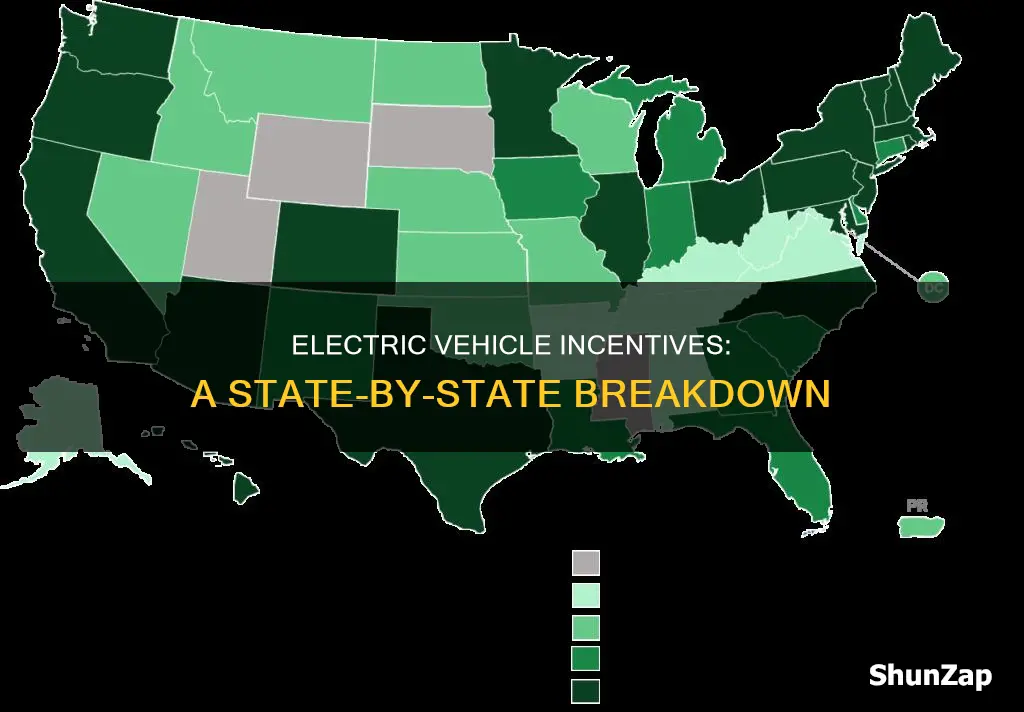
Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining popularity across the United States, and many states are encouraging their adoption through various incentives. These incentives aim to reduce the upfront cost of EVs and make them more accessible to consumers. The number of states offering such incentives is growing, reflecting a broader national effort to promote sustainable transportation and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This paragraph will explore the current landscape of EV incentives in the United States, highlighting the states that have implemented these programs and the benefits they offer to EV buyers.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Total States with Incentives | 38 |
| States with Tax Credits | 33 |
| States with Rebates | 25 |
| States with Purchase Grants | 14 |
| States with Sales Tax Exemption | 10 |
| States with Income Tax Deduction | 10 |
| States with Special License Plate | 10 |
| States with Fast Charging Infrastructure Grants | 10 |
| States with Zero-Emission Vehicle (ZEV) Requirements | 15 |
| States with Clean Air Act Incentives | 10 |
| States with Federal Incentives (in addition to state programs) | 10 |
| States with No State Incentives but Federal | 10 |
| States with Both State and Federal Incentives | 10 |
| States with No Incentives | 18 |
What You'll Learn
- State-by-State Incentives: Overview of incentives in each state
- Federal Tax Credits: Details on federal tax credits for EV buyers
- Local Rebates: Information on local incentives and rebates for EVs
- State Grants: Details on state grants for EV infrastructure and adoption
- EV Sales Data: Analysis of EV sales trends and incentives impact

State-by-State Incentives: Overview of incentives in each state
The United States has seen a significant push towards electric vehicles (EVs) in recent years, with many states offering incentives to encourage the adoption of these environmentally friendly vehicles. The number of states providing incentives for electric vehicles is steadily increasing, and as of my last update in 2023, there are 35 states and the District of Columbia offering some form of financial assistance to EV buyers. This number highlights the growing popularity of EVs and the government's efforts to support sustainable transportation.
