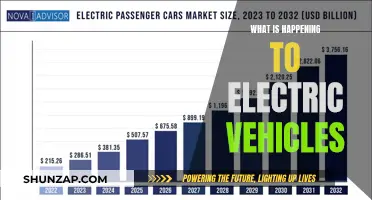
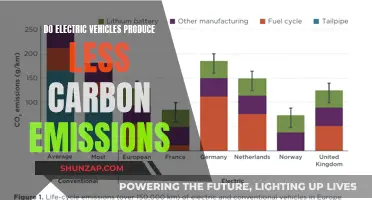
Electric vehicles (EVs) are known for their eco-friendly nature, but you might wonder why they don't come equipped with solar panels. While solar power is a popular and sustainable energy source, EVs have their own unique energy requirements and limitations. The primary reason is that solar panels are typically used to generate electricity for stationary objects or to power homes, not for the dynamic energy needs of vehicles. EVs rely on batteries and charging stations for their power, and integrating solar panels into the vehicle's design would add complexity and potentially reduce efficiency. Additionally, the space and weight constraints of vehicles make it challenging to incorporate large solar panels without compromising performance and aesthetics. This introduction sets the stage for a discussion on the technical and practical considerations behind the absence of solar panels in electric vehicles.
What You'll Learn
- Cost and Efficiency: Solar panels add weight and reduce range, making them less efficient for electric vehicles
- Energy Storage: Limited battery space in EVs hinders the practical use of solar panels for continuous power
- Weather Dependence: Solar efficiency varies with weather, making it unreliable for consistent EV charging
- Space Constraints: EVs have tight space requirements, making it challenging to integrate solar panels without compromising design
- Weight and Aerodynamics: Solar panels add weight, affecting EV performance and range, a critical consideration for manufacturers

Cost and Efficiency: Solar panels add weight and reduce range, making them less efficient for electric vehicles
The integration of solar panels into electric vehicles (EVs) presents a unique set of challenges, primarily centered around cost and efficiency. One of the most significant drawbacks is the additional weight that solar panels introduce to the vehicle's design. Electric cars are already optimized for efficiency, and any extra weight can have a substantial impact on their performance. Solar panels, while generating electricity, contribute to the overall mass of the vehicle, which directly affects its range. The more weight an EV carries, the less efficient its battery usage becomes, leading to a reduced driving range per charge. This is a critical consideration for EV manufacturers and potential buyers, as range anxiety is a common concern in the EV market.
The efficiency of solar panels in generating electricity is another factor to consider. While solar technology has advanced significantly, the conversion efficiency of solar panels is generally lower compared to the efficiency of the batteries used in EVs. This means that the electricity generated by solar panels might not be sufficient to power the vehicle, especially during periods of low sunlight or in regions with less sunny weather. As a result, solar-powered EVs may still rely heavily on their batteries, which could drain faster, impacting the overall efficiency and driving experience.
Furthermore, the cost of implementing solar panels in EVs is a significant barrier. Solar panels, along with the necessary infrastructure and integration into the vehicle's design, add a substantial expense to the manufacturing process. This increased cost is then passed on to consumers, making solar-powered EVs more expensive to purchase. In contrast, the savings on fuel costs over time might not justify the higher upfront investment for many buyers. The economic viability of solar-powered EVs is a complex issue, requiring a careful balance between technological advancements, manufacturing costs, and consumer demand.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development in the field of solar-powered EVs aim to address these concerns. Engineers are exploring innovative ways to minimize the weight of solar panels and maximize their efficiency, ensuring that the technology can be both practical and cost-effective. Additionally, advancements in battery technology are crucial to improving the overall efficiency of EVs, potentially reducing the reliance on solar power for extended driving. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, the idea of solar-powered EVs may become more feasible, offering a sustainable and efficient transportation solution.
Dodge Hornet: Electric Vehicle or Not? Unveiling the Truth
You may want to see also

