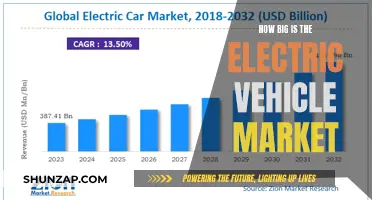
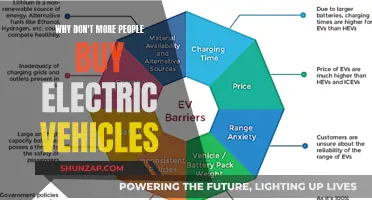
Despite the growing environmental concerns and technological advancements, the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has been slower than expected. This paragraph aims to explore the reasons behind this phenomenon, considering factors such as high upfront costs, limited charging infrastructure, consumer skepticism, and the influence of traditional automotive industries. By examining these aspects, we can gain a deeper understanding of the challenges hindering the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and potentially uncover solutions to accelerate the transition to a more sustainable transportation future.
What You'll Learn
- Cost and Infrastructure: High upfront costs and limited charging stations hinder EV adoption
- Consumer Behavior: Lack of awareness and trust in technology may slow adoption
- Government Policies: Incentives and regulations can either accelerate or hinder EV market growth
- Technological Barriers: Range anxiety, battery technology, and charging time are concerns for potential buyers
- Cultural and Social Factors: Cultural norms and social perceptions influence the acceptance of electric vehicles

Cost and Infrastructure: High upfront costs and limited charging stations hinder EV adoption
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is facing significant challenges due to two primary factors: cost and infrastructure. The high upfront costs of EVs and the limited availability of charging stations are major barriers to their integration into mainstream transportation.
Firstly, the initial purchase price of electric cars is a significant deterrent for many potential buyers. Despite the long-term cost savings associated with lower fuel and maintenance expenses, the initial investment can be substantial. This is especially true for high-end electric vehicles, which often carry a premium price tag. For instance, luxury EVs like the Tesla Model S or the Lucid Air can cost upwards of $100,000, making them unaffordable for a large segment of the population. In contrast, more affordable options like the Nissan Leaf or the Hyundai Ioniq 5, while more accessible, still carry a higher price tag than their gasoline counterparts, which can be a significant obstacle for cost-conscious consumers.
Secondly, the lack of a comprehensive charging infrastructure is a critical issue. The range anxiety associated with EVs is a real concern, and the availability of charging stations plays a pivotal role in alleviating this anxiety. However, the current charging infrastructure is inadequate to support the rapid growth of EV ownership. The number of public charging stations is limited, and the process of finding and using these stations can be cumbersome. This is particularly true in rural areas and less-traveled routes, where the distance between charging stations can be vast. As a result, EV owners often face the challenge of planning their trips meticulously to ensure they have access to charging points, which can be time-consuming and inconvenient.
To address these issues, governments and private entities must work together to implement several strategies. Firstly, incentives and subsidies can be offered to reduce the upfront cost of EVs, making them more affordable for a broader range of consumers. This could include tax credits, rebates, or low-interest loans for EV purchases. Secondly, investments in the development of a robust charging infrastructure are essential. This involves expanding the network of public charging stations, especially in areas with limited access, and implementing smart charging solutions that optimize energy usage and reduce wait times. Additionally, encouraging the installation of home charging stations can empower individuals to charge their vehicles conveniently, addressing range anxiety and promoting a more seamless transition to electric mobility.
In conclusion, the slow adoption of electric vehicles can be attributed, in part, to the high upfront costs and the limited charging infrastructure. By addressing these issues through financial incentives and infrastructure development, we can make EVs more accessible and practical for the general public, fostering a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation ecosystem.
South Carolina's EV Tax Exemption: A Green Car Owner's Guide
You may want to see also

Consumer Behavior: Lack of awareness and trust in technology may slow adoption
The slow adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) can be attributed to several factors, and one of the key aspects is consumer behavior, particularly the lack of awareness and trust in this new technology. Many potential buyers are still unfamiliar with the benefits and capabilities of electric cars, which often leads to hesitation and uncertainty. This lack of awareness can be addressed through effective marketing and education campaigns that highlight the advantages of EVs over traditional gasoline vehicles. For instance, showcasing the environmental benefits, such as reduced carbon emissions and lower air pollution, can appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. Additionally, emphasizing the long-term cost savings, improved performance, and the convenience of home charging can help shift consumer perceptions.
Another critical aspect is the trust factor. Consumers often have concerns about the reliability and performance of electric vehicles, especially regarding battery life, charging infrastructure, and the overall driving experience. To address this, manufacturers and policymakers should focus on building trust by providing transparent information. This includes sharing data on battery technology advancements, real-world driving range, and the expanding network of charging stations. By presenting factual and reliable data, the industry can alleviate fears and misconceptions, encouraging more people to consider EVs as a viable and attractive option.
Furthermore, the current automotive market dynamics play a role in slowing down EV adoption. Traditional car manufacturers have a strong presence, and consumers may be hesitant to switch due to brand loyalty and the perceived higher costs associated with electric vehicles. However, as more EV models become available and prices become more competitive, this barrier is gradually reducing. It is essential for the industry to continue developing affordable, high-quality electric vehicles to cater to a wider range of consumers.
In summary, to accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles, it is crucial to address consumer behavior by increasing awareness and building trust. This can be achieved through comprehensive marketing strategies, educational initiatives, and providing transparent information. Additionally, the industry should focus on making EVs more accessible, affordable, and reliable to cater to a broader market. By tackling these aspects, the potential for widespread EV adoption becomes more feasible and sustainable.
Powering Your Ride: The Secrets of Vehicle Electricity
You may want to see also