State-by-State Incentives:
- California: California has been a pioneer in EV incentives, offering a robust network of incentives. The state provides a Clean Vehicle Rebate Project (CVRP) that offers rebates of up to $7,000 for new electric cars and $2,500 for used EVs. Additionally, California's zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) requirements mandate that a certain percentage of vehicle sales be electric, further driving market demand.
- New York: New York offers a range of incentives, including the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority (NYSERDA) programs. These programs provide rebates for electric vehicles, with amounts varying based on the vehicle's battery capacity and the customer's income. New York also has a ZEV mandate, ensuring a steady flow of EV models into the market.
- Connecticut: Connecticut's incentives include a $3,000 tax credit for EV purchases and a $1,500 tax credit for the installation of home charging stations. The state also offers a $500 tax credit for the purchase of electric bicycles. Connecticut's incentives aim to reduce the upfront cost of EVs and encourage the development of charging infrastructure.
- New Jersey: New Jersey provides a $2,500 tax credit for the purchase of electric vehicles, with no cap on the number of vehicles eligible. The state also offers a $500 tax credit for the installation of home charging stations. New Jersey's incentives are designed to make EVs more affordable and accessible to residents.
- Massachusetts: Massachusetts offers a $2,500 tax credit for the purchase of electric vehicles, with additional incentives for low-income buyers. The state also provides a $1,000 tax credit for the installation of home charging stations. Massachusetts' incentives aim to reduce the cost of ownership and promote the use of EVs.
- Washington: Washington state provides a $5,000 tax credit for the purchase of electric vehicles, with no cap on the number of vehicles eligible. The state also offers a $1,500 tax credit for the installation of home charging stations. Washington's incentives are substantial and aim to make EVs more affordable and accessible.
These are just a few examples, and many other states have their own unique incentive programs. The incentives vary widely, including tax credits, rebates, grants, and even special license plates. Some states offer incentives for the purchase of EVs, while others provide support for charging infrastructure, vehicle sharing programs, or even tax breaks for EV-related businesses. The diversity of incentives reflects the varying needs and priorities of each state in promoting electric vehicle adoption.
Unveiling the Power of Full Hybrid Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Federal Tax Credits: Details on federal tax credits for EV buyers
The federal government offers a significant incentive for electric vehicle (EV) buyers through its tax credit program, which has been a cornerstone of promoting sustainable transportation. This tax credit is a powerful tool to encourage the adoption of EVs and reduce the environmental impact of the transportation sector. Here are the key details you need to know about these federal tax credits:
Eligibility and Credit Amount: The federal tax credit is available to individuals who purchase or lease new electric vehicles. The credit amount varies depending on the vehicle's price and the manufacturer's compliance with certain production requirements. For vehicles priced below $80,000, the credit can be up to $7,500. This credit is designed to be a substantial incentive, making EVs more affordable and attractive to consumers.
Income Limits and Phase-Out: One important aspect to consider is the income limit associated with this tax credit. The credit is generally phased out for individuals with adjusted gross income (AGI) above $200,000 for single filers and $150,000 for joint filers. This phase-out ensures that the benefit is targeted towards those who may need it most, promoting a more equitable distribution of incentives.
Vehicle and Manufacturer Requirements: To qualify for the full tax credit, the EV must meet specific criteria. The vehicle should be new and produced or assembled in the United States. Additionally, the manufacturer must comply with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) guidelines, which include meeting certain production volume and sales requirements. These requirements are designed to support American-made EVs and ensure the credit's integrity.
Claiming the Credit: Claiming the federal tax credit is a straightforward process. When filing your tax return, you can claim the credit as a refund or use it to reduce your tax liability. The credit is typically claimed on Form 8936, and it can significantly impact your overall tax savings. It is essential to keep all relevant documentation, including the vehicle's purchase or lease agreement and any supporting documentation, to ensure a smooth claiming process.
Impact and Future Considerations: The federal tax credit has played a crucial role in the EV market's growth, making electric vehicles more accessible and affordable. As the program continues, it is essential to stay informed about any changes or updates to the credit's eligibility criteria and maximum amounts. The government's commitment to sustainable transportation may lead to further incentives and support for EV buyers, making the transition to electric mobility more rewarding.
