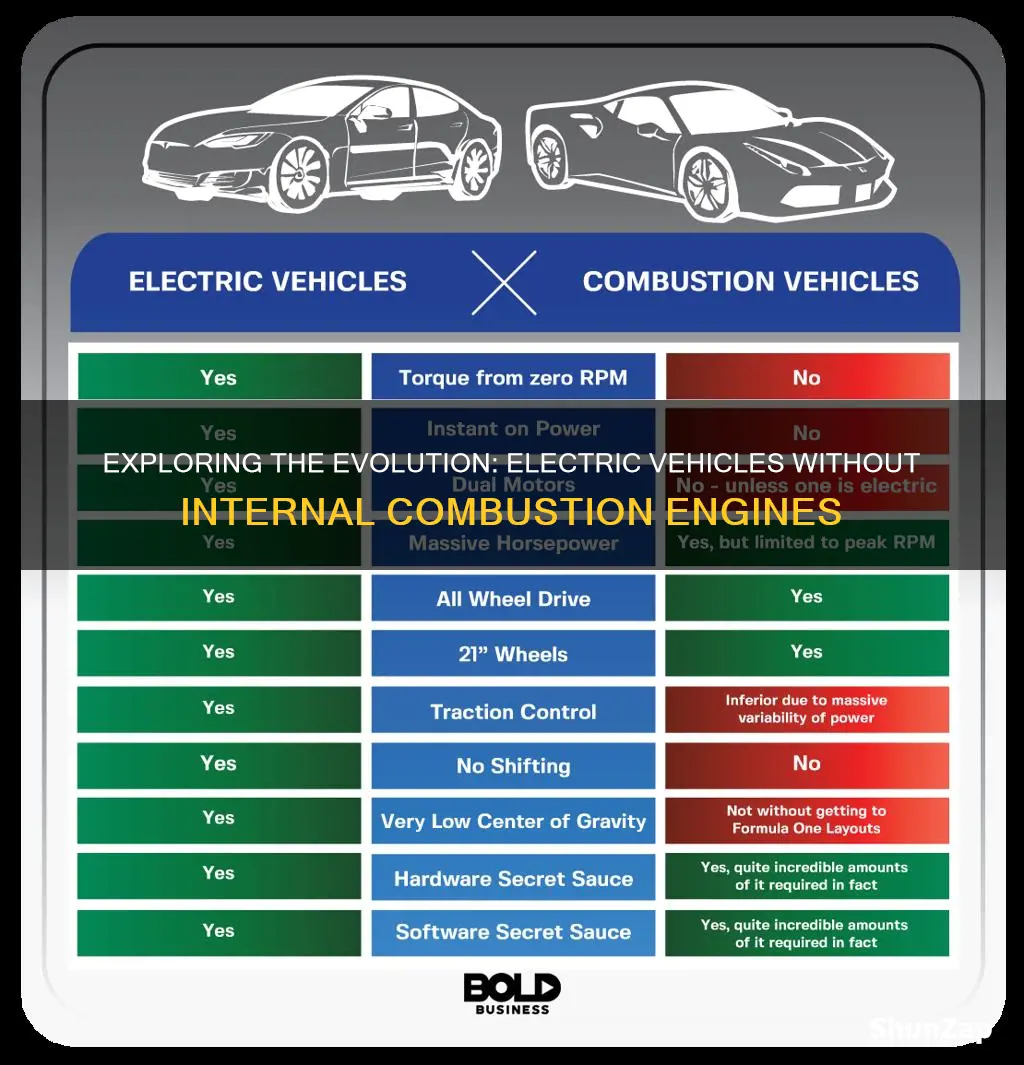
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. Among the various types of EVs, some stand out for their unique design and lack of internal combustion components. These innovative vehicles utilize electric motors and batteries as their primary power sources, eliminating the need for fuel and reducing environmental impact. This paragraph will explore the different types of electric vehicles that have successfully transitioned away from internal combustion engines, highlighting their contributions to a more sustainable future.
