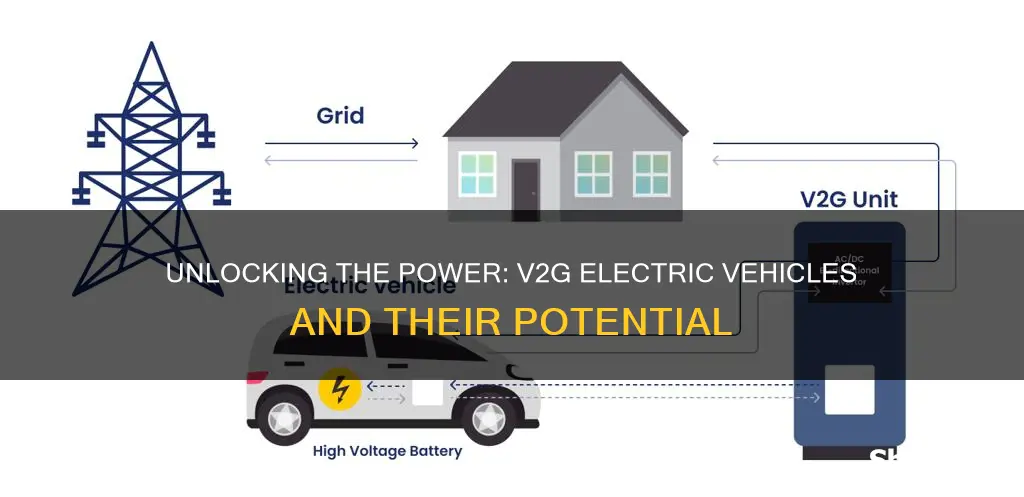
V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) electric vehicles are a revolutionary concept in the automotive and energy sectors. These vehicles are designed to not only draw power from the grid but also to feed electricity back into it, essentially becoming mobile energy storage units. This technology enables vehicles to act as a two-way communication system, allowing for the exchange of power between the vehicle's battery and the electrical grid. V2G vehicles can help balance the grid by providing additional power during peak demand and absorbing excess power when it's available, all while offering vehicle owners potential cost savings and the opportunity to participate in a more sustainable energy ecosystem.
What You'll Learn
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology: Powering the Grid with Electric Vehicles
- Energy Storage: How V2G EVs Act as Mobile Battery Packs
- Smart Charging: Optimizing EV Charging for Grid Stability
- Grid Services: V2G EVs Providing Ancillary Services to Utilities
- Economic Benefits: Cost Savings and Revenue Streams for V2G Owners

Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology: Powering the Grid with Electric Vehicles
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology is an innovative concept that aims to revolutionize the way electric vehicles (EVs) interact with the power grid. It involves a two-way communication and energy exchange system between EVs and the electrical grid infrastructure. V2G technology allows EVs not only to draw power from the grid but also to feed electricity back to the grid when needed, essentially transforming individual vehicles into mobile power sources. This concept is particularly crucial in the context of the growing EV market and the increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions.
The core idea behind V2G is to optimize energy usage and management. During periods of high electricity demand, when the grid is under stress, EVs can be programmed to supply power back to the grid, reducing the strain on the existing infrastructure. This is especially valuable in regions with limited power generation capacity or those facing frequent blackouts. By utilizing the battery storage of EVs, V2G technology can help balance the grid, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply. For instance, electric vehicles can be charged during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower and then discharge power to the grid during peak hours, helping to stabilize energy prices and reduce the need for additional power plants.
Implementing V2G technology offers several benefits. Firstly, it provides EV owners with potential revenue streams. By selling excess energy back to the grid, vehicle owners can monetize their EVs, especially during peak demand periods when electricity prices are higher. This not only encourages the adoption of EVs but also creates a new business model for vehicle owners. Secondly, V2G technology enhances grid resilience and flexibility. It enables the grid to absorb and manage renewable energy sources more effectively, as EVs can store and supply power based on real-time grid needs. This is particularly important as the world shifts towards a more sustainable energy mix, with increased reliance on intermittent renewable sources like wind and solar.
The technical aspects of V2G involve advanced communication and control systems. EVs are equipped with smart chargers and communication modules that allow them to communicate with the grid. These modules can monitor grid conditions, receive commands, and manage the charging and discharging of the vehicle's battery accordingly. The technology ensures that EVs are charged and discharged safely and efficiently, adhering to specific voltage and current limits. Additionally, V2G systems can be integrated with smart home technologies, allowing for further optimization of energy usage and cost savings for consumers.
In summary, Vehicle-to-Grid technology presents a promising solution to the challenges of managing a growing EV fleet and an evolving power grid. It offers a sustainable and efficient approach to energy management, providing benefits for both vehicle owners and the grid operators. As the world embraces the transition to electric mobility, V2G technology is set to play a pivotal role in shaping a more resilient and environmentally friendly energy infrastructure. This technology's potential to create a more flexible and responsive grid is a significant step towards a greener and more sustainable future.
Chevy Spark: Electric Vehicle or Gas-Powered Mystery?
You may want to see also