Government Policies: Incentives and regulations can either accelerate or hinder EV market growth
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has been slower than expected, despite the numerous environmental and economic benefits they offer. One of the primary factors influencing this slow growth is government policy, which can either incentivize or discourage the transition to electric mobility.
Incentives for EV Adoption:
Governments worldwide have implemented various incentives to encourage citizens to purchase and use electric vehicles. These incentives often include financial rewards, tax breaks, and subsidies. For instance, many countries offer tax credits or rebates to consumers when they buy EVs, making them more affordable and attractive. Additionally, governments might provide grants to businesses for installing charging infrastructure, which is essential for EV owners. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost of EVs, making them more accessible to a broader population. For example, the United States' federal tax credit of up to $7,500 for EV purchases has been instrumental in boosting sales. Similarly, Norway's generous incentives, including a zero-emission car quota and a reduced sales tax, have led to a high EV market share.
Regulations and Standards:
Government regulations and standards also play a crucial role in shaping the EV market. Stringent emissions regulations have been a significant driver for EV adoption, as they force the market to transition to cleaner technologies. Many countries have set ambitious targets to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which often include a significant EV component. For instance, the European Union's 'Roadmap for Mobility and Transport' aims to achieve climate neutrality by 2050, with a focus on promoting electric mobility. Such regulations can create a favorable environment for EV manufacturers and encourage the development of more efficient and sustainable vehicles.
Hinderance through Regulations:
However, not all government policies are conducive to EV growth. Some regulations can inadvertently slow down the market. For instance, strict safety standards and complex certification processes can increase the cost and time required to bring new EV models to market. This might discourage manufacturers from investing in EV technology, especially for smaller producers who may not have the resources to navigate these regulatory hurdles. Moreover, inconsistent or changing regulations can create uncertainty for consumers and businesses, potentially hindering investment in EV infrastructure and technology.
Balancing Incentives and Regulations:
The key to accelerating EV market growth lies in finding a balance between incentives and regulations. Governments should aim to create an environment that encourages innovation and investment while also ensuring consumer protection and environmental sustainability. This includes providing clear and consistent guidelines for manufacturers, investors, and consumers. Additionally, governments can offer incentives for research and development in EV technology, battery storage, and charging infrastructure to foster long-term growth.
In summary, government policies, including incentives and regulations, have a profound impact on the pace of EV adoption. Well-designed incentives can make EVs more affordable and desirable, while thoughtful regulations can ensure the market's sustainability and environmental benefits. By understanding and addressing these factors, policymakers can play a pivotal role in accelerating the transition to electric mobility.
Uncovering the Profitable Segments in the EV Supply Chain
You may want to see also

Technological Barriers: Range anxiety, battery technology, and charging time are concerns for potential buyers
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has been slower than expected, and several technological barriers are significant factors contributing to this delay. One of the primary concerns is range anxiety, which refers to the fear of running out of battery power during a journey. While modern EVs have made significant strides in terms of range, with some models now offering over 300 miles on a single charge, this still falls short of the comfort and convenience of traditional gasoline vehicles. Many potential buyers are hesitant to make the switch due to the fear of being stranded with no power, especially for long-distance travel or in areas with limited charging infrastructure.
Battery technology is another critical aspect that influences the adoption of EVs. The development of more efficient and powerful batteries is essential to address range anxiety and other performance issues. Current lithium-ion batteries have limitations in terms of energy density, which directly impacts the vehicle's range. Researchers and engineers are working on improving battery chemistry and design to increase energy storage capacity while reducing weight and size. Solid-state batteries, for example, are being explored as a potential solution, offering higher energy density and faster charging times. However, these advancements are still in the research and development phase, and it will take time for them to become commercially viable and widely available.
Charging time is a significant concern for EV owners, especially when compared to the quick refueling process of gasoline vehicles. While charging times have improved with the introduction of faster charging stations, the process still takes significantly longer than a traditional gas fill-up. The development of ultra-fast charging technology, which can replenish a substantial amount of battery charge in a matter of minutes, is an ongoing area of focus. However, the widespread availability of such charging infrastructure is still limited, and the technology needs to be refined to ensure reliability and safety.
Overcoming these technological barriers requires continued investment in research and development, as well as collaboration between automotive manufacturers, energy companies, and governments. Addressing range anxiety, improving battery technology, and expanding charging infrastructure are crucial steps in accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles. As these challenges are tackled, we can expect to see a more widespread acceptance of EVs, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation ecosystem.
Georgia's EV Incentives: Unlocking the Green Car Revolution
You may want to see also

