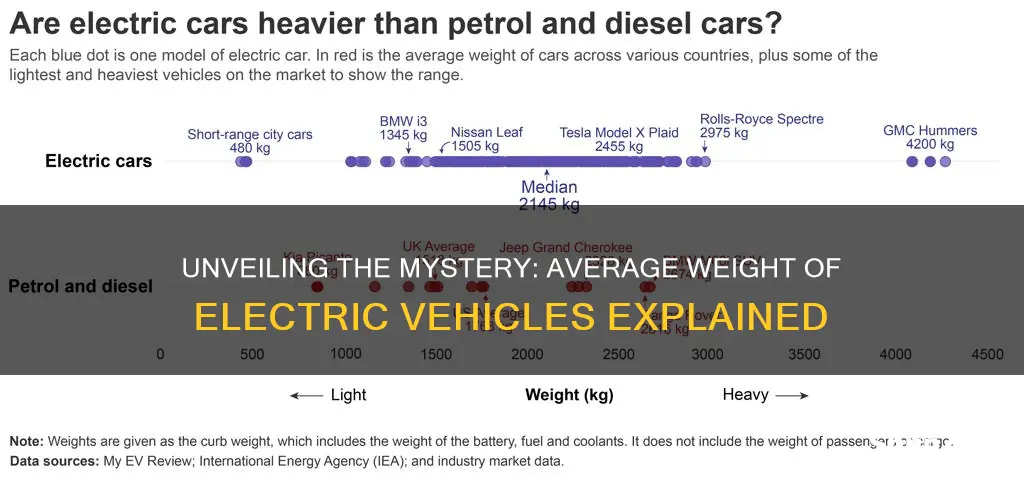
The average weight of an electric vehicle (EV) is a crucial factor to consider when evaluating their performance and efficiency. While the weight of EVs can vary significantly depending on the model, size, and battery capacity, it is generally lower than that of traditional gasoline-powered cars. On average, electric vehicles weigh between 3,000 and 5,000 pounds (1,360 to 2,270 kilograms), with some compact models tipping the scales at around 2,500 pounds (1,134 kilograms) and larger SUVs reaching upwards of 5,500 pounds (2,500 kilograms). This reduced weight is often attributed to the absence of heavy internal combustion engines and the use of lightweight materials in their construction. Understanding the average weight of EVs provides valuable insights into their handling, acceleration, and overall driving experience, making it an essential aspect for consumers and manufacturers alike.
What You'll Learn

Battery Size and Weight Impact
The average weight of an electric vehicle (EV) is a crucial factor to consider when evaluating its performance and efficiency. While the weight of an EV can vary depending on the model and its specifications, it is generally lighter than traditional gasoline-powered cars due to the absence of heavy internal combustion engines. On average, electric cars weigh between 3,000 and 4,000 pounds (1,360 to 1,814 kilograms), with some models even lighter. This reduced weight is primarily attributed to the placement of the battery pack, which is often positioned low in the vehicle, contributing to a lower center of gravity and improved handling.
Battery size and weight play a significant role in the overall weight of an electric vehicle. The battery pack is one of the heaviest components in an EV, and its size and capacity directly impact the vehicle's weight. Larger batteries with higher energy storage capabilities tend to be heavier, which can affect the overall weight distribution and handling characteristics. For instance, a compact EV with a smaller battery pack might weigh less, offering a more agile driving experience, while a larger, more powerful EV with an extended-range battery may have a higher weight, potentially impacting acceleration and overall performance.
The impact of battery size on weight is particularly important for EV manufacturers. As battery technology advances, the trend is towards larger, more powerful batteries to increase driving range. However, this increase in battery size directly translates to more weight, which can affect the vehicle's performance and efficiency. Engineers and designers must carefully consider the placement and design of the battery pack to ensure optimal weight distribution and maintain the desired handling characteristics.
In addition to weight, battery size also influences the range and charging capabilities of an electric vehicle. Larger batteries can store more energy, resulting in extended driving ranges, which is a significant advantage for EV owners. However, the increased weight may also impact the vehicle's efficiency, especially during acceleration and uphill climbs. Therefore, finding the right balance between battery size and weight is essential for manufacturers to create efficient and high-performing electric vehicles.
Understanding the relationship between battery size and weight is crucial for consumers when choosing an electric vehicle. While larger batteries offer extended range, the additional weight might be a consideration for those seeking a more agile and responsive driving experience. On the other hand, buyers prioritizing range and long-distance travel may opt for larger batteries, accepting the trade-off of increased weight. This knowledge empowers consumers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and preferences.
Powering Up: Understanding the Safety of Plugging In Your EV
You may want to see also

Vehicle Type and Average Weight
The average weight of an electric vehicle (EV) is a crucial factor to consider when evaluating their performance, efficiency, and environmental impact. While the weight of an EV can vary significantly depending on the make, model, and specific configuration, understanding the average weight provides valuable insights into the vehicle's characteristics.