Energy Storage: How V2G EVs Act as Mobile Battery Packs
V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) electric vehicles are an innovative concept that revolutionizes the way we think about energy storage and distribution. These vehicles are designed to not only consume electricity from the grid but also to feed power back to it, essentially acting as mobile battery packs. This two-way energy exchange has significant implications for both the vehicle owner and the power grid as a whole.
The core idea behind V2G EVs is to utilize the large batteries already present in electric vehicles (EVs) to store excess energy during periods of low demand and then discharge this energy back to the grid when needed. This process is facilitated by specialized charging infrastructure and software that manages the energy flow. When the grid experiences a surge in power demand, V2G EVs can release stored energy, helping to stabilize the grid and reduce the reliance on additional power plants. This dynamic energy storage system offers a flexible and efficient way to manage electricity supply and demand.
During periods of low electricity prices or when the grid has surplus power, V2G EVs can charge their batteries, storing energy in a cost-effective manner. This stored energy can then be utilized during peak hours when electricity prices are typically higher, allowing vehicle owners to take advantage of cheaper rates and potentially save on energy costs. By participating in this energy exchange, V2G EVs contribute to a more balanced and efficient power grid while also providing economic benefits to their owners.
The technology behind V2G EVs involves advanced battery management systems and communication protocols. These systems ensure that the vehicle's battery is charged and discharged safely and efficiently. When connected to the grid, the vehicle's battery management system communicates with the grid infrastructure, allowing for precise control of energy flow. This enables the vehicle to become an active participant in the power market, providing services such as load balancing and peak shaving.
In summary, V2G electric vehicles represent a significant advancement in energy storage and management. By acting as mobile battery packs, these vehicles can help stabilize the power grid, reduce energy costs for owners, and contribute to a more sustainable and efficient energy system. As the technology continues to evolve, V2G EVs have the potential to play a crucial role in the transition to a cleaner and more resilient energy infrastructure.
Unveiling the Secrets: Electric Vehicle Battery Materials
You may want to see also

Smart Charging: Optimizing EV Charging for Grid Stability
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) has brought about a significant shift in energy consumption patterns, with the potential to impact grid stability. Smart charging is an innovative approach to optimizing EV charging processes, ensuring a harmonious relationship between the increasing number of EVs and the electrical grid. This technology-driven strategy involves the use of advanced algorithms and communication systems to manage the charging of EVs in a way that supports grid stability and efficiency.
At its core, smart charging aims to balance the demand for electricity from EVs with the available supply, especially during peak hours when the grid might be under strain. By implementing intelligent charging protocols, EVs can be programmed to charge at specific times, often when electricity rates are lower or when the grid has surplus capacity. This dynamic approach ensures that charging sessions are scheduled efficiently, reducing the risk of overloading the grid and preventing potential blackouts or voltage fluctuations.
The key to smart charging lies in its ability to communicate and interact with the grid. EVs equipped with smart charging capabilities can receive signals from the grid, indicating the optimal time and conditions for charging. These signals might include real-time electricity prices, grid capacity, and even weather forecasts, which can influence energy demand. For instance, during a heatwave, EVs could be instructed to charge at night when electricity demand is typically lower, helping to stabilize the grid.
Furthermore, smart charging systems can employ predictive analytics to anticipate future energy needs and adjust charging rates accordingly. This proactive approach ensures that EVs are charged to their desired levels without compromising the grid's stability. It also encourages users to adopt flexible charging habits, promoting a more responsive and efficient energy management system.
In summary, smart charging is a crucial aspect of managing the growing EV market and its impact on the grid. By optimizing charging processes, we can ensure that the increasing number of EVs contributes to a stable and reliable energy infrastructure. This technology enables a more sustainable and efficient future, where EVs and the grid coexist harmoniously, meeting the energy demands of a modern society.
Unraveling the Challenges: Electric Vehicles' Hidden Hurdles
You may want to see also

