The production of electric vehicle (EV) batteries involves a complex process that begins with the extraction of raw materials. These batteries are a crucial component of the EV industry, powering vehicles and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. The journey starts with the mining of essential minerals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are then refined and processed to create the battery cells. This process is a significant aspect of the EV ecosystem, as it highlights the environmental and ethical considerations surrounding the sourcing of these materials, especially in the context of sustainable practices and the global supply chain.
What You'll Learn
- Mineral Extraction: Mining lithium, cobalt, and nickel from the earth for battery materials
- Recycling Processes: Recovery of materials from used batteries to reduce environmental impact
- Sustainable Sourcing: Focus on eco-friendly mining practices and responsible supply chains
- Global Trade: International trade in raw materials and battery components
- Innovation in Materials: Research and development of new, more efficient battery materials

Mineral Extraction: Mining lithium, cobalt, and nickel from the earth for battery materials
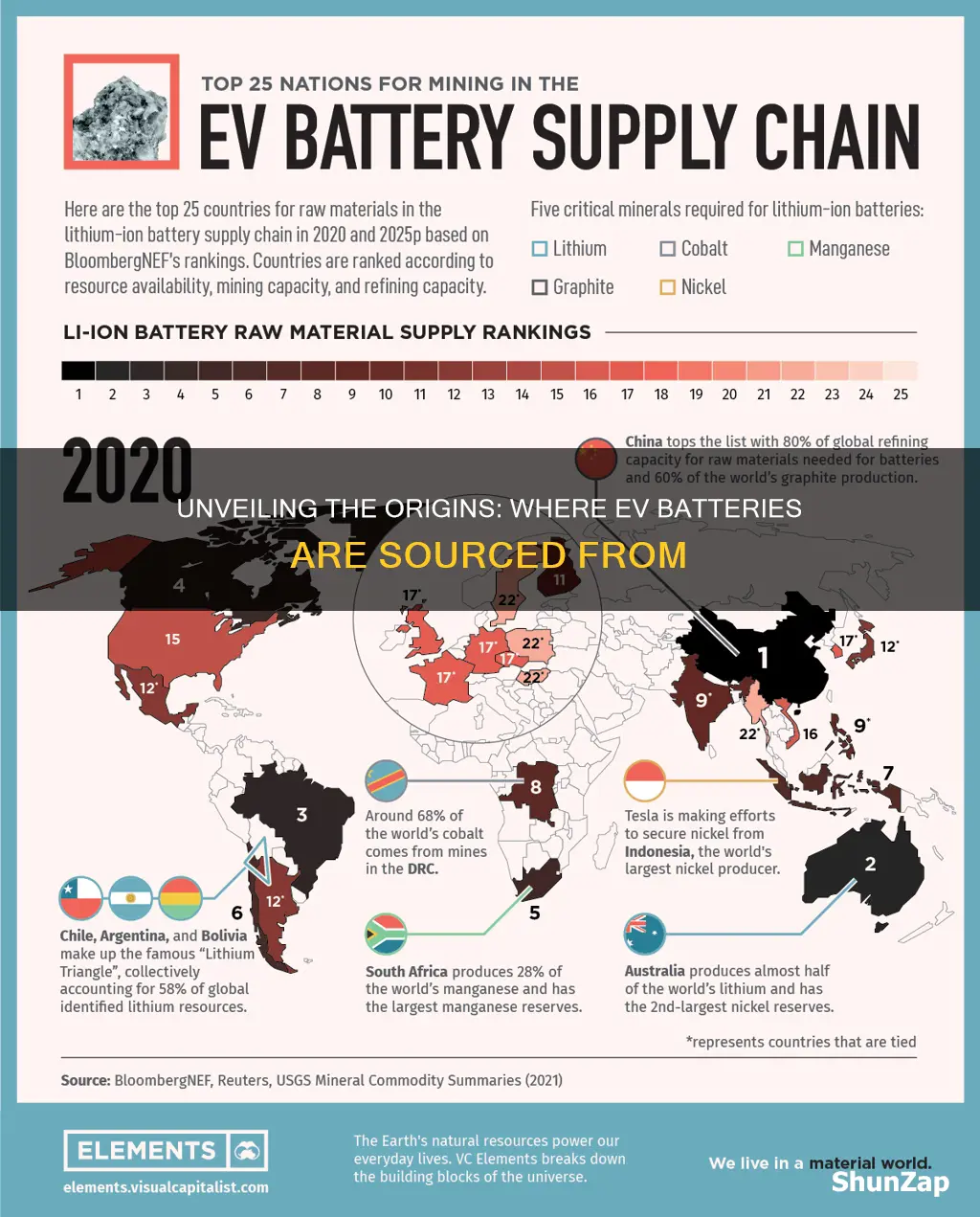
The process of creating electric vehicle (EV) batteries begins with the extraction of essential minerals from the Earth, primarily lithium, cobalt, and nickel. These elements are crucial components in the production of lithium-ion batteries, which power most EVs. The mining of these materials is a complex and resource-intensive process, often involving various techniques to extract the desired minerals from the ground.
