The rise of low-speed vehicles (LSVs) has sparked debates about their environmental impact and future sustainability. While many LSVs are electric, the question remains: do low-speed vehicles necessarily have to be electric? This paragraph explores the various factors and considerations that determine the necessity of electric power in low-speed vehicles, including their intended use, environmental impact, and technological advancements.
What You'll Learn
- Environmental Impact: Low-speed vehicles emit fewer pollutants when electric, reducing air pollution and carbon footprint
- Energy Efficiency: Electric motors are more efficient at low speeds, conserving energy and extending range
- Noise Reduction: Electric low-speed vehicles operate quietly, improving urban mobility and reducing noise pollution
- Cost Considerations: Initial costs of electric vehicles may be higher, but long-term savings can be significant
- Infrastructure Development: Charging stations for electric low-speed vehicles require investment in infrastructure for widespread adoption

Environmental Impact: Low-speed vehicles emit fewer pollutants when electric, reducing air pollution and carbon footprint
The environmental benefits of low-speed vehicles, particularly when powered by electricity, are significant and often overlooked. These vehicles, designed for urban and residential areas, typically operate at speeds below 25 miles per hour, making them ideal for short-distance travel and last-mile connectivity. When it comes to their environmental impact, the choice of power source plays a crucial role.
Electric low-speed vehicles (LSVs) produce zero tailpipe emissions, which is a substantial advantage over their gasoline or diesel counterparts. Traditional internal combustion engines in LSVs release a range of pollutants, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which contribute to air pollution and have detrimental effects on human health and the environment. In contrast, electric motors in LSVs are clean and efficient, emitting only electricity and water vapor, thus minimizing air pollution and improving air quality in densely populated areas.
The reduction in air pollution is not the only environmental benefit. Electric LSVs also contribute to a lower carbon footprint. The carbon footprint of a vehicle is the total greenhouse gas emissions caused by its production, operation, and end-of-life disposal. Since electric vehicles are powered by electricity, their carbon emissions are directly related to the source of that electricity. When renewable energy sources like solar or wind power are used to generate electricity, the carbon footprint of electric LSVs can be significantly lower compared to conventional vehicles. This is especially true in regions where the electricity grid has a high proportion of renewable energy.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of LSVs extends beyond their operation. The manufacturing and disposal of these vehicles also play a role in their overall sustainability. Electric LSVs often use lightweight materials and have simpler mechanical systems, reducing the energy and resources required for production. Additionally, the end-of-life recycling of electric vehicle batteries can be more efficient, as these batteries can be repurposed for energy storage or other applications, minimizing waste.
In summary, low-speed vehicles, when electric, offer a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional LSVs. Their zero-emission nature, combined with the potential for low carbon emissions from renewable energy sources, contributes to reduced air pollution and a smaller carbon footprint. As cities and urban areas strive for sustainable transportation solutions, the adoption of electric LSVs can play a vital role in achieving cleaner and greener urban environments.
Switzerland's Electric Vehicle Ban: A Misconception Explored
You may want to see also

Energy Efficiency: Electric motors are more efficient at low speeds, conserving energy and extending range
The concept of energy efficiency in low-speed vehicles is a crucial aspect of their design, especially when considering the widespread adoption of electric powertrains. Electric motors, when utilized in these vehicles, offer a significant advantage in terms of efficiency, particularly at low speeds. This is a critical factor for several reasons. Firstly, low-speed driving is a common scenario for many urban and neighborhood vehicles, such as golf carts, delivery vans, and personal mobility devices. During these low-speed maneuvers, the energy requirements are relatively low, and an efficient motor can ensure that the vehicle's range is maximized. This is especially important for electric vehicles (EVs) as range anxiety is a significant concern for potential buyers. By optimizing energy usage at low speeds, EVs can provide a more reliable and stress-free driving experience, encouraging their adoption.
The efficiency of electric motors is inherently higher at low RPM (revolutions per minute) compared to their internal combustion engine (ICE) counterparts. Electric motors can maintain high efficiency across a wide speed range, but they truly excel at low speeds. This is because electric motors provide high torque from a standstill, which is essential for low-speed performance. When an electric vehicle needs to accelerate slowly or maintain a steady speed, the motor's efficiency ensures that energy is not wasted. This is in contrast to ICEs, which often experience reduced efficiency at low speeds due to the need for a high engine speed to maintain power output.