What You'll Learn
- Battery-Powered EVs: Electric motors, batteries, and power electronics dominate these vehicles
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells: These EVs use hydrogen and oxygen to generate electricity
- Solar-Powered Cars: Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity for propulsion
- Hybrid Vehicles: Combine electric and internal combustion systems for improved efficiency
- Biofuel-Powered EVs: Biodiesel and bioethanol can power some electric vehicle types

Battery-Powered EVs: Electric motors, batteries, and power electronics dominate these vehicles
Battery-powered electric vehicles (EVs) are a cornerstone of the modern automotive industry's shift towards sustainable transportation. These vehicles are designed to run exclusively on electric power, eliminating the need for internal combustion engines and, consequently, the emission of harmful pollutants. At the heart of this technology are three key components: electric motors, batteries, and power electronics.
Electric Motors: These are the driving force behind battery-powered EVs. Electric motors convert electrical energy from the vehicle's battery into mechanical energy, which propels the car forward. They are highly efficient and provide instant torque, resulting in smooth acceleration. The design of these motors has evolved to offer high power-to-weight ratios, ensuring that EVs can match or even surpass the performance of their conventional counterparts. Modern electric motors are also known for their reliability and longevity, contributing to the overall appeal of electric vehicles.
Batteries: The energy storage system in battery-powered EVs is a critical component. These batteries store electrical energy and supply it to the electric motor when needed. The most common type used in EVs is the lithium-ion battery, known for its high energy density and ability to provide rapid charging and discharging. Over the years, battery technology has advanced significantly, leading to increased range and reduced charging times. Modern EVs can travel over 300 miles on a single charge, addressing a major concern for potential buyers. The development of more efficient and sustainable battery materials is an ongoing area of research, aiming to further enhance the performance and longevity of EV batteries.
Power Electronics: This component acts as the intermediary between the battery and the electric motor, managing the flow of electrical energy. Power electronics include devices such as inverters, converters, and switches, which regulate the voltage and current to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. These systems are responsible for converting the direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) required by the motor and also manage regenerative braking, where kinetic energy is converted back into stored electrical energy. The efficiency of power electronics is crucial in maximizing the overall efficiency of the EV, ensuring that energy losses are minimized.
In summary, battery-powered EVs are a testament to the successful integration of electric motors, advanced batteries, and sophisticated power electronics. This combination has led to the creation of vehicles that are not only environmentally friendly but also offer impressive performance and convenience. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in these key components, making electric vehicles even more accessible and appealing to a wide range of consumers.
Exploring the World of Fully Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Hydrogen Fuel Cells: These EVs use hydrogen and oxygen to generate electricity
Hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) represent a unique and innovative approach to powering automobiles, offering a clean and efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. These vehicles operate on a simple yet powerful principle: they convert the chemical energy of hydrogen and oxygen into electricity through a process called electrochemical reaction, which is facilitated by a fuel cell. This technology is a cornerstone of the push towards sustainable transportation, as it eliminates the need for fossil fuels and significantly reduces environmental impact.
At the heart of a hydrogen fuel cell is a membrane-electrode assembly (MEA), which is a critical component that facilitates the electrochemical reaction. The MEA consists of a polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) sandwiched between two electrodes, typically made of a catalyst material like platinum. When hydrogen gas is supplied to one side of the MEA and oxygen (from the air) is supplied to the other, a series of chemical reactions occur. These reactions produce electricity, water, and heat, with the only emission being water vapor, making FCEVs a zero-emission vehicle technology.
The process begins when the hydrogen gas is compressed and fed into the fuel cell stack. Here, the hydrogen molecules are split into protons and electrons through a process called electrolysis. The protons pass through the PEM, which acts as a selective barrier, while the electrons are directed through an external circuit, providing the electrical power needed to run the vehicle. Simultaneously, the oxygen from the air combines with the protons and electrons in the fuel cell to form water, completing the reaction cycle.
One of the key advantages of hydrogen fuel cell technology is its rapid refueling capability. Similar to conventional gasoline or diesel vehicles, FCEVs can be refueled in a matter of minutes, providing a convenient and efficient solution for drivers. Additionally, the energy density of hydrogen is high, allowing for a longer driving range compared to battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) with similar battery capacities. This makes hydrogen fuel cell vehicles particularly appealing for long-distance travel and heavy-duty applications.
