand surges, manufacturers face the challenge of scaling up production to meet this increased need. This process involves a series of strategic steps to ensure efficient and sustainable manufacturing. Firstly, companies must conduct a thorough analysis of their current production capabilities and identify areas for improvement. This includes assessing the availability of resources, such as skilled labor, raw materials, and manufacturing facilities, to determine the potential for expansion. By understanding their current limitations, manufacturers can make informed decisions about where to focus their efforts.
One key aspect of scaling up production is investing in advanced manufacturing technologies. Electric vehicle assembly requires precision and efficiency, and manufacturers are turning to automation and robotics to streamline processes. Automated systems can handle repetitive tasks with speed and accuracy, reducing production times and minimizing human error. For instance, robotic arms can be employed for precise component placement, ensuring that every vehicle meets the required quality standards. Additionally, the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and data analytics, enables real-time monitoring and optimization of production lines, allowing for quick adjustments to meet changing market demands.
Another critical factor in scaling production is the development of a robust supply chain. Electric vehicles rely on a complex network of suppliers for components, and ensuring a steady and reliable supply is essential. Manufacturers should focus on building strong relationships with suppliers, implementing just-in-time inventory management, and exploring alternative sourcing options to mitigate risks. By diversifying the supply chain, companies can maintain a consistent flow of raw materials and components, enabling them to meet production targets without disruptions.
Furthermore, as production scales up, manufacturers must prioritize quality control and assurance. With increased output, the risk of defects and inconsistencies rises. Implementing rigorous testing and inspection procedures at various stages of production is crucial. This includes automated quality checks, where sensors and cameras can identify defects, and manual inspections by trained personnel. By catching issues early in the production process, manufacturers can maintain high-quality standards and build a reliable reputation.
Lastly, environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important in the EV market. As the industry expands, manufacturers must adopt sustainable practices to reduce their carbon footprint. This involves optimizing energy usage in production facilities, implementing recycling programs for materials, and exploring renewable energy sources. By integrating eco-friendly practices into their production processes, companies can appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and contribute to a greener future. Scaling up production for electric vehicles requires a comprehensive approach, combining technological advancements, supply chain management, quality control, and sustainability initiatives to meet the growing market demand while maintaining a competitive edge.
Powering the Engine: The Secret to Vehicle Electricity
You may want to see also

Distribution & Sales: Strategies for reaching customers and building a market presence
The electric vehicle (EV) market is experiencing rapid growth and evolution, presenting unique challenges and opportunities for manufacturers and retailers. Understanding the distribution and sales strategies that have proven effective in this emerging industry is crucial for building a strong market presence. Here are some key approaches to consider:
Online Presence and Digital Marketing: With the rise of e-commerce, establishing a robust online presence is essential for EV manufacturers and retailers. This includes creating user-friendly websites that showcase the features and benefits of electric vehicles, as well as utilizing digital marketing techniques such as search engine optimization (SEO) and targeted online advertising. By optimizing their online presence, businesses can reach a wider audience, especially younger consumers who are often early adopters of new technologies. Social media platforms can also be powerful tools to engage with customers, share news and updates, and build a community around the brand.
Specialized Retail Networks: Traditional car dealerships may not be the primary distribution channel for EVs, as this market often caters to a different customer base. Instead, consider partnering with specialized EV retailers, showrooms, or even eco-friendly lifestyle stores. These outlets can provide a unique and appealing shopping experience, allowing customers to interact with the vehicles and learn about their benefits. Additionally, consider pop-up stores or temporary exhibition spaces in urban areas to generate buzz and attract potential buyers.
Subscription and Leasing Models: Offering flexible payment options can be a game-changer for the EV market. Subscription-based services and leasing programs provide customers with the opportunity to try out electric vehicles without a long-term commitment. This strategy is particularly appealing to those who want the latest technology but may be hesitant to invest in a high-value asset. By providing access to a range of EV models, businesses can cater to diverse customer preferences and build a loyal customer base.
Targeted Customer Outreach: Identifying and engaging with potential EV buyers is crucial. This can be achieved through targeted marketing campaigns, such as offering test drives, hosting events, or providing personalized consultations. For instance, reaching out to environmentally conscious consumers or those with a history of interest in sustainable transportation can be effective. Building relationships with these potential customers and providing them with the necessary information and support can significantly impact sales.
After-Sales Support and Community Building: Distribution and sales strategies should also focus on post-purchase customer satisfaction. Providing excellent after-sales support, including maintenance, repair, and customer service, is essential to build trust and loyalty. Additionally, creating an online community for EV owners can foster a sense of belonging and encourage word-of-mouth promotion. This community can share experiences, offer advice, and provide a platform for manufacturers to gather valuable feedback.
In the electric vehicle lifecycle, distribution and sales strategies should be adaptable and innovative. By combining online and offline approaches, businesses can effectively reach and engage their target audience, ultimately driving the adoption of electric vehicles and shaping the future of sustainable transportation.
Electric Fleet Incentives: Unlocking Corporate Tax Benefits for Green Transportation
You may want to see also