The benefits of this efficiency are twofold. Firstly, it directly contributes to energy conservation. Electric motors can convert a higher percentage of the energy stored in the battery into useful work, reducing the overall energy consumption. This is particularly important for low-speed vehicles, which often have smaller batteries and need to optimize their energy usage. Secondly, the improved efficiency at low speeds can lead to an extended range for these vehicles. With better energy management, EVs can cover more distance on a single charge, making them more practical for daily use.
Furthermore, the efficiency of electric motors at low speeds can also contribute to a quieter and smoother driving experience. Since electric motors produce torque directly, they can provide instant power to the wheels, resulting in a more responsive and linear acceleration. This characteristic is especially beneficial for low-speed maneuvers, where a gentle and controlled acceleration is often desired.
In summary, the energy efficiency of electric motors in low-speed vehicles is a key factor in their overall performance and appeal. It allows for better energy conservation, extended range, and a more enjoyable driving experience. As the automotive industry continues to embrace electrification, optimizing the efficiency of electric powertrains at low speeds will play a pivotal role in making electric vehicles a viable and attractive option for a wide range of applications.
India's Electric Revolution: Are We Ready for the EV Shift?
You may want to see also

Noise Reduction: Electric low-speed vehicles operate quietly, improving urban mobility and reducing noise pollution
The quiet operation of electric low-speed vehicles (LSVs) is a significant advantage that contributes to their growing popularity in urban environments. These vehicles, often designed for short-distance travel within cities, are typically powered by electric motors, which offer a clean and efficient alternative to traditional combustion engines. One of the most notable benefits of this technology is the substantial reduction in noise pollution.
In urban settings, where traffic congestion and noise levels are already high, the quiet nature of electric LSVs can make a significant difference. These vehicles produce minimal noise, especially when compared to the typical sounds of gasoline or diesel engines. This characteristic is particularly important for several reasons. Firstly, it enhances the overall urban experience by reducing the constant, disruptive noise associated with traditional vehicles. This can lead to a more peaceful and pleasant environment for residents and visitors alike.
The noise-reducing benefits of electric LSVs extend beyond just the reduction of sound. Lower noise levels can also improve the safety and comfort of passengers. In crowded urban areas, where pedestrians and other road users are in close proximity, the quiet operation of these vehicles ensures that everyone can hear and be aware of their surroundings. This is especially crucial for the visually impaired or those with hearing impairments, as it allows them to navigate the urban landscape more safely and confidently.
Furthermore, the quiet operation of electric LSVs contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly urban mobility solution. By reducing noise pollution, these vehicles help to create a more harmonious and healthy urban ecosystem. This is particularly important in densely populated areas, where noise-related health issues, such as stress, sleep disturbances, and hearing loss, are more prevalent.
In summary, the quiet operation of electric low-speed vehicles is a key feature that enhances their appeal in urban settings. It not only improves the overall urban experience by reducing noise pollution but also contributes to a safer and more sustainable environment. As cities continue to embrace innovative transportation solutions, the adoption of electric LSVs can play a significant role in creating a more livable and environmentally conscious urban future.
The Birth of Hybrid Electric Vehicles: A Revolutionary Invention
You may want to see also

Cost Considerations: Initial costs of electric vehicles may be higher, but long-term savings can be significant
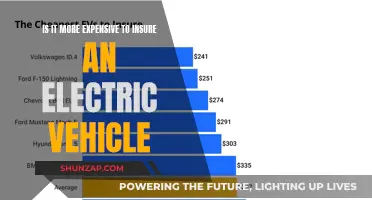
The initial cost of electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant consideration for many consumers, especially when compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars. While the upfront expense can be higher, it's essential to understand the long-term financial benefits that electric vehicles offer. This is particularly relevant for low-speed vehicles, which are often used for short-distance travel and may not require the same level of performance as high-speed cars.
One of the primary cost advantages of electric vehicles is the elimination of fuel expenses. Electric motors are powered by electricity, which is generally much cheaper than gasoline. Over the lifetime of an EV, the savings on fuel can be substantial. For instance, if a low-speed vehicle is driven 15,000 miles annually, the cost of electricity for charging would be significantly lower than the cost of gasoline for a similar distance. This is especially true when considering the current and projected fuel price trends, which often show gasoline prices on an upward trajectory.