Despite the promise of hydrogen fuel cell technology, there are challenges to its widespread adoption. The production, storage, and distribution of hydrogen gas require significant infrastructure and can be energy-intensive. Additionally, the cost of fuel cell vehicles and the availability of refueling stations are factors that need to be addressed for the technology to become more mainstream. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on overcoming these hurdles, with the goal of making hydrogen fuel cell vehicles more accessible and environmentally friendly.
Powering Electric Vehicles: The Role of Inverters in Energy Conversion
You may want to see also

Solar-Powered Cars: Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity for propulsion
The concept of solar-powered cars is an innovative approach to sustainable transportation, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. These cars harness the power of the sun through advanced solar panel technology, providing a clean and renewable energy source for propulsion. This method of powering vehicles is a significant step towards reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating the environmental impact of transportation.
Solar panels, typically mounted on the roof or hood of the vehicle, are designed to capture sunlight and convert it directly into electricity. This process is made possible by the photovoltaic effect, where sunlight excites electrons in the solar cells, generating a flow of electricity. The electricity produced is then used to power the car's electric motor, which drives the wheels and propels the vehicle forward. This direct conversion of solar energy to electricity is a key advantage, as it eliminates the need for complex mechanical systems found in conventional cars.
The efficiency of solar-powered cars has improved significantly over the years, allowing for longer travel distances on a single charge of sunlight. Modern solar panels can achieve conversion rates of around 20-30%, meaning a substantial portion of the sun's energy is successfully transformed into usable electricity. This efficiency, combined with advancements in battery technology, enables solar-powered vehicles to store excess energy for use during periods of low sunlight, ensuring a consistent power supply.
One of the most significant advantages of solar-powered cars is their minimal environmental impact. By utilizing a renewable energy source, these vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions associated with traditional combustion engines. This makes solar-powered cars an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers and contributes to global efforts to combat climate change.
In addition to their environmental benefits, solar-powered cars offer a unique driving experience. The quiet operation of electric motors and the smooth acceleration provide a calm and serene driving environment. Furthermore, the integration of solar power with other electric vehicle (EV) technologies, such as regenerative braking, can enhance the overall efficiency and performance of the vehicle. As solar panel technology continues to advance, we can expect to see more efficient and practical solar-powered cars, further expanding the options for sustainable transportation.
Boosting EV Adoption: Creative Incentives for a Greener Future
You may want to see also

Hybrid Vehicles: Combine electric and internal combustion systems for improved efficiency
Hybrid vehicles represent a significant advancement in the automotive industry, offering a unique blend of electric and internal combustion systems to enhance efficiency and performance. These vehicles are designed to optimize power delivery and reduce fuel consumption, making them an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers. The key to their success lies in the seamless integration of two distinct power sources, creating a harmonious driving experience.
At the heart of hybrid vehicles is the ability to switch between electric and internal combustion modes effortlessly. When the vehicle is idling or traveling at low speeds, it primarily operates in electric mode, utilizing the electric motor to power the wheels. This mode is highly efficient as it eliminates the need for traditional engine idling, which is a significant source of fuel waste. The electric motor provides smooth acceleration and a quiet, clean driving experience, making it ideal for urban environments and short-distance travel.
During higher-speed cruising or when more power is required, the hybrid system engages the internal combustion engine. This engine is typically smaller and more fuel-efficient than traditional gasoline or diesel engines, designed to work in conjunction with the electric motor. By combining the strengths of both systems, hybrids can achieve superior fuel economy, often exceeding 40 miles per gallon in city driving conditions. This efficiency is a result of the engine's ability to run at optimal speeds and the electric motor's instant torque delivery, ensuring a responsive and smooth driving experience.
One of the most remarkable aspects of hybrid vehicles is their ability to recover and store energy. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy. This energy is then stored in the vehicle's battery pack, which can be used to power the electric motor during subsequent acceleration or to assist the internal combustion engine. This regenerative braking system not only improves efficiency but also extends the overall driving range, making hybrids a practical choice for daily commutes.