Use & Adoption: Consumer behavior, charging infrastructure, and environmental impact
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is an intriguing phase in the product lifecycle, marked by a unique interplay of consumer behavior, the development of charging infrastructure, and the environmental impact of these vehicles. As EVs mature in the market, understanding these aspects is crucial to unlocking their full potential.
Consumer Behavior:
Consumer behavior plays a pivotal role in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Initially, early adopters, often environmentally conscious individuals, were drawn to EVs due to their eco-friendly nature. However, as the market matures, a shift is observed. The primary drivers now include cost savings, technological advancements, and the desire for a more sustainable lifestyle. This change in motivation is significant as it indicates a broader acceptance of EVs beyond the niche market. Consumers are increasingly recognizing the long-term benefits of reduced fuel costs and the positive environmental impact, making EVs a more appealing choice for the average car buyer.
Charging Infrastructure:
The development of a robust charging infrastructure is essential to support the growing number of electric vehicles on the road. The availability of charging stations significantly influences consumer confidence and the overall experience of EV ownership. Governments and private entities are investing in expanding charging networks, ensuring that EV owners have convenient access to charging points. This includes the installation of fast-charging stations along highways and in urban areas, addressing range anxiety—a common concern among potential EV buyers. As the charging infrastructure becomes more comprehensive, it encourages more people to make the switch, knowing they can rely on a reliable charging network.
Environmental Impact:
The environmental impact of electric vehicles is a critical aspect of their lifecycle. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. This environmental benefit is a powerful incentive for governments and organizations to promote EV adoption. As more EVs hit the roads, the collective reduction in carbon emissions becomes substantial. Moreover, the shift towards electric mobility contributes to the broader goal of achieving a sustainable transportation ecosystem. The environmental impact extends beyond the vehicle itself, as the charging process can be powered by renewable energy sources, further enhancing the eco-friendly nature of EVs.
In summary, the use and adoption of electric vehicles are influenced by a combination of consumer preferences, the development of charging infrastructure, and the positive environmental consequences. As the market progresses, these factors will continue to shape the EV lifecycle, driving innovation and encouraging a more sustainable future. Understanding and addressing these aspects are vital for the continued growth and success of the electric vehicle industry.
Unlocking EV Tax Savings: A Guide to Maximizing Your Credit
You may want to see also

End-of-Life Management: Recycling, disposal, and second-life applications for retired EVs
The end-of-life management of electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical aspect of their lifecycle, ensuring that these vehicles are properly recycled, disposed of, or repurposed after their useful life. As the number of EVs on the road continues to grow, so does the importance of implementing sustainable practices to handle their end-of-life stages. This is particularly crucial due to the unique components and materials used in EVs, which differ significantly from traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
Recycling and Disposal:
When an EV reaches the end of its life, the recycling and disposal process begins. This process involves carefully disassembling the vehicle to extract valuable materials and components. The battery, for instance, is a critical component that requires specialized handling. Lead-acid batteries can be recycled, but lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in EVs, need to be managed with care due to their potential environmental and health hazards. Recycling centers use advanced techniques to recover materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can then be reused in new batteries or other products. The disposal of other vehicle parts, such as the electric motor and electronics, should also follow strict guidelines to minimize environmental impact. Proper disposal ensures that hazardous materials are managed safely, preventing soil and water contamination.
Second-Life Applications:
Instead of disposing of retired EVs entirely, there is a growing trend of finding second-life applications for these vehicles. Second-life use refers to repurposing EVs for new functions after their initial operational period. For example, EV batteries can be utilized in energy storage systems for homes or businesses, providing backup power during outages or for off-grid applications. The electric motor and power electronics can be integrated into other machinery or vehicles, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional power sources. Some companies are also exploring the use of retired EVs as mobile charging stations, ensuring a second useful life for the vehicle while supporting the broader EV charging infrastructure.
The end-of-life management of EVs presents both challenges and opportunities. While the recycling and disposal of these vehicles require specialized knowledge and infrastructure, it also opens doors for innovative solutions. Second-life applications demonstrate the potential for extended product lifecycles, reducing waste and promoting sustainability. As the EV market expands, developing comprehensive end-of-life management strategies will be essential to ensure a circular economy for these vehicles, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing resource efficiency. This approach will contribute to a more sustainable future, where retired EVs are given new purposes, reducing the strain on natural resources and promoting a greener transportation ecosystem.
The Future of Driving: Electric Vehicles: A Sustainable Choice?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles are in the growth and maturity stage of their lifecycle. The market for EVs has been rapidly expanding due to increasing environmental concerns, government incentives, and technological advancements. This stage involves a significant increase in sales, infrastructure development, and consumer adoption, leading to a more mature and established market presence.
Several factors contribute to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Firstly, environmental awareness and the desire to reduce carbon emissions are driving forces. Governments and organizations worldwide are offering incentives, subsidies, and tax benefits to encourage EV purchases. Technological improvements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and vehicle performance have also made EVs more appealing to consumers.
Electric vehicles are revolutionizing the automotive industry and shaping its future. The shift towards EVs is leading to a transformation in manufacturing processes, supply chains, and dealership networks. Many traditional automakers are investing heavily in EV technology and infrastructure, while also exploring sustainable practices. This transition is expected to result in a more environmentally friendly industry, with reduced reliance on internal combustion engines and a focus on sustainable transportation solutions.