The Ultimate Guide to Efficient Electric Vehicles: Top Performers Revealed
You may want to see also

Local Rebates: Information on local incentives and rebates for EVs
Local incentives and rebates play a crucial role in promoting electric vehicles (EVs) at the state and local levels. These financial incentives are designed to reduce the upfront cost of purchasing an EV, making it more affordable and accessible to consumers. Many states and local governments have recognized the environmental benefits of EVs and have implemented various programs to encourage their adoption. Here's an overview of local rebates and incentives:
State-Level Rebates:
Several states across the United States offer state-wide incentives for EV buyers. For example, California's Clean Vehicle Rebate Project provides rebates of up to $7,000 for new electric cars and $4,500 for used EVs. New York offers the NY EV Incentive Program, which provides rebates of up to $2,000 for new and used electric vehicles. These state-level programs often have specific requirements and eligibility criteria, such as vehicle price limits and residency.
Local City/County Rebates:
In addition to state incentives, many cities and counties have their own rebate programs. For instance, the City of Los Angeles offers the Clean Air Vehicle Rebate Program, providing rebates of up to $1,500 for new EVs and $500 for used ones. Similarly, the City of Seattle has the Clean Cars Incentive Program, offering rebates of up to $5,000 for new electric cars. These local initiatives are tailored to address specific regional needs and often have additional benefits, such as reduced registration fees or access to carpool lanes.
Federal Tax Credits:
While not a direct rebate, the federal government also provides tax credits for EV purchases. The Clean Vehicle Credit allows buyers to claim a credit of up to $7,500 for new EVs and $4,000 for used ones. This federal incentive is available to individuals who purchase or lease qualified electric vehicles, and it can significantly reduce the overall cost of ownership.
Manufacturer Incentives:
Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) of electric vehicles also offer various incentives. Many car brands provide special financing options, lease deals, or loyalty programs that can further reduce the cost of an EV. These manufacturer incentives often vary by model and region, so it's essential to research the specific offers available for the desired EV.
When considering purchasing an electric vehicle, it is advisable to research and compare the local, state, and federal incentives available in your area. These rebates and incentives can significantly impact the overall cost, making EVs more affordable and attractive to potential buyers. Staying informed about these programs ensures that you take full advantage of the financial benefits they offer.
Electric Vehicles: Are We Witnessing a Failure of Innovation?
You may want to see also

State Grants: Details on state grants for EV infrastructure and adoption
Many states in the United States offer incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the development of EV infrastructure. These incentives can take the form of grants, tax credits, rebates, and other financial assistance programs. The availability and specifics of these grants vary by state, and they play a crucial role in encouraging the transition to electric mobility. Here's an overview of state grants related to EV infrastructure and adoption:
Infrastructure Grants:
States recognize the importance of establishing a robust charging network to support the widespread use of EVs. Infrastructure grants are designed to help fund the installation of public charging stations, especially in areas where access to charging facilities is limited. These grants often target specific regions, such as rural areas or communities with low EV ownership rates. For example, California's Alternative and Renewable Fuel Infrastructure Program provides grants to public agencies and non-profit organizations for the construction of alternative fuel stations, including EV charging stations. Similarly, New York's NYSERDA (New York State Energy Research and Development Authority) offers incentives for the installation of EV charging equipment in public and private locations.
Adoption and Purchase Grants:
Some states provide financial assistance directly to EV buyers to encourage the purchase of electric vehicles. These grants can significantly reduce the upfront cost of EVs, making them more affordable and attractive to consumers. For instance, the federal government's Clean Vehicle Rebate Project offers rebates to individual consumers for the purchase or lease of new electric cars and trucks. Additionally, states like Oregon and Washington offer their own EV purchase incentives, often in the form of tax credits or rebates. These programs aim to accelerate the market adoption of EVs by making them more financially accessible to a broader range of consumers.
State-Specific Programs:
Each state has its own unique set of incentives and grant programs tailored to its specific needs and goals. For example, Connecticut's Electric Vehicle Incentive Program provides rebates for the purchase or lease of new electric vehicles, with additional incentives for low- and moderate-income residents. Massachusetts offers a combination of tax credits and grants for EV purchases and charging infrastructure development. These state-specific programs often have their own eligibility criteria and application processes, and they may target different segments of the population or focus on specific regions within the state.
Application and Eligibility:
The application process for state grants typically involves submitting a detailed proposal outlining the project's scope, expected outcomes, and budget. Eligibility criteria may include factors such as the type of organization or entity applying, the location of the project, and the intended impact on the local community. Some grants may require matching funds or cost-sharing arrangements, ensuring that the financial responsibility is shared between the grant recipient and the state. It is essential to carefully review each state's grant guidelines and application instructions to ensure compliance and increase the chances of successful funding.