Cultural and Social Factors: Cultural norms and social perceptions influence the acceptance of electric vehicles
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has been slower than expected, despite the growing awareness of environmental concerns and technological advancements. One significant factor contributing to this delay is cultural and social norms, which play a pivotal role in shaping people's perceptions and behaviors.
Cultural norms often dictate the preferences and choices individuals make regarding transportation. In many societies, the traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles have been deeply ingrained in the cultural fabric for decades. These vehicles are often associated with status, power, and freedom, especially in cultures where driving is a symbol of independence and personal achievement. For instance, in countries with a strong car culture, like the United States, the idea of owning a powerful, high-performance ICE vehicle is deeply rooted in the national psyche. This cultural association makes it challenging to shift the perception of driving as a symbol of environmental responsibility when considering EVs.
Social perceptions also play a critical role in the adoption of EVs. The fear of being perceived as environmentally conscious or 'tree-hugging' can deter individuals from making the switch. In some communities, there is a social stigma attached to owning an EV, especially in regions where fossil fuel-powered vehicles are the norm and are seen as a symbol of success and luxury. This social pressure to conform to traditional vehicle ownership can hinder the adoption of EVs, as individuals may worry about being judged or seen as less prestigious. Moreover, the lack of social support and understanding for EV owners can create a sense of isolation, making it less appealing to make the change.
Additionally, cultural and social factors influence the perception of EV technology itself. Misinformation and a lack of understanding about EVs' capabilities and benefits are prevalent. Some people believe that EVs are underpowered, have short ranges, or are not suitable for long-distance travel, which is a significant barrier to adoption. Cultural biases and stereotypes can also contribute to this misinformation, as certain groups may have preconceived notions about the reliability and performance of EVs, especially in regions where traditional vehicles have dominated the market for a long time.
To accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles, it is essential to address these cultural and social factors. This can be achieved through targeted education campaigns, community engagement, and social initiatives that highlight the benefits of EVs while challenging the existing cultural norms. By changing the social perception and understanding of EVs, we can encourage a more rapid transition towards a more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
Powering the Engine: The Secret to Vehicle Electricity
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are several reasons why the adoption of electric vehicles is slower compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. Firstly, the initial cost of EVs is often higher, which can be a significant barrier for potential buyers, especially when considering the purchase price and the potential for higher upfront costs compared to similar ICE vehicles. However, it's important to note that the cost of EVs is decreasing as technology advances and production scales, making them more affordable over time. Secondly, the availability of charging infrastructure is a concern. While charging stations are becoming more common, the current infrastructure may not be as extensive as gas stations, leading to range anxiety and convenience issues for EV owners. Lastly, consumer behavior and perception play a role. Some individuals may be hesitant to switch due to a lack of awareness about the benefits of EVs, concerns about performance, or simply a preference for the familiar.
The main obstacles can be categorized into three key areas: infrastructure, cost, and consumer behavior. Firstly, the charging infrastructure for EVs is still developing, and the current network may not be sufficient to support a rapid increase in EV sales. This includes the availability of charging stations, their distribution, and the time required to charge an EV, which can be longer than refueling a gas car. Secondly, the cost of EVs, including the vehicle itself and potential installation of home charging equipment, can be a significant deterrent. While the total cost of ownership over the vehicle's lifetime may be lower, the initial investment can be a hurdle. Lastly, consumer perception and habits are important factors. Some buyers may be hesitant due to range concerns, lack of awareness about the environmental benefits, or simply a preference for the existing automotive ecosystem.
Accelerating the adoption of EVs requires a multi-faceted approach involving governments, businesses, and consumers. Firstly, governments can play a crucial role by offering incentives such as tax credits, subsidies, and grants to reduce the purchase price for consumers. They can also invest in expanding the charging infrastructure network, making it more accessible and convenient. Businesses can contribute by providing incentives for employees to adopt EVs, offering company cars with lower emissions, and investing in EV-related technologies. On the consumer side, raising awareness about the benefits of EVs, such as reduced environmental impact, lower running costs, and improved performance, can help address misconceptions. Additionally, providing accessible information about charging options, range, and available models can empower buyers to make informed decisions.