On average, electric cars tend to weigh less compared to their conventional gasoline counterparts. This is primarily due to the absence of a heavy internal combustion engine and associated components. Electric powertrains are generally simpler and more compact, often consisting of an electric motor, battery pack, and associated electronics. As a result, the overall weight of an EV is reduced, contributing to improved handling, acceleration, and energy efficiency.
The weight distribution in electric vehicles is also an essential aspect to consider. Typically, the battery pack, which is a significant component of an EV's weight, is positioned low in the vehicle. This design choice helps to lower the center of gravity, enhancing stability and cornering capabilities. Additionally, the placement of the battery pack near the floor contributes to a lower overall vehicle height, which can improve aerodynamics and reduce drag.
It's worth noting that the average weight of an electric vehicle can vary widely based on several factors. For instance, compact city cars designed for urban environments often have lighter weights, typically ranging from 1,500 to 2,000 pounds (680 to 907 kg). In contrast, larger SUVs or crossovers, which offer more interior space and off-road capabilities, tend to weigh more, often exceeding 4,000 pounds (1,814 kg). The use of lightweight materials, such as aluminum or carbon fiber, in EV construction can further reduce weight, making these vehicles even more efficient and responsive.
Understanding the average weight of electric vehicles is essential for various reasons. Firstly, it influences the vehicle's performance, with lighter EVs often delivering quicker acceleration and better handling. Secondly, weight plays a role in energy consumption, as lighter vehicles require less energy to move, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced environmental impact. Lastly, the weight distribution and overall design of an EV contribute to its safety and stability, especially during high-speed maneuvers or in challenging road conditions.
The Future of Driving: Embracing All-Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Efficiency and Weight Relationship
The relationship between efficiency and weight is a critical aspect of electric vehicles (EVs) and their performance. The average weight of an electric vehicle is a crucial factor that influences its overall efficiency and performance. Generally, EVs tend to be lighter than their conventional counterparts, and this lighter weight is a significant advantage in terms of efficiency.
Lighter vehicles have a lower power-to-weight ratio, which means they can accelerate more quickly and efficiently. This is because less weight needs to be accelerated, resulting in improved energy efficiency. For every pound or kilogram of weight, the vehicle must exert more force to move forward, and this additional force requires more energy. Therefore, reducing the weight of an EV directly contributes to its ability to travel farther on a single charge.
The design and materials used in the construction of an EV play a vital role in achieving this lightweight efficiency. Modern EVs often utilize lightweight materials such as aluminum, carbon fiber composites, and advanced alloys. These materials offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios, allowing engineers to create sturdy yet lightweight structures. By employing these innovative materials, manufacturers can reduce the overall weight of the vehicle without compromising its structural integrity.
Furthermore, the efficiency of an EV is also influenced by its battery weight. Batteries are heavy components, and their weight can significantly impact the overall efficiency of the vehicle. However, advancements in battery technology have led to the development of more lightweight and energy-dense batteries. These batteries provide the necessary power while keeping the overall weight of the EV competitive.
In summary, the average weight of an electric vehicle is a key consideration for efficiency. Lighter EVs offer improved acceleration, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced range. The use of advanced materials and lightweight battery designs further contributes to this efficiency-weight relationship, making electric vehicles a more sustainable and appealing choice for environmentally conscious consumers. Understanding this relationship is essential for both manufacturers and consumers to fully appreciate the benefits of electric mobility.
Tech Giants: The Company Powering EVs and Phones
You may want to see also

Design Choices and EV Weight
The weight of an electric vehicle (EV) is a critical factor in its design and performance, impacting everything from handling and efficiency to range and overall driving experience. The average weight of an EV can vary significantly depending on the type, size, and intended use of the vehicle. For instance, compact city cars like the Mini Cooper SE or the Smart Fortwo Electric Drive typically weigh around 1,500 to 1,800 kg (3,300 to 4,000 lbs), while larger SUVs like the Tesla Model X or the Jaguar I-Pace can weigh upwards of 2,000 kg (4,400 lbs) or more. This significant difference in weight is primarily due to the materials used in construction and the placement of heavy components, such as batteries and electric motors.
Design choices play a pivotal role in determining the weight of an EV. One of the most significant design considerations is the choice of materials. Modern EVs often utilize lightweight materials such as aluminum, high-strength steel, and carbon fiber composites to reduce weight without compromising structural integrity. For example, the Tesla Model 3, a popular mid-size sedan, employs a combination of aluminum and steel in its body and chassis, contributing to its lightweight yet robust design. The use of lightweight materials not only reduces the vehicle's overall weight but also helps in managing the distribution of mass, which is crucial for handling and stability.