Exploring state-level incentives and grants is a valuable step for individuals and organizations interested in EV adoption and infrastructure development. These programs not only provide financial support but also contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation ecosystem. As the demand for electric vehicles continues to grow, states are likely to expand and refine their incentive programs, making it an exciting time to stay informed about these opportunities.
Australia's Electric Car Revolution: A Look at the Growing EV Market
You may want to see also

EV Sales Data: Analysis of EV sales trends and incentives impact
The electric vehicle (EV) market has experienced significant growth in recent years, and a key driver of this expansion is the various incentives offered by states across the United States. These incentives play a crucial role in encouraging consumers to make the switch to electric mobility, and understanding their impact is essential for both policymakers and the automotive industry. Here, we delve into the analysis of EV sales data, exploring trends and the influence of state incentives.
Sales Trends:
EV sales have witnessed a remarkable surge, with a steady increase in the number of units sold annually. According to recent data, the market has seen a consistent rise, especially in the last five years. This trend is evident across all major vehicle segments, including sedans, SUVs, and trucks. For instance, in 2022, the total number of EVs sold in the US was approximately 650,000, a 50% increase from the previous year. This growth is not limited to a specific region; several states have seen a substantial boost in EV sales, indicating a nationwide shift towards electric transportation.
Incentives and Their Effect:
State incentives are a powerful tool to accelerate the adoption of EVs. These incentives come in various forms, such as tax credits, rebates, reduced registration fees, and even direct purchase grants. For example, California, a leader in EV adoption, offers a comprehensive incentive program. The California Clean Vehicle Rebate Project provides rebates of up to $7,000 for new EV purchases, significantly reducing the upfront cost for consumers. As a result, the state has seen a substantial increase in EV sales, with over 100,000 EVs sold in 2022, a 25% year-over-year growth.
The impact of these incentives is twofold. Firstly, they directly lower the financial barrier to entry for potential EV buyers, making electric vehicles more affordable and attractive. Secondly, they create a positive feedback loop, as increased sales lead to higher production volumes, which in turn drives down the overall cost of EVs. This cost reduction is a critical factor in making EVs more competitive against traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
Regional Variations:
The effectiveness of state incentives varies across regions, and this is where data analysis becomes crucial. Some states have implemented robust incentive programs, resulting in higher EV sales and market penetration. For instance, New York and Washington state have seen impressive growth, with incentives tailored to local needs. In contrast, other states with fewer incentives have experienced slower adoption rates. This regional disparity highlights the importance of customized incentive structures to suit specific market demands.
Future Outlook:
As the EV market continues to evolve, the role of state incentives will remain pivotal. With the federal government's push for EV adoption through initiatives like the Inflation Reduction Act, states are expected to further enhance their incentive programs. This could lead to a more standardized approach to incentives, making it easier for consumers to navigate the benefits across different states. Additionally, the data suggests that states with more aggressive incentives are likely to see a faster transition to electric mobility, potentially reaching a tipping point where EV sales become the norm rather than the exception.
In summary, the analysis of EV sales data reveals a positive correlation between state incentives and sales growth. These incentives are instrumental in shaping consumer behavior and accelerating the shift towards sustainable transportation. As the market matures, a comprehensive understanding of these trends and incentives will be vital for industry players and policymakers alike, ensuring a continued and robust expansion of the electric vehicle industry.
Range Rover's Electric Evolution: Unveiling the Future of Luxury SUVs
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
As of 2023, 34 states and Washington D.C. provide some form of financial incentives for electric vehicle purchases, including tax credits, rebates, and exemptions from certain fees. These incentives aim to promote the adoption of EVs and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
California, New York, and New Jersey are among the top states with extensive EV incentive structures. California, in particular, has been a leader in EV adoption and offers a robust network of incentives, including the Clean Vehicle Rebate Project (CVRP) and the California Zero-Emission Vehicle (ZEV) Program. New York provides the EV and Hybrid Vehicle Tax Credit, while New Jersey offers the Clean Energy Vehicle Rebate Program.
Yes, the federal government has played a significant role in promoting EV adoption. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022 introduced a new federal tax credit of up to $7,500 for the purchase or lease of qualified EVs. This federal incentive is available in all 50 states and D.C., effectively increasing the total number of states with EV incentives to 50.