Lithium, for instance, is primarily obtained through the extraction of lithium-rich brine from underground salt flats or hard-rock mining. In the brine method, large-scale evaporation of water from salt flat pans is used to concentrate the lithium. This process can take several months to a year, and the resulting lithium carbonate is then processed further to create battery-grade lithium. Hard-rock mining, on the other hand, involves extracting lithium from mineral-rich rocks, often through open-pit or underground mining techniques. Both methods require significant water usage and can have environmental impacts, including potential water pollution and habitat disruption.
Cobalt, another critical mineral, is predominantly sourced through mining in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), where it is often associated with conflict minerals. The mining process involves extracting cobalt-rich ore from the ground, which is then processed to separate the cobalt from other minerals. This extraction can be environmentally damaging, and the labor conditions in some mining regions have raised ethical concerns. Despite these challenges, cobalt remains a vital component in the production of high-performance batteries due to its ability to enhance battery capacity and stability.
Nickel, an essential element in the cathode of lithium-ion batteries, is primarily obtained through the mining of nickel-rich ore bodies. This process often involves open-pit mining, where large quantities of ore are extracted from the ground. The ore is then processed to extract the nickel, which is further refined to create battery-grade nickel. Nickel mining can have significant environmental impacts, including soil erosion and water pollution, especially if proper waste management practices are not followed.
The extraction and processing of these minerals are crucial steps in the supply chain of EV batteries. However, the environmental and social implications of mining these materials cannot be overlooked. As the demand for EVs and their batteries increases, sustainable and responsible mining practices become even more critical to ensure a continuous supply of these essential minerals while minimizing the ecological footprint of the industry.
India's Electric Revolution: Unlocking the EV Percentage Mystery
You may want to see also

Recycling Processes: Recovery of materials from used batteries to reduce environmental impact
The recycling of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a crucial process to ensure a sustainable future for the automotive industry and to minimize the environmental impact of these powerful energy storage systems. When EV batteries reach the end of their useful life, they can be recycled to recover valuable materials and reduce the demand for raw resources. The recycling process involves several stages, each designed to extract and reuse materials efficiently.
One common method is called 'hydrometallurgical processing,' which utilizes chemical processes to dissolve and separate battery components. This technique is particularly effective for lithium-ion batteries, which are prevalent in EVs. The process begins by dismantling the battery packs and carefully removing the individual cells. Each cell contains a cathode and anode, typically made of lithium-based materials, and an electrolyte. By immersing the cells in a specialized chemical solution, the lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese can be extracted from the cathode and anode materials. This liquid-based approach allows for the recovery of these metals, which can then be recycled and reused in new battery production.
Another recycling method is 'pyrometallurgy,' which involves high-temperature processes to recover materials. This technique is often used for lead-acid batteries, commonly found in older EVs. Pyrometallurgy melts the battery components, allowing for the separation of lead, lead oxide, and other metals. The molten materials are then refined to obtain pure metals, which can be recycled for manufacturing new batteries or other products. This process is energy-intensive but is effective in handling large volumes of batteries and can be more cost-effective for certain battery types.
Additionally, mechanical processes play a vital role in recycling EV batteries. These methods involve physically breaking down the batteries to access individual components. For instance, shredding or milling can be used to reduce the battery size, making it easier to handle and process. This step is crucial as it prepares the battery for further recycling and ensures a more efficient recovery of materials. After mechanical processing, the shredded battery material undergoes additional treatments to separate and purify the various metals and chemicals.