Energy Storage: Limited battery space in EVs hinders the practical use of solar panels for continuous power
The integration of solar panels on electric vehicles (EVs) is a concept that has been explored, but it faces significant challenges due to the limited energy storage capacity of EV batteries. One of the primary reasons why solar panels are not commonly used on EVs is the space constraint within the vehicle's battery compartment.
Electric vehicles are designed with efficient energy storage systems, and the available space is often dedicated to maximizing battery capacity to ensure sufficient range. The batteries in EVs are typically large and occupy a substantial portion of the vehicle's interior. Adding solar panels to this already crowded space becomes a logistical challenge. Solar panels, while efficient at converting sunlight into electricity, require a significant amount of surface area to generate a meaningful power output. This means that to produce a substantial amount of energy, a large number of solar panels would be needed, which would take up valuable real estate inside the vehicle.
The limited battery space in EVs is a critical factor in hindering the practical use of solar panels. When a vehicle's battery is already at its maximum capacity, accommodating additional panels becomes nearly impossible without compromising the vehicle's structural integrity or passenger/cargo space. This constraint is further exacerbated by the need for efficient energy management systems in EVs, which are designed to optimize power usage and minimize waste.
To address this issue, some innovative solutions have been proposed, such as integrating solar panels into the vehicle's exterior, like the roof or hood. While this approach can provide some additional power, it may not be sufficient for significant energy generation, especially for long-range EVs. Moreover, the efficiency of solar panels can be affected by factors like weather conditions and the angle of sunlight, which further complicates their practical implementation in EVs.
In summary, the limited battery space in electric vehicles is a primary obstacle to the widespread adoption of solar panels for continuous power generation. Overcoming this challenge requires advancements in energy storage technology and innovative design solutions to make solar-powered EVs a more viable and practical option for the future of sustainable transportation.
Unlock EV Tax Savings: A Guide to Qualification
You may want to see also

Weather Dependence: Solar efficiency varies with weather, making it unreliable for consistent EV charging
The integration of solar panels on electric vehicles (EVs) is a concept that has been explored, but it presents several challenges, particularly when considering weather dependence. Solar efficiency is inherently variable and highly dependent on environmental factors, which can significantly impact its reliability for consistent EV charging.
One of the primary issues is the variability of sunlight. Solar panels generate electricity based on the amount of sunlight they receive. However, weather conditions such as cloud cover, rain, snow, and even air pollution can reduce the intensity and duration of sunlight, leading to decreased solar efficiency. In regions with frequent overcast skies or seasonal weather patterns, solar panels may struggle to provide a consistent power source for EVs, especially during extended periods of low sunlight.
Additionally, the angle and orientation of solar panels play a crucial role in their efficiency. Optimal positioning requires precise alignment with the sun's path, which is not always feasible or practical for vehicles in motion. As a result, solar panels on EVs might not capture sunlight at the most efficient angle, further reducing their overall performance. This issue becomes more pronounced when considering the dynamic nature of vehicle movement and the varying positions of the sun throughout the day.
Another factor is the temperature. High temperatures can reduce the efficiency of solar cells, as they tend to lose energy as heat. In regions with extreme heat, the overall efficiency of solar panels may decrease, impacting the charging capabilities of EVs. This temperature-related inefficiency could potentially limit the effectiveness of solar-powered charging, especially in warmer climates.
Furthermore, the storage capacity of batteries in EVs is a critical consideration. Solar panels can store excess energy in batteries, but the limited storage capacity of EV batteries may not be sufficient to accommodate the variable power output from solar panels. This constraint could result in reduced charging rates or the need for additional infrastructure to manage the energy supply.
In summary, while solar panels offer an appealing concept for powering EVs, weather dependence poses significant challenges. The variability of sunlight, temperature effects, and storage limitations all contribute to the unreliability of solar power for consistent EV charging. Overcoming these weather-related hurdles would require advanced technologies and innovative solutions to ensure a stable and efficient power supply for electric vehicles.
Understanding Electric Auxillary Controls: Powering Vehicle Convenience
You may want to see also

Space Constraints: EVs have tight space requirements, making it challenging to integrate solar panels without compromising design
The integration of solar panels into electric vehicles (EVs) is a complex challenge due to the limited space available within the vehicle's design. EVs, by their very nature, are compact and efficient, aiming to maximize passenger and cargo space while minimizing weight and drag. This tight space requirement poses a significant obstacle for the installation of solar panels, which need to be strategically placed to capture sunlight effectively.
One of the primary concerns is the placement of solar panels without compromising the vehicle's aesthetics and functionality. Solar panels, typically made of rigid and relatively heavy materials, cannot be easily integrated into the existing body panels or windows without altering the vehicle's design. The sleek and streamlined look of EVs often relies on a smooth surface, making it difficult to find suitable locations for solar panels that do not interfere with the vehicle's overall appearance.
Furthermore, the limited space inside an EV's cabin and trunk further restricts the potential areas for solar panel installation. The battery pack, for instance, occupies a significant portion of the vehicle's floor space, leaving minimal room for additional components. Attempting to fit solar panels in these confined spaces can lead to design challenges, such as reduced passenger or cargo capacity, compromised comfort, or increased vehicle weight.
To address this issue, engineers and designers are exploring innovative solutions. One approach is to develop flexible or thin-film solar panels that can be more easily integrated into the vehicle's structure. These panels might be incorporated into the windshield, roof, or even the exterior mirrors, allowing for a more seamless blend with the vehicle's design. Additionally, advancements in solar panel efficiency are crucial, enabling the use of smaller panels that can still generate a significant amount of power without taking up excessive space.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of integrating solar panels into EVs are substantial. Solar-powered EVs could reduce the reliance on external power sources, increase the vehicle's range, and provide a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation option. However, achieving this goal requires a careful balance between space optimization, design aesthetics, and the efficient integration of solar technology.
Maximize Your EV Purchase: A Guide to Claiming Tax Credits
You may want to see also