Furthermore, hybrid vehicles offer a unique driving experience by providing the driver with a choice of power sources. Many hybrid models feature a 'power split' system, allowing the driver to manually select between electric, hybrid, or internal combustion modes. This control empowers drivers to customize their driving experience, whether they prefer the instant torque of electric power or the smooth, efficient operation of the combined system. This flexibility is a significant advantage, catering to various driving preferences and needs.
In summary, hybrid vehicles are a testament to the successful marriage of electric and internal combustion technologies. By combining these systems, hybrids offer improved efficiency, reduced fuel consumption, and a unique driving experience. With their ability to seamlessly switch between power sources, hybrids provide a practical and environmentally friendly solution for modern transportation, appealing to a wide range of consumers seeking both performance and sustainability.
Unleash the Future: Top Stocks for Electric Vehicle Revolution
You may want to see also

Biofuel-Powered EVs: Biodiesel and bioethanol can power some electric vehicle types
The world of electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly evolving, and while many focus on battery-powered cars, there are other innovative approaches to powering EVs without traditional internal combustion engines. One such method involves the use of biofuels, specifically biodiesel and bioethanol, which can be utilized in certain electric vehicle types.
Biofuels are derived from organic matter, such as vegetable oils, animal fats, and even waste materials. Biodiesel, for instance, is produced from oils like sunflower or rapeseed oil, while bioethanol is created from renewable sources such as corn, sugarcane, or wheat. These biofuels offer an eco-friendly alternative to conventional fossil fuels, reducing the carbon footprint of vehicles.
In the context of EVs, biofuels can be used in two primary ways. Firstly, they can be employed in modified internal combustion engines, where the traditional fuel is replaced with biodiesel or bioethanol. This approach allows for the continued use of existing vehicle designs and infrastructure, making it a relatively straightforward adaptation. Secondly, biofuels can be used in direct injection systems, where the fuel is injected directly into the engine's cylinders, providing a more efficient and cleaner burn compared to conventional gasoline or diesel engines.
Electric vehicles powered by biofuels offer several advantages. Firstly, they can help reduce reliance on non-renewable resources, as biofuels are derived from sustainable sources. This contributes to a more environmentally friendly transportation system. Secondly, the use of biofuels can provide a cost-effective solution, especially in regions where these fuels are readily available and locally produced. This can potentially lower the overall cost of EV ownership, making it more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
However, it is important to note that not all electric vehicle types are compatible with biofuel-powered systems. The design and engineering of the vehicle play a crucial role in determining its suitability. For instance, some electric vehicles may require specific modifications to accommodate the different fuel injection systems or engine configurations. Additionally, the infrastructure for refueling with biofuels may not be as widespread as that for conventional fuels, which could impact the practicality of owning such vehicles.
In summary, biofuel-powered EVs, utilizing biodiesel and bioethanol, present an intriguing concept in the realm of electric transportation. While they offer environmental and economic benefits, careful consideration of vehicle design, infrastructure, and availability of biofuels is necessary to ensure a successful implementation. As the EV market continues to evolve, exploring diverse power sources and technologies will contribute to a more sustainable and diverse future for the automotive industry.
Peach Pass: Free EV Charging or a Rip-Off?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles (EVs) that do not feature internal combustion components include battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs). BEVs are powered solely by electric motors and batteries, while FCEVs utilize hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity for their propulsion.
BEVs are fully electric, meaning they rely on electric motors and batteries as their primary power source. These vehicles are charged by plugging into an external power source, typically an electric socket or a charging station. The batteries store electrical energy, which is then used to power the motor, propelling the vehicle forward.
BEVs and HEVs are both types of electric vehicles but differ in their power sources and driving characteristics. HEVs, such as the Toyota Prius, combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor and battery. They can switch between the two power sources, allowing for improved fuel efficiency. In contrast, BEVs are solely powered by electricity and do not have an internal combustion engine.
Yes, fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) are designed to run on hydrogen. These vehicles use a fuel cell stack to convert hydrogen gas and oxygen from the air into electricity, which then powers the electric motor. FCEVs offer a longer driving range compared to some BEVs and can be refueled quickly, similar to conventional vehicles.