The recycling of EV batteries is essential to close the loop on the circular economy, reducing the environmental footprint of the automotive industry. By implementing these recycling processes, we can minimize the extraction of raw materials, decrease waste, and promote a more sustainable approach to battery production and disposal. Furthermore, the recovery of valuable metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel ensures a steady supply for the growing demand in the EV market, contributing to a greener and more resilient future for transportation.
Electric Vehicles: Unlocking the Power of All-Wheel Drive
You may want to see also

Sustainable Sourcing: Focus on eco-friendly mining practices and responsible supply chains
The journey of electric vehicle (EV) batteries begins with the careful and sustainable sourcing of raw materials, a critical aspect often overlooked in the broader discussion of EV technology. The primary focus on reducing carbon footprints and promoting eco-friendly practices has led to a spotlight on the mining industry, which is a crucial step in the supply chain for EV batteries. The process starts with the extraction of key minerals and metals, such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, which are essential components of lithium-ion batteries. These materials are sourced from various regions around the world, and the method of extraction plays a pivotal role in determining the environmental impact.
Eco-friendly mining practices are gaining prominence as the industry strives to minimize its ecological footprint. This involves implementing sustainable techniques that reduce soil erosion, prevent water pollution, and minimize the release of toxic chemicals. For instance, in lithium mining, traditional methods often involve extensive water usage and can lead to water scarcity in the surrounding areas. However, innovative approaches, such as in-situ leaching, use less water and reduces the environmental impact on the local ecosystem. This method involves dissolving lithium in underground water and then extracting it, making it a more sustainable alternative.
The responsible sourcing of these minerals also extends to the social and economic aspects of mining communities. Ethical mining practices ensure fair wages, safe working conditions, and community engagement. This is particularly important in regions where mining operations have historically led to social and environmental issues. By prioritizing transparency and accountability, mining companies can build trust with local communities and ensure that the benefits of mining are shared equitably. This approach fosters a more sustainable and long-lasting relationship between the industry and the regions where these resources are extracted.
Furthermore, the supply chain for EV batteries must be meticulously managed to ensure sustainability. This includes implementing rigorous recycling and reuse programs for spent batteries, which can contain valuable materials that can be recovered and reused in new batteries. Additionally, the development of efficient transportation and logistics systems is vital to minimize the carbon emissions associated with the movement of raw materials and finished products. By optimizing the supply chain, the industry can further reduce its environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable future.
In summary, the sourcing of materials for EV batteries is a complex process that requires a multi-faceted approach to sustainability. From eco-friendly mining practices to responsible supply chain management, each step plays a crucial role in reducing the environmental and social impact of the industry. As the demand for electric vehicles continues to grow, adopting and promoting these sustainable practices will be essential to ensure a cleaner and more responsible future for the automotive industry.
Unlocking California's EV Future: Exploring Tax Credits and Incentives
You may want to see also

Global Trade: International trade in raw materials and battery components
The production of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a complex process that relies heavily on international trade in raw materials and components. The demand for EVs is rising globally, and with it, the need for the raw materials that make up these batteries. These materials include lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, which are extracted from various regions around the world. For instance, lithium, a key component in lithium-ion batteries, is primarily sourced from countries like Chile, Australia, and Argentina, which have significant lithium reserves. These countries often export their lithium to manufacturers in other parts of the world, such as China, South Korea, and Japan, which are major players in the EV battery production sector.
The supply chain for EV batteries is intricate, with each component requiring specific raw materials. For example, the cathode, a critical part of the battery, is made from a blend of cobalt, nickel, and manganese. Cobalt, a metal with unique properties, is predominantly sourced from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), where it is mined under often challenging and controversial conditions. The DRC's rich cobalt deposits have made it a significant player in the global cobalt market, supplying a substantial portion of the world's cobalt to battery manufacturers. International trade agreements and partnerships are crucial in ensuring a steady supply of these raw materials to meet the growing demand for EV batteries.
International trade in battery components is a multi-billion-dollar industry. Countries with advanced manufacturing capabilities, such as South Korea and Japan, have established themselves as key players in the EV battery market. These countries import raw materials and then process and assemble the batteries, often exporting the final product to EV manufacturers worldwide. The intricate web of international trade allows for the efficient distribution of resources, ensuring that the production of EV batteries can keep up with the increasing demand for sustainable transportation.