Weight and Aerodynamics: Solar panels add weight, affecting EV performance and range, a critical consideration for manufacturers
The integration of solar panels on electric vehicles (EVs) presents a unique challenge that manufacturers are keenly aware of. One of the primary concerns is the impact of solar panels on the overall weight and aerodynamics of the vehicle. Solar panels, while a sustainable energy source, contribute significantly to the overall mass of the EV. This added weight can have a substantial effect on the vehicle's performance and range, which are critical factors in the competitive automotive market.
The weight of solar panels, especially when integrated into the vehicle's body or roof, can lead to a noticeable increase in the EV's overall mass. This additional weight affects the vehicle's power-to-weight ratio, which is a crucial determinant of its acceleration and top speed. Heavier EVs may experience reduced performance, making them less appealing to consumers who prioritize dynamic driving experiences. Moreover, the extra weight can impact the vehicle's range, as it requires more energy to propel the vehicle, potentially reducing the distance an EV can travel on a single charge.
Aerodynamics is another critical aspect that solar panels can influence. The design and placement of solar panels must consider their effect on the vehicle's airflow. If not properly integrated, solar panels can create drag, increasing the vehicle's frontal area and reducing its aerodynamic efficiency. This can result in higher wind resistance, which in turn affects the EV's energy consumption and overall range. Manufacturers strive to optimize the vehicle's shape and structure to minimize drag, and the addition of solar panels requires careful consideration to maintain or even improve the vehicle's aerodynamic performance.
To address these challenges, automotive engineers are exploring innovative solutions. One approach is to develop lightweight solar panels that reduce the overall weight impact. This involves using advanced materials and designs to minimize the mass of the panels while still generating sufficient power. Additionally, manufacturers are experimenting with various panel placements, such as integrating them into the roof or even the windshield, to optimize both weight distribution and aerodynamics.
In summary, while solar panels offer a sustainable energy solution for EVs, their implementation must carefully consider the vehicle's weight and aerodynamics. Manufacturers are tasked with finding a balance between incorporating solar panels and maintaining the performance and efficiency that consumers expect from electric vehicles. This includes optimizing panel design, placement, and materials to ensure that the benefits of solar power are realized without compromising the overall driving experience.
Unveiling the Origins: Electric Vehicle Battery Material Sources
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
While solar panels can be a great way to generate clean energy, they are not commonly integrated into electric vehicles for several reasons. Firstly, the primary function of EVs is to provide efficient transportation, and adding solar panels would increase the vehicle's weight, complexity, and cost. Secondly, the efficiency of solar panels in converting sunlight into electricity is relatively low, especially when compared to the advanced battery technology used in EVs. The energy generated by solar panels on a vehicle's surface might not be sufficient to power the car, and it could even reduce the overall range.
Yes, there have been some experimental and concept vehicles that incorporate solar panels. For example, the Sunseeker solar car and the Solar Impulse project have demonstrated the potential of solar-powered flight and mobility. However, these are not common in the mainstream EV market. Some companies, like Toyota, have explored solar-powered charging stations for their hybrid vehicles, but dedicated solar-powered EVs are not widely available.
Integrating solar panels into EVs could offer several advantages. It could provide an additional power source, extending the vehicle's range, especially for urban commuters who drive shorter distances. Solar energy is renewable and clean, reducing the carbon footprint of the vehicle. This could be particularly beneficial for delivery vehicles or taxis that operate in sunny regions. However, the practical implementation of this technology is still a challenge due to the space constraints and efficiency considerations mentioned earlier.
The future might see more innovative designs and technologies that combine the two. For instance, solar panels could be integrated into the vehicle's roof or hood, providing a more aesthetic and efficient solution. Advances in solar cell technology could lead to higher efficiency, making solar-powered EVs more viable. Additionally, the development of wireless charging technology might reduce the reliance on solar panels, as EVs could be charged wirelessly from solar-powered stations. This could create a more sustainable and efficient transportation ecosystem.