Battery placement is another critical design aspect that influences EV weight. The batteries in EVs are typically large and heavy, and their placement can significantly affect the vehicle's center of gravity. To optimize weight distribution, engineers often position the batteries low in the vehicle, close to the wheels. This design choice not only helps in achieving a lower center of gravity, enhancing stability, but also allows for a lower ride height, which can improve aerodynamics and overall efficiency. For instance, the Porsche Taycan, an all-electric sports car, places its battery pack low and central, contributing to its impressive handling and performance.
The design of the underbody and the use of underbody shielding also contribute to the overall weight of an EV. Underbody shielding is essential for protecting the vehicle's electrical components from road debris and potential damage. However, the materials used for shielding can vary, with some manufacturers opting for lightweight options to minimize added weight. Additionally, the design of the underbody can influence the vehicle's aerodynamic efficiency, which in turn affects its weight by reducing drag and improving overall performance.
In summary, the average weight of an electric vehicle is a result of careful design choices that balance performance, efficiency, and safety. Engineers must consider the placement of heavy components, the use of lightweight materials, and the overall design of the vehicle to achieve the desired weight. By optimizing these design elements, manufacturers can create EVs that offer a perfect blend of power, range, and driving experience while adhering to the ever-evolving standards of the automotive industry.
Unveiling the Surprising Environmental Impact of Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Manufacturing Processes and Average EV Weight
The average weight of an electric vehicle (EV) is a crucial factor in its performance, efficiency, and overall design. While the exact weight can vary depending on the make, model, and specific features, understanding the manufacturing processes behind EVs can provide insight into this average.
EVs, compared to their internal combustion engine (ICE) counterparts, often utilize lightweight materials to achieve better performance and efficiency. This is primarily due to the reduced weight of the battery pack, which is a significant component of an EV's overall weight. The manufacturing process of these vehicles involves several key steps. Firstly, the design phase is critical, where engineers and designers work to optimize the vehicle's structure while ensuring it meets safety and performance standards. This often involves using advanced computer-aided design (CAD) software to create detailed models and simulations.
The manufacturing process typically begins with the production of the battery pack. Lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in EVs, are composed of multiple cells arranged in modules. These cells are carefully assembled, often in a process called "cell stacking," where individual cells are stacked and connected to form a compact, high-capacity battery pack. The weight of this pack is a significant contributor to the overall vehicle weight. After the battery pack is manufactured, it is integrated into the vehicle's chassis, where it is securely mounted to distribute the weight evenly.
The chassis itself is a critical component, as it provides structural integrity and supports the vehicle's electrical and mechanical systems. Modern EVs often employ lightweight materials such as aluminum or advanced high-strength steel to reduce weight while maintaining rigidity. The manufacturing process involves precision welding and assembly techniques to ensure the chassis is robust and lightweight.
In addition to the battery pack and chassis, other components like the electric motor, inverter, and power electronics also contribute to the overall weight. These components are carefully selected and designed to be as lightweight and efficient as possible. The manufacturing process involves advanced machining, casting, and assembly techniques to minimize weight without compromising performance.
The average weight of an EV can vary widely, typically ranging from around 1,500 to 4,000 pounds (680 to 1,814 kilograms) for compact and mid-size models, and even heavier for larger SUVs and luxury vehicles. This wide range is due to the various factors mentioned above and the diverse range of EV models available in the market. Understanding the manufacturing processes and the careful selection of materials can help explain this variation in average weight.
Apple's Electric Vehicle: Rumors, Speculations, and the Future of Apple Cars
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The average weight of an electric vehicle (EV) can vary significantly depending on the type and size of the car. Generally, electric cars tend to be lighter than their gasoline counterparts due to the use of lightweight materials like aluminum and carbon fiber for the battery pack and body structure. On average, a compact electric car might weigh around 3,000 to 4,000 pounds (1,361 to 1,814 kilograms), while a larger sedan or SUV could weigh between 4,000 to 5,000 pounds (1,814 to 2,268 kilograms) or more.
Electric vehicles are often lighter because they don't require a heavy internal combustion engine and associated components like a transmission and exhaust system. The battery pack, while heavy, is usually more compact and lightweight compared to the fuel tank and associated plumbing in traditional cars. This reduction in weight can improve handling, acceleration, and overall efficiency.
No, the weight of electric vehicles can vary widely. Factors such as battery capacity, vehicle size, design choices, and intended use all play a role. For example, a high-performance electric sports car might prioritize lightweight materials and design to enhance performance, resulting in a lower weight. Conversely, some electric vehicles are designed for long-range and passenger comfort, which may lead to a heavier build.
The weight of an EV can influence its performance characteristics. Lighter vehicles often offer better acceleration and handling due to reduced rotational inertia. They can also improve energy efficiency, as less power is required to move the car. However, very lightweight EVs might sacrifice some structural rigidity and passenger comfort. Finding the right balance between weight and other factors is a key consideration in EV design.