The global trade in raw materials and components for EV batteries also presents opportunities and challenges. On one hand, it fosters economic growth and development in regions rich in these resources. However, it also raises concerns about ethical sourcing, environmental impact, and the potential for exploitation. As such, there is a growing emphasis on responsible sourcing and supply chain transparency, with companies and governments working towards ensuring that the extraction and trade of these raw materials are conducted sustainably and ethically.
In summary, the production of electric vehicle batteries is a global endeavor, with international trade playing a pivotal role in sourcing the necessary raw materials and components. The intricate supply chain involves multiple countries, each contributing specific resources and expertise. As the world transitions towards more sustainable transportation, understanding and managing this complex web of international trade will be essential to ensuring a consistent supply of EV batteries while also addressing the ethical and environmental considerations associated with their production.
Powering Electric Vehicles: Unlocking the Secrets of Component Swapping
You may want to see also

Innovation in Materials: Research and development of new, more efficient battery materials
The quest for more efficient and sustainable electric vehicle (EV) batteries has led to significant research and development efforts in the field of materials science. The primary goal is to enhance battery performance, increase energy density, and reduce the environmental impact of battery production and disposal. One of the key areas of innovation is the exploration and development of new materials that can revolutionize battery technology.
Scientists and engineers are focusing on several aspects to improve battery materials. Firstly, there is a drive to discover and synthesize novel compounds with unique properties. For instance, researchers are investigating metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and porous materials that can act as highly efficient catalysts for electrochemical reactions. These materials could potentially increase the power density of batteries, allowing for longer driving ranges with a single charge. Additionally, the development of new electrode materials is crucial. Graphene, a single-atom-thick layer of carbon, has shown promise as an electrode material due to its high surface area and excellent electrical conductivity. By incorporating graphene into battery designs, researchers aim to enhance charge and discharge rates, making EVs more responsive and efficient.
Another strategy is to optimize existing materials. Scientists are working on improving the performance of traditional battery materials like lithium cobalt oxide (LCO) and nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC). These materials are currently used in many EVs, but researchers are exploring ways to enhance their energy storage capacity and stability. For example, they are investigating methods to reduce the amount of cobalt, a rare and expensive metal, in NMC cathodes while maintaining or improving performance. This approach not only reduces the cost of battery production but also addresses the environmental concerns associated with cobalt mining.
Furthermore, the recycling and upcycling of battery materials is a critical aspect of sustainable development. Researchers are developing advanced recycling techniques to recover valuable metals from spent batteries, reducing the need for mining and minimizing environmental degradation. This process involves creating new materials from the recycled components, ensuring a circular economy for battery production. By implementing these recycling methods, the industry can move towards a more sustainable and efficient battery supply chain.
In summary, the innovation in materials for EV batteries is a multifaceted endeavor. It involves the discovery of novel compounds, the optimization of existing materials, and the development of advanced recycling processes. Through these research and development efforts, scientists and engineers aim to create batteries that are more powerful, longer-lasting, and environmentally friendly, ultimately driving the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Unlocking EV Benefits: A Guide to Claiming Your MA Electric Vehicle Credit
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The raw materials for electric vehicle batteries are primarily sourced from various mineral deposits around the world. These minerals include lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, which are essential components in lithium-ion battery technology. Mining operations extract these materials from the earth, often from specific geological formations.
Yes, the supply of these materials is concentrated in a few regions. For instance, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is a significant producer of cobalt, while Chile and Australia are major suppliers of lithium. Other countries like the United States, China, and Russia also contribute to the global supply chain.
Mining and extraction processes can have significant environmental consequences. These include habitat destruction, soil erosion, water pollution, and the release of toxic substances. Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of battery production can also contribute to carbon emissions. However, efforts are being made to adopt more sustainable practices and recycling methods to minimize these impacts.
Ethical concerns are prevalent in the battery material supply chain. Child labor and unsafe working conditions have been reported in some mining operations, particularly in the DRC. There are also issues related to land rights and community engagement. To address these concerns, many companies are implementing due diligence processes and working towards responsible sourcing practices.
Recycling plays a crucial role in sustaining the electric vehicle battery industry. Recycling processes can recover valuable materials like cobalt, nickel, and lithium from used batteries, reducing the need for primary mining. It also helps minimize the environmental impact by reducing the demand for new mining operations. Many countries and companies are investing in recycling technologies to improve the sustainability of the battery supply chain.