Grid Services: V2G EVs Providing Ancillary Services to Utilities
The concept of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology is an innovative approach to utilizing electric vehicles (EVs) as a flexible resource for the power grid. V2G EVs can provide a range of grid services, acting as a mobile energy storage system and enabling two-way power flow between the vehicle and the electrical grid. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we manage and optimize energy distribution, especially with the increasing adoption of EVs.
One of the key grid services that V2G EVs can offer is load balancing. As more EVs come online, they can be programmed to charge during periods of low grid demand and discharge when the grid needs additional power. This load-shifting capability helps to prevent overloading the grid infrastructure and ensures a more stable and efficient power supply. During peak hours, when the grid is under stress, V2G EVs can release stored energy, reducing the strain on the central power generation systems.
V2G technology also enables the provision of ancillary services, which are essential for maintaining grid stability. These services include voltage regulation, where EVs can adjust their charging or discharging rates to maintain optimal voltage levels on the grid. Frequency regulation is another critical function, as V2G EVs can respond rapidly to changes in grid frequency, ensuring a consistent power supply. By providing these ancillary services, V2G EVs become an integral part of the grid's management system, enhancing its reliability and resilience.
The benefits of V2G EVs in grid services are twofold. Firstly, it allows utilities to better manage the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources. By storing excess energy from solar or wind power during periods of high generation, V2G EVs can release this energy back to the grid when needed, ensuring a more consistent power supply. Secondly, V2G technology provides an opportunity to reduce the overall cost of energy management. Utilities can offer incentives to EV owners to participate in grid services, potentially lowering electricity rates for consumers during peak demand periods.
Implementing V2G technology requires a coordinated effort between vehicle manufacturers, energy companies, and grid operators. Standardization of communication protocols and infrastructure development are essential to ensure seamless integration. As the technology advances, V2G EVs have the potential to become a significant asset for utilities, helping to manage the growing complexity of modern power grids and contributing to a more sustainable and efficient energy future. This innovative approach to grid management highlights the evolving relationship between transportation and energy systems.
Unveiling the Risks: Navigating Challenges in Electric Vehicle Ownership
You may want to see also

Economic Benefits: Cost Savings and Revenue Streams for V2G Owners
The concept of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology offers a range of economic advantages for electric vehicle (EV) owners, transforming their vehicles into active participants in the energy market. V2G-enabled EVs can not only draw power from the grid but also feed electricity back to it, creating a two-way energy exchange. This capability opens up numerous opportunities for cost savings and revenue generation.
One of the primary economic benefits is the potential for significant cost savings. V2G owners can optimize their energy usage by charging their vehicles during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower. By storing excess energy in their batteries, they can then discharge this energy back to the grid during peak demand periods, often when electricity prices are higher. This strategic approach allows V2G owners to take advantage of lower rates and potentially sell excess energy at a profit, thus reducing their overall energy costs.
The revenue streams for V2G owners are diverse. Firstly, they can participate in demand response programs, where they are compensated for reducing their electricity usage or supplying power during peak times. This not only provides a stable income but also contributes to grid stability and reliability. Secondly, V2G owners can engage in energy trading platforms, buying and selling electricity based on market prices. With the ability to forecast energy demand and supply, they can make informed decisions to maximize their revenue. Additionally, some utility companies offer incentives and rebates for V2G-equipped vehicles, further enhancing the financial benefits for owners.
The economic model of V2G technology is particularly attractive to EV owners who want to maximize the efficiency of their vehicles. By actively managing their energy usage and contributing to the grid, they can reduce their reliance on traditional energy sources and lower their carbon footprint. This not only benefits the environment but also provides a sense of financial security and control over energy expenses.
In summary, V2G electric vehicles offer a compelling economic proposition for owners. Through strategic energy management and participation in the energy market, they can achieve cost savings, generate revenue, and contribute to a more sustainable energy future. As V2G technology continues to evolve, it is likely to play a significant role in shaping the economic landscape of the EV industry.
Rivian's Electric Revolution: Unlocking the Future of Sustainable Driving
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) is a technology that enables electric vehicles (EVs) to not only draw power from the grid but also feed electricity back to it. This two-way communication between the vehicle and the grid allows for a more efficient and flexible energy management system.
V2G technology utilizes the bidirectional charging system, where EVs can charge from the grid during periods of low demand and low cost, and then discharge electricity back to the grid when needed. This process is controlled and optimized to ensure a stable power supply and potentially reduce energy costs for vehicle owners.
V2G EVs offer several advantages. Firstly, they can provide backup power during outages, ensuring that essential electricity needs are met. Secondly, vehicle owners can earn revenue by selling excess energy back to the grid. Additionally, V2G technology supports a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure.
Yes, V2G has the potential to reduce environmental impacts. By utilizing renewable energy sources for charging and discharging, V2G EVs can contribute to lower carbon emissions. This technology also supports the integration of more sustainable energy practices into the transportation sector.
V2G technology is compatible with most electric vehicles, including passenger cars, buses, and commercial fleets. However, the specific implementation and infrastructure requirements may vary depending on the vehicle model and the local power grid capabilities.