In addition to fuel savings, electric vehicles also offer reduced maintenance costs. Internal combustion engines require regular services, oil changes, and part replacements, which can be expensive. In contrast, electric motors have fewer moving parts, resulting in less wear and tear. This simplicity means that electric vehicles often require less frequent maintenance, and when repairs are needed, they tend to be less costly. Over time, these savings can offset the higher initial purchase price.
Furthermore, governments and local authorities worldwide are offering incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, and grants, which directly reduce the purchase price of EVs. For low-speed vehicles, which are often used for urban commuting or recreational purposes, these incentives can make the transition to electric more affordable. Many regions also provide subsidies for charging infrastructure, further reducing the long-term costs of owning an electric vehicle.
While the initial investment in an electric vehicle might seem daunting, it is essential to view it as a long-term investment. The savings on fuel, maintenance, and potential incentives can add up significantly over the vehicle's lifetime. For low-speed vehicles, which are typically used for shorter commutes or recreational activities, the cost-effectiveness of electric powertrains becomes even more apparent. As technology advances and production scales, the prices of electric vehicles are expected to continue decreasing, making them an increasingly attractive and affordable option for consumers.
The Global Electric Vehicle Manufacturing Landscape: A Comprehensive Overview
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Development: Charging stations for electric low-speed vehicles require investment in infrastructure for widespread adoption
The widespread adoption of electric low-speed vehicles (ELSVs) is closely tied to the development of adequate charging infrastructure. These vehicles, often used for short-distance travel in urban areas, have gained popularity due to their environmental benefits and cost-effectiveness. However, their range limitations and the lack of a robust charging network can hinder their market penetration. To address this challenge, significant investment in charging station infrastructure is essential.
Charging stations for ELSVs need to be strategically placed to ensure convenience and accessibility for users. These stations should be located in residential areas, office parks, and commercial districts, allowing for convenient charging during short stops. The placement of these stations should consider the natural flow of traffic and the daily routines of potential users. For instance, in residential neighborhoods, charging stations could be integrated into community centers, public parks, or even residential complexes, ensuring that ELSV owners have easy access to charging facilities.
The investment in charging infrastructure should also focus on technological advancements. Modern charging stations can incorporate smart technologies that optimize charging processes, manage energy distribution, and provide real-time data on vehicle usage and charging status. These smart charging systems can help reduce waiting times, improve energy efficiency, and ensure a seamless user experience. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, can make charging stations more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
Financial incentives and subsidies play a crucial role in encouraging the development of charging infrastructure. Governments and private investors can offer grants, tax benefits, or low-interest loans to businesses and individuals setting up charging stations. These incentives can help offset the initial costs associated with installing and maintaining charging infrastructure, making it more financially viable for investors. Moreover, the creation of partnerships between energy providers, vehicle manufacturers, and charging station operators can further drive the development of a comprehensive charging network.
In summary, the widespread adoption of electric low-speed vehicles relies heavily on the establishment of a robust charging infrastructure. Strategic placement of charging stations, technological advancements, and financial incentives are key components of this development. By investing in these areas, we can create a more sustainable and user-friendly environment for ELSV owners, fostering a greener and more efficient transportation ecosystem. This approach will not only benefit the environment but also contribute to the economic growth of the electric vehicle industry.
Unraveling the Mystery: Hyundai's Electric Vehicle Credit
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, low-speed vehicles are not exclusively electric. While many modern LSVs are electric, there are also gas-powered models available. The choice of power source depends on various factors, including local regulations, environmental considerations, and personal preferences.
Gas-powered LSVs offer several benefits. They provide a longer range compared to electric models, which is advantageous for longer trips or when charging infrastructure is limited. Gas-powered vehicles also tend to have a lower initial cost and can be more readily available in certain regions.
Electric low-speed vehicles have a reduced environmental impact compared to their gas-powered counterparts. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to improved air quality and reduced carbon footprint. Additionally, electric LSVs are often more energy-efficient, leading to lower energy consumption and a smaller environmental impact over